File
advertisement

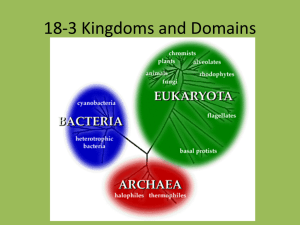
Kingdom Brochure Project Objective You will demonstrate your knowledge of the 5 kingdoms of organisms by gathering information from the attached readings, your notes and the Biology book and creating a brochure on the 5 kingdoms in which scientists classify organisms. Your Brochure will be organized as follows: 1. The brochure will be made of one piece of paper, folded into thirds 2. The cover should have a title and a picture that goes with the title. Your name should be written on the bottom right hand corner of the cover. 3. Inside you brochure, you will have one section for each of the five kingdoms. Use the front and back of the paper. 4. You must include the following information in each kingdom’s section: Are they multi-cellular, unicellular, or both Do they have a nucleus in their cells? How do they get food (energy)? One interesting fact about the organisms in the kingdom At least one picture showing an example of an organism The brochure must be neat and colorful (not everyone is an artist but I can tell when effort is made!) The five Kingdoms are: 1) Animal 2) Plant 3) Fungi 4) Protist 5) Monera (includes Eubacteria and Archaebacteria…make sure to include all information from #4 above for BOTH types!) Animal Kingdom Humans are part of the animal kingdom. All members of the animal kingdom are eukaryotes. Their cells contain a nucleus and organelles. Like many other life forms, animals are multicellular. These cells come together to form tissues, organs, and organ systems that help sustain the life of the animal. From elephants to snails, animals come in many shapes and sizes, and can be found all over the world. Animals cannot make their own food. They are heterotrophs (consumers) and must rely on other living things, such as plants, fungi, and other animals to sustain them. Without other food sources, animals could not survive. Plant Kingdom The plant kingdom includes all land plants: mosses, ferns, grass, trees, flowering plants and more. Plants do not move. They are autotrophs (producers), which mean that they make their own food through photosynthesis. Plants are multicellular. They are also eukaryotic so all their cells have a nucleus. Plant cells also have a cell wall. The most important feature of plants is their green color, the result of a pigment called chlorophyll. Plants use chlorophyll to capture light energy, which fuels the manufacture of food—sugar, starch, and other carbohydrates. Without these food sources, most life on Earth would be impossible. There would still be mushrooms and algae but there would be no fruits, vegetables, grains, or any animals! Another important role of plants is that they help shape the environment. Plants give us oxygen to breathe and provide food and habitats for many species of animals. Without plants, we could not survive! Fungi Kingdom The fungi kingdom includes some of the most important organisms. By decomposing dead material, they continue the cycle of nutrients through ecosystems. In addition, most plants could not grow without the fungi that live in their roots and supply essential nutrients. Other fungi provide numerous drugs like penicillin and other antibiotics, foods like mushrooms, truffles, and morels, as well as bubbles in bread (yeast), champagne, and beer. Fungi are eukaryotes, which mean their cells have a nucleus. Their cells also have a cell wall. Fungi can be either unicellular or multicellular organisms that can usually be seen without a microscope. Fungi do not move on their own, nor do they make their own food. Fungi are heterotrophs (consumers) which mean that they get their food from other living things. Fungi use external digestion, they secrete (let out) digestive enzymes that dissolve their food, and then they absorb the nutrients they need from the environment. Protist Kingdom Protists are organisms that are classified into the protist kingdom. The protists form a group of organisms that really do not fit into any other kingdom. Although there is a lot of variety within the protists, they do share some common characteristics. All protists live in moist environments. All protists are eukaryotes, so their cells have a nucleus. Most protists are unicellular. Most protists can move. Some are autotrophs (producers), making their own food by photosynthesis. Others are heterotrophs (consumers) and must ingest their food (eat other living things). Amoeba, algae, paramecium, diatoms are some examples of protists. Monera Kingdom The Monera Kingdom is often broken down into two separate kingdoms: The Archaebacteria and Eubacteria Kingdoms. Archaebacteria Archaebacteria consist of prokaryotic organisms that are unicellular. Archaebacteria do not have a nucleus or complex organelles. These organisms are found in extreme environments. For example, some archaebacteria live in hot springs at extremely high temperatures. Others are found in the arctic, where it is very cold. Some live in very salty or acidic environments. Archaebacteria include both autotrophs (producers) and heterotrophs (consumers) so some can create their own food while others rely on other organisms as their food source. Eubacteria Eubacteria consist of unicellular life forms. Eubacteria are all prokaryotes. These cells are far simpler and more basic than the cells of other life forms. These cells have no nucleus and are also missing many of the organelles commonly found in other types of organisms. Eubacteria include both autotrophs (producers) and heterotrophs (consumers) so some can create their own food while others rely on other organisms as their food source. Eubacteria are considered by many scientists to be the oldest life forms on Earth…the ancestors of all other life types. Eubacteria are extremely important. They help us digest food, break down waste, and make products like yogurt and cheese. Some eubacteria are pathogens (organisms that cause sickness) such as streptococcus or salmonella.