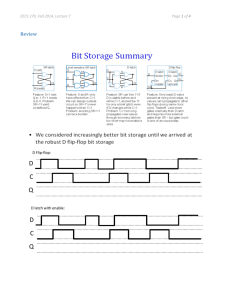
Stu-Chapter4 - EECS People Web Server
advertisement

Information Security Policy EECS 711: Security Management and Audit Molly Coplen Dan Hein Dinesh Raveendran Learning Objectives • Define Information security policy and understand its central role in a successful information security program • Recognize the three major types of information security policy and know what goes into each type • Develop, implement, and maintain various types of information security policies 2 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy Introduction • The success of any information security program lies in policy development • Policy is the essential foundation of an effective information security program • The centrality of information security polices to virtually everything that happens in the information security field • An effective information security training and awareness effort cannot be initiated without writing information security policies 3 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy NIST–Executive guide to the Protection of Information Resources • “The success of an information resources protection program depends on the policy generated, and on the attitude of management toward securing information on automated systems. You, the policy maker, set the tone and the emphasis on how important a role information security will have within your agency. Your primary responsibility is to set the information resource security policy for the organization within the objectives of reduced risk, compliance with laws and regulations and assurance of operational continuity, information integrity, and confidentiality.” 4 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy Basic Rules in Shaping a Policy • Policy should never conflict with law • Policy must be able to stand up in court, if challenged • Policy must be properly supported and administered • Example: Enron’s dubious business practices and misreporting the financial records - Policy of shredding working papers by accountants 5 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy Why Policy • A quality information security program begins and ends with policy • Although information security policies are the least expensive means of control to execute, they are often the most difficult to implement • Policy controls cost only the time and effort that the management team spends to create, approve and communicate them, and that employees spend integrating the policies into their daily activities • Cost of hiring a consultant is minimal compared to technical controls 6 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy Guidelines for IT policy • All policies must contribute to the success of the organization • Management must ensure the adequate sharing of responsibility for proper use of information systems • End users of information systems should be involved in the steps of policy formulation 7 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy Bull’s Eye Model • Proven mechanism for prioritizing complex changes • Issues are addressed by moving from general to specifics • Focus of systemic solutions instead of individual problems 8 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy Bull’s Eye Model (Contd) 9 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy Bull’s Eye Model Layers • Policies – the outer layer in the bull’s eye diagram • Networks – the place where threats from public networks meet the organization’s networking infrastructure; in the past, most information security efforts have focused on networks, and until recently information security was often thought to be synonymous with network security • Systems – computers used as servers, desktop computers, and systems used for process control and manufacturing systems • Application – all applications systems, ranging from packed applications such as office automation and e-mail programs, to high-end ERP packages and custom application software developed by the organization 10 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy Charles Cresson Wood’s Need for Policy …policies are important reference documents for internal audits and for the resolution of legal disputes about management’s due diligence [and] policy documents can act as a clear statement of management’s intent… 11 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy Policy, Standards, and Practices • Policy represents the formal statement of the organization’s managerial policy, in case of our focus, the organization’s information security philosophy • Tradition communities of interest use policy to express their views which then becomes the basis of planning, management and maintenance of the information security profile • Policies – set of rules that dictate acceptable and unacceptable behavior within an organization • Policies should not specify the proper operation of equipment or software 12 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy Policy, Standards, and Practices (Contd) • Policies must specify the penalties for unacceptable behavior and define an appeals process • To execute the policy, the organization must implement a set of standards that clarify and define exactly what is inappropriate in the workplace and to what degree the org will stop to act the inappropriate behavior • Standard – More detailed statement of what must be done to comply with policy • Technical controls and their associated procedures might be established such that the network blocks access to pornographic websites 13 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy Policy, Standards, and Practices (Contd) 14 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy Type of InfoSec policies • Based on NIST Special Publication 800-14, the three types of information security policies are – Enterprise information security program policy – Issue-specific security policies – System-specific security policies • The usual procedure – First – creation of the enterprise information security policy – the highest level of policy – Next – general policies are met by developing issue- and system-specific policies 15 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy Enterprise Information Security Policy (EISP) • EISP sets the strategic direction, scope, and tone for all of an organization’s security efforts • EISP assigns responsibilities for the various areas of information security including maintenance of information security policies and the practices and responsibilities of other users. • EISP guides the development, implementation, and management requirements of the information security program • EISP should directly support the mission and vision statements 16 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy Integrating an Organization’s Mission and Objectives into the EISP • EISP plays a number of vital roles • One of the important role is to state the importance of InfoSec to the organization’s mission and objectives. • InfoSec strategic planning derives from IT strategic planning which is itself derived from the organization’s strategic planning • Policy will become confusing if EISP does not directly reflect the above association 17 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy EISP Elements • An overview of the corporate philosophy on security • Information on the structure of the InfoSec organization and individuals who fulfill the InfoSec role • Fully articulated responsibilities for security that are shared by all members of the organization • Fully articulated responsibilities for security that are unique to each role within the organization 18 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy Components of a good EISP • • • • Statement of Purpose Information Technology Security Elements Need for Information Technology Security Information Technology Security Responsibilities and Roles • Reference to Other Information Technology Standards and Guidelines 19 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy Issue-Specific Security Policy (ISSP) • Provides a common understanding of the purposes for which an employee can and cannot use a technology – Should not be presented as a foundation for legal prosecution • Protects both the employee and organization from inefficiency and ambiguity 20 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy Effective ISSP • Articulates expectations for use of technology-based system • Identifies the processes and authorities that provide documented control • Indemnifies the organization against liability for an employee’s inappropriate or illegal use of the system 21 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy ISSP Topics • Use of Internet, e-mail, phone, and office equipment • Incident response • Disaster/business continuity planning • Minimum system configuration requirements • Prohibitions against hacking/testing security controls • Home use of company-owned systems • Use of personal equipment on company networks 22 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy ISSP Components • Statement of Purpose – • Authorized Uses – • Outlines scope and applicability: what is the purpose and who is responsible for implementation Users have no particular rights of use, outside that specified in the policy Prohibited Uses – 23 Common prohibitions: criminal use, personal use, disruptive use, and offensive materials EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy ISSP Components • Systems Management – Users relationship to systems management – Outline users’ and administrators’ responsibilities • Violations of Policy – Penalties specified for each kind of violation – Procedures for (often anonymously) reporting policy violation • Policy Review/Modification • Limitations of Liability 24 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy ISSP Implementation • Three common approaches for creating/managing ISSP – Create individual independent ISSP documents, tailored for specific issues – Create a single ISSP document covering all issues – Create a modular ISSP document unifying overall policy creation/management while addressing specific details with respect to individual issues 25 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy System Specific Security Policy (SysSPs) • SysSPs provide guidance and procedures for configuring specific systems, technologies, and applications – Intrusion detection systems – Firewall configuration – Workstation configuration • SysSPs are most often technical in nature, but can also be managerial – Guiding technology application to enforce higher level policy (e.g. firewall to restrict Internet access) 26 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy Guidelines for Effective Policy • Developed using industry-accepted practices • Distributed using all appropriate methods • Reviewed or read by all employees • Understood by all employees • Formally agreed to by act or assertion • Uniformly applied and enforced 27 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy Developing Information Security Policy • • • • • Investigation Phase Analysis Phase Design Phase Implementation Phase Maintenance Phase 28 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy Investigation Phase • Support from senior management • Support and active involvement of IT management • Clear articulation of goals • Participation by the affected communities of interest • Detailed outline of the scope of the policy development project 29 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy Analysis Phase • The analysis phase should produce the following: – A new or recent risk assessment or IT audit documenting the information security needs of the organization. – Gathering of key reference materials – including any existing policies 30 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy Design Phase • Users or organization members acknowledge they have received and read the policy – Signature and date on a form – Banner screen with a warning 31 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy Implementation Phase • Policy development team writes policies • Resources: – The Web – Government sites such as NIST – Professional literature – Peer networks – Professional consultants 32 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy Maintenance Phase • Policy development team responsible for monitoring, maintaining, and modifying the policy 33 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy Policy Distribution • • • • • Hand policy to employees Post policy on a public bulletin board E-mail Intranet Document management system 34 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy Policy Reading • Barriers to employees’ reading policies – Literacy: 14% of American adults scored “below basic” level in prose literacy – Language: non-English speaking residents 35 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy Policy Comprehension • Language – At a reasonable reading level – With minimal technical jargon and management terminology • Understanding of issues – Quizzes 36 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy Policy Compliance • Policies must be agreed to by act or affirmation • Corporations incorporate policy confirmation statements into employment contracts, annual evaluations 37 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy Policy Enforcement • Uniform and impartial enforcement – must be able to withstand external scrutiny • High standards of due care with regard to policy management – to defend against claims made by terminated employees 38 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy Automated Tools • VigilEnt Policy Center – a centralized policy approval and implementation center – Manage the approval process – Reduces need to distribute paper copies – Manage policy acknowledgement forms 39 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy VigilEnt Policy Center Architecture User Site Company Intranet Users view policies and quizzes. User information to the company intranet. Users read policy docs and complete quizzes. VPC Server 40 Policy docs and quizzes and news items to the Intranet. Administrators publish policy docs and quizzes. VPC server sends published policy docs and quizzes to the server for distribution to the user sites. EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy Administrators receive policy docs and quizzes. Administration Site Policy Management • • • • Policy administrator Review schedule Review procedures and practices Policy and revision dates 41 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy Policy Administrator • Policy administrator – Champion – Mid-level staff member – Solicits input from business and information security communities – Makes sure policy document and subsequent revisions are distributed 42 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy Review Schedule • Periodically reviewed for currency and accuracy, and modified to keep current – Organized schedule of review – Reviewed at least annually – Solicit input from representatives of all affected parties, management, and staff 43 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy Review Procedures and Practices • Easy submission of recommendations • All comments examined • Management approved changes implemented 44 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy Policy and Revision Date • Often published without a date – Legal issue – are employees “complying with an out-of-date policy • Should include date of origin, revision dates – don’t use “today’s date” in the document • Sunset clause (expiration date) 45 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy Information Securities Policy Made Easy Approach • • • • • Gather key reference materials Develop a framework for policies Prepare a coverage matrix Make critical systems design decisions Structure review, approval, and enforcement processes 46 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy Information Securities Policy Made Easy Approach • Next Steps – Post policies – Develop a self-assessment questionnaire – Develop revised user ID issuance forms – Develop agreement to comply with InfoSec policies form – Develop tests to determine if workers understand policies 47 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy Information Securities Policy Made Easy Approach • Next steps (continued) – Assign information security coordinators – Train information security coordinators – Prepare and deliver a basic information security training course – Develop application-specific information security policies 48 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy Information Securities Policy Made Easy Approach • Next steps (continued) – Develop a conceptual hierarchy of information security requirements – Assign information ownership and custodianship – Establish an information security management committee 49 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy Information Securities Policy Made Easy Approach • Next steps (continued) – Develop an information security architecture document – Automate policy enforcement through policy servers 50 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy Final Note • Policies are a countermeasure to protect assets from threats – Policies exist to inform employees of acceptable (unacceptable) behavior – Are meant to improve employee productivity and prevent potentially embarrassing situations – Communicate penalties for noncompliance 51 EECS 711 Chapter 4 Information Security Policy