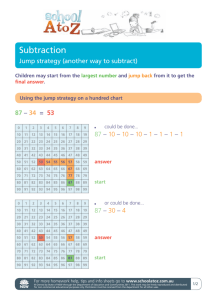
10. What is quality?
advertisement

Case Analysis for Quiz 5 The Manchester United Soccer Tournament project team has identified the following potential risks to their project: Referees failing to show up at designated games. Fighting between teams. Pivotal error committed by a referee that determines the outcome of a game. Abusive behavior along the sidelines by parents. Inadequate parking. Not enough teams sign up for different age brackets. Serious injury. Jump to first page Event Response Contingency Referees fail to show up Mitigate---contact referees night before games Referee (s) on call who can fill in Fighting Mitigate---train referees on how to diffuse potentially violent situations/publicize stiff penalties for fighting Referees, game officials, and coaches intervene Error Mitigate---recruit seasoned referees and assign best referees to most important games Have a tournament czar who adjudicates appeals Abusive parents Transfer---assign responsibility to coaches to manage Referees empowered to penalize team and dismiss parents Inadequate parking Mitigate: level game schedule Shuttle service Not enough teams Mitigate: PR campaign Collapse age groups Injury Accept Contact ER in advance, setup field communication 2 system Jump to first page 10. Managing quality Many people joke about the poor quality of IT products (cars and computers joke) People seem to accept systems being down occasionally or needing to reboot their PCs There are many examples in the news about quality-related problems 3 Jump to first page 10. Managing quality In one of the biggest software errors in banking history, Chemical Bank mistakenly deducted about $15 million from more than 100,000 customer accounts one evening. The problem resulted from a single line of code in an updated computer program that caused the bank to process every withdrawal and transfer at its automated teller machines (ATMs) twice. For example, a person who withdrew $100 from an ATM had $200 deducted from his or her account, though the receipt only indicated a withdrawal of $100. The mistake affected 150,000 transactions from Tuesday night through Wednesday afternoon. In 1996 Apple Computer's PowerBook 5300 model had problems with lithium-ion battery packs catching fire, causing Apple to halt shipments and replace all the packs with nickelmetal-hydride batteries. Other quality problems also surfaced, such as cracks in the PowerBook's plastic casing and a faulty electric power adapter. 4 Jump to first page 10. Software quality – Gates & GM At a COMDEX exposition, Bill Gates stated, “If General Motors had kept up with technology like the computer industry has, we would all be driving twenty-five dollar cars that got 1000 miles to the gallon.” In response to Gates’ comments, General Motors issued a press release stating, “If GM had developed technology like Microsoft, we would all be driving cars with the following characteristics: 5 Jump to first page 10. Software quality – Gates & GM For no reason whatsoever your car would crash twice a day. Every time they repainted the lines on the road you would have to buy a new car. Occasionally your car would die on the freeway for no reason, and you would just accept this, restart, and drive on. Occasionally, executing a maneuver such as a left turn, would cause your car to shut down and refuse to restart, in which case you would have to reinstall the engine. The airbag system would say ‘Are you sure?’ before going off. 6 Jump to first page 10. Software quality – Gates & GM Occasionally, for no reason whatsoever, your car would lock you out and refuse to let you in until you simultaneously lifted the door handle, turned the key, and grabbed hold of the radio antenna. Every time GM introduced a new model car, buyers would have to learn how to drive all over again because none of the controls would operate in the same manner as the old car. You would press the Start button to shut off the engine. 7 Jump to first page 10. Quality matters Software quality is a critical success factor. Software quality must: Have the support of the management Be planned early in the design phase Be understood and followed by everyone on the team Be monitored continuously Be documented for accountability and reference 8 Jump to first page 10. Quality matters Several factors influenced system developers to consider system quality: End user computing environment User friendly tools User satisfaction as surrogate for system success Fourth generation languages/products 9 Jump to first page 10. Quality advantage Emphasis on quality has several advantages: Financial – maintenance, time Operational – rework, bugs Legal – privacy, security Contractual – compliance Customer relation – CRM Reputation – image Moral – being part of a winning team Appraisal – performance evaluation 10 Jump to first page 10. What is quality? The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) defines quality as the totality of characteristics of an entity that bear on its ability to satisfy stated or implied needs Other experts define quality based on conformance to requirements: meeting written specifications fitness for use: ensuring a product can be used as it was intended 11 Jump to first page 10. Quality management Modern quality management requires customer satisfaction prefers prevention to inspection recognizes management responsibility for quality Noteworthy quality experts include Deming, Juran, Crosby, Ishikawa, Taguchi, and Feigenbaum 12 Jump to first page 10. Quality pioneers Deming was famous for his work in rebuilding Japan and his 14 points Juran wrote the Quality Control Handbook and 10 steps to quality improvement Crosby wrote Quality is Free and suggested that organizations strive for zero defects Ishikawa developed the concept of quality circles and using fishbone diagrams Taguchi developed methods for optimizing the process of engineering experimentation Feigenbaum developed the concept of total quality control 13 Jump to first page 10. Quality awards The Malcolm Baldrige Quality Award was started in 1987 to recognize companies with world-class quality ISO 9000 provides minimum requirements for an organization to meet their quality certification standards 14 Jump to first page 10. Quality management Plan it: identifying which quality standards are relevant to the project and how to satisfy them Implement it: evaluating overall project performance to ensure the project will satisfy the relevant quality standards Monitor it: monitoring specific project results to ensure that they comply with the relevant quality standards while identifying ways to improve overall quality 15 Jump to first page 10. Quality planning It is important to design for quality and communicate important factors that directly contribute to meeting the customer’s requirements Design of experiments helps identify which variables have the most influence on the overall outcome of a process Many scope aspects of IT projects