Polygenetic inheritance
advertisement

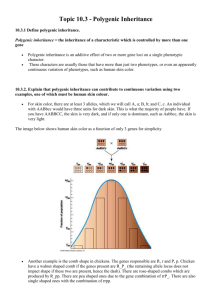
Objectives Outcomes Outline what polygenetic inheritance is. 3: Describe an example of polygenetic inheritance. 5: Explain why polygenetic inheritance arises. 7: Evaluate the importance of polygenetic characteristics in variation and evolution. Key terms: polygenetic inheritance, continuous, variation. 10.3.1 Define Polygenic inheritance Polygenic Inheritance – When a single trait is influenced by many genes. Each allele of a polygenic character often contributes only a small amount to the over all phenotype. This makes studying the individual alleles difficult. In addition environmental effects smooth out the genotypic variation to give continuous distribution curves. Skin colour video Outcomes 3: Describe an example of polygenetic inheritance. 5: Explain why polygenetic inheritance arises. 7: Evaluate the importance of polygenetic characteristics in variation and evolution. Key terms: polygenetic inheritance, continuous, variation. Outcomes 3: Describe an example of polygenetic inheritance. 5: Explain why polygenetic inheritance arises. 7: Evaluate the importance of polygenetic characteristics in variation and evolution. Key terms: polygenetic inheritance, continuous, variation. Outcomes 3: Describe an example of polygenetic inheritance. 5: Explain why polygenetic inheritance arises. 7: Evaluate the importance of polygenetic characteristics in variation and evolution. Key terms: polygenetic inheritance, continuous, variation. Outcomes 3: Describe an example of polygenetic inheritance. 5: Explain why polygenetic inheritance arises. 7: Evaluate the importance of polygenetic characteristics in variation and evolution. Key terms: polygenetic inheritance, continuous, variation. Outcomes 3: Describe an example of polygenetic inheritance. 5: Explain why polygenetic inheritance arises. 7: Evaluate the importance of polygenetic characteristics in variation and evolution. Key terms: polygenetic inheritance, continuous, variation. Polygenic Inheritance of skin color At least four loci and possibly more genes are involved. Example 3 loci: each has two possible alleles: A,a B,b C,c, each capital allele adds one unit of darkness each lower case allele adds nothing Parents with intermediate tone aabbcc AABBCC Offspring can have tone darker or lighter than either parent Polygenic Inheritance of skin color 0 1 2 3 4 5 Number of ‘darker’ alleles 6 1. A. B. C. D. Which human trait shows a pattern of polygenetic inheritance? ABO blood type Sickle cell anaemia Skin colour Co-dominant alleles 2. Why is it sometimes difficult to identify how certain characteristics are inherited in humans. A. Most genes are linked. B. Rates of mutation are high. C. The inheritance may be polygenic. D. The environment varies so little. 3. Describe the effects of polygenic inheritance using two specific examples. (5) Key terms: polygenetic inheritance, continuous, variation. 1. C 2. C 3. More than one gene controls / affects one characteristic; Reject more than 2 alleles can cause continuous variation / many different possible phenotypes; eg skin colour / other valid example; allele of each gene promotes melanin production or not / other valid example; eg grain colour in wheat / other valid example; allele of each gene promotes pigment production or not / other valid example; 5 max If first or second example is incorrect do not accept third or subsequent examples. Key terms: polygenetic inheritance, continuous, variation.