Chemical Formulas: Writing and Naming Rules
advertisement

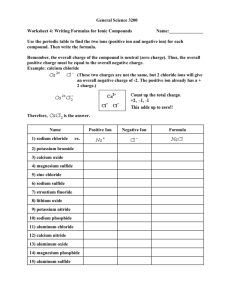
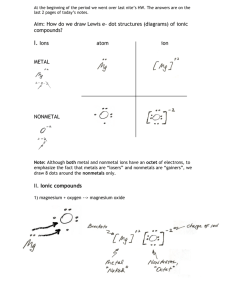
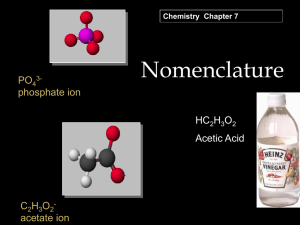
Writing and Naming Chemical Formulas Six Rules Are The Key…….. Rule