affect quality like functionality, features, system outputs, performance, reliability, and maintainability 16 Jump to first page 10. Quality implementation Quality assurance includes all the activities related to satisfying the relevant quality standards for a project Another goal of quality assurance is continuous quality improvement Benchmarking can be used to generate ideas for quality improvements Quality audits help identify lessons learned that can improve performance on current or future projects 17 Jump to first page 10. Quality control The main outputs of quality control are: Acceptance decisions Rework Process adjustments Some tools and techniques include: Pareto analysis Statistical sampling Quality control charts Testing 18 Jump to first page 10. Quality pioneers suggest Top management involvement Start early at the design phase Make it part of the process Keep it continuous Empower team members to manage quality Train team members for quality control and assessment Reward teams for quality performance eliminate fear and promote free and open communication 19 Jump to first page 10. Pareto analysis Pareto analysis involves identifying the vital few contributors that account for the most quality problems in a system Also called the 80-20 rule, meaning that 80% of problems are often due to 20% of the causes Pareto diagrams are histograms that help identify and prioritize problem areas 20 Jump to first page 10. Sample Pareto diagram 21 Jump to first page 10. Statistical sampling and standard deviation Statistical sampling involves choosing part of a population of interest for inspection The size of a sample depends on how representative you want the sample to be Sample size formula: Sample size = .25 X (certainty factor/acceptable error) 22 Jump to first page 10. Commonly used certainty factors Desired Certainty Certainty Factor 95% 1.960 90% 1.645 80% 1.281 95% certainty: Sample size = 0.25 X (1.960/.05) = 384 90% certainty: Sample size = 0.25 X (1.645/.10) = 68 80% certainty: Sample size = 0.25 X (1.281/.20) = 10 23 Jump to first page 10. Standard deviation Standard deviation measures how much variation exists in a distribution of data A small standard deviation means that data cluster closely around the middle of a distribution and there is little variability among the data A normal distribution is a bell-shaped curve that is symmetrical about the mean or average value of a population 24 Jump to first page 10. Normal distribution and S. D. 25 Jump to first page 10. Sigma and defective units Specification Range Percent of Population (in +/- Sigmas) Defective Units Per Billion Within Range 1 68.27 317,300,000 2 95.45 45,400,000 3 99.73 2,700,000 4 99.9937 63,000 5 99.999943 57 6 99.9999998 2 26 Jump to first page 10. Six sigma and seven run rule Operating at a higher sigma value, like 6 sigma, means the product tolerance or control limits have less variability The seven run rule states that if seven data points in a row are all below the mean, above the mean, or increasing or decreasing, then the process needs to be examined for non-random problems 27 Jump to first page 10.Sample Quality Control Chart 28 Jump to first page 10. Fishbone diagram 29 Jump to first page 10. Testing Many IT professionals think of testing as a stage that comes near the end of IT product development Testing should be done during almost every phase of the IT product development life cycle 30 Jump to first page 10. Types of tests A unit test is done to test each individual component (often a program) to ensure it is as defect free as possible Integration testing occurs between unit and system testing to test functionally grouped components System testing tests the entire system as one entity User acceptance testing is an independent test performed by the end user prior to accepting the delivered system 31 Jump to first page 10. Gantt Chart for building testing into a systems development project plan 32 Jump to first page 10. Improving IT project quality Several suggestions for improving quality for IT projects include Leadership that promotes quality Understanding the cost of quality Focusing on organizational influences and workplace factors that affect quality Following maturity models to improve quality 33 Jump to first page 10. Leadership “It is most important that top management be quality-minded. In the absence of sincere manifestation of interest at the top, little will happen below.” (Juran, 1945) A large percentage of quality problems are associated with management, not technical issues 34 Jump to first page 10. The cost of quality The cost of quality is the cost of conformance or delivering products that meet requirements and fitness for use the cost of nonconformance or taking responsibility for failures or not meeting quality expectations 35 Jump to first page 10. Cost categories related to quality Prevention cost: the cost of planning and executing a project so it is error-free or within an acceptable error range Appraisal cost: the cost of evaluating processes and their outputs to ensure quality Internal failure cost: cost incurred to correct an identified defect before the customer receives the product External failure cost: cost that relates to all errors not detected and corrected before delivery to the customer Measurement and test equipment costs: capital cost of equipment used to perform prevention and appraisal activities 36 Jump to first page 10. Organizational influences, workplace factors, and quality A study by DeMarco and Lister showed that organizational issues had a much greater influence on programmer productivity than the technical environment or programming languages Programmer productivity varied by a factor of one to ten across organizations, but only by 21% within the same organization The study found no correlation between productivity and programming language, years of experience, or salary A dedicated workspace and a quiet work environment were key factors to improving programmer productivity 37 Jump to first page 38 Jump to first page 9. Discussion questions Describe three factors that influence quality. How would you plan for quality control? Does statistical quality control make sense in all situations? Do you find quality charts useful to your monitoring of quality. Does seven run rule make sense to you? 39 Jump to first page 9. Discussion questions The study by DeMarco and Lister showed that organizational issues had a much greater influence on programmer productivity than the technical environment or programming languages Programmer productivity varied by a factor of one to ten across organizations, but only by 21% within the same organization. Does this make sense? 40 Jump to first page 9. Discussion questions The study found no correlation between productivity and programming language, years of experience, or salary A dedicated workspace and a quiet work environment were key factors to improving programmer productivity Does this make sense to you? 41 Jump to first page