review guide link
advertisement

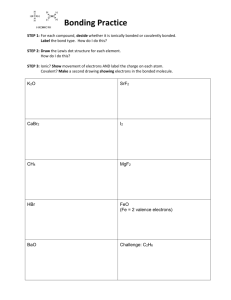
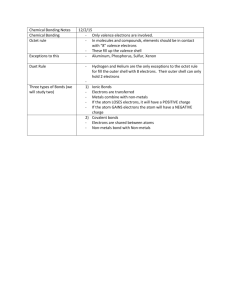
Chemistry Review Guide for Electrons, Bonding, and Geometry. The topics covered during this unit have been: Electrons- Energy levels, sublevels, and orbitals. Electron Notation- How we describe and notate the electrons in a certain atom. Valence Electrons- The electrons that actually interact with their surroundings and participate in most bonding. Types of bonds – The three types of bonds; Metallic, Ionic, and Covalent. The typical properties of compounds with metallic, ionic, and covalent bonds. Molecular Geometry- The way our molecules take shape due to their bonded and nonbonded electrons. VSEPR Model, stick and ball 3D models, shapes, and angles. The two different covalent bonds- Polar and Non-Polar Periodic trends- Electronegativity Polarity in molecules- How the types of atoms in a molecule affect the molecules polarity. When you are studying for this unit test please remember that you have multiple resources for help. I have posted my power points used, Khan Academy links, Podcast links/ and you have your notes, the chemistry book, your old homework, quizzes, and your peers and I. Please recognize the many avenues available to help yourself prepare for the test. If you have an urgent question you can email me for answers. I am also available after class and sometimes before. Please take time to look over the unit as a whole system, these individual concepts and ideas about the atom and bonding all interlink. They are what create the multitude of different types of matter around us! I will go over the basic concepts that will be addressed in the test, but I am not going to go over each and every detail about how to work every scenario out on this guide. I will also be linking some place where applicable. Electrons We took a close look at how electrons situate themselves around their nucleus. We learned how there were different levels and in the levels there were even more specific sublevels. For every electron around a nucleus there is a specific energy level, sublevel, orbit and spin assigned to it. We use these to help us understand where electrons are around our atom and how they will affect the way the atom interacts with other atoms and matter it comes in contact with. We know how this looks on a Bohr diagram and also how we assign these electrons in proper notation. Electron notation We have 3 different ways to notate electron around an atom 1. Orbital notation 2. Electron configuration 1s22s22p63s23p6…………. 3. Noble gas configuration, remember go back to the last noble gas, not the next!! [He]2s1 Valence Electrons Valence electrons are the electrons that are in a incomplete energy level and that directly affect bonding between atoms. We must always take into account these electrons when we are creating bonds. Valence electrons often want to create an octet (full energy level) when bonding occurs. https://www.khanacademy.org/science/chemistry/periodic-table-trends-bonding/v/valenceelectrons YOU MUST BE ABLE TO DRAW LEWIS DOT STRUCTURES CONTAINING THE VALENCE ELECTRONS!!!! Types of bonds You will need to understand the 3 major types of bonds; metallic, covalent, and ionic. You will need to know that metallic is like a sea of electrons surrounding the positively charged metal cations. You will need to be able explain how ionic bonds are when an atom takes an electorn form another, creating a positive and negatively charged ions, and that these charges then create an attractions that bonds them together. Covalent bonds have two types, polar and nonpolar, both of which share electrons in order to create a bonded connection. Polar is when the electronegativity of one of the bonded atoms attracts the bonded electrons closer to it. This attractions leads to a partial positive and partial negative charge to the atoms in the bond. Nonpolar covalent bonds, on the other hand, have very little different in electronegative charge and lead to a more equally shared bonding of the electrons. http://www.khanacademy.org/science/chemistry/periodic-table-trends-bonding/v/ionic-covalent--and-metallic-bonds http://www.nthurston.k12.wa.us/cms/lib/WA01001371/Centricity/Domain/2297/bonding7.mp 4 Remember only polar bonds lead to polar molecules, and only when there is an unequal and/or nonsymmetrical electronegative bond(s) in the molecule. YOU WILL NEED TO KNOW HOW SOLUBILITY, CONDUCTIVITY, MELTING POINTS AND TYPES OF ELEMENTS DIFFER IN THESE BONDS!!!!!!!!!! Pg 193 and 195 Molecular Geometry The way our molecules take shape due to their bonded and non-bonded electrons. VSEPR Model, stick and ball 3D models, shapes, and angles. You will need to understand the basic shapes such as linear, bent, trigonal planar, trigonal pyramidal, and tetrahedral. You will also need to be able to draw the molecule with bonded and non-bonded pairs. You will need to be able to draw lewis structure both dot and bonded lewis structures. You will need to be able to describe why the VSEPR model creates the different shapes in molecules. Remember bonded and non-bonded pairs (lone pairs) repulsion creates the overall shape of the molecule!!!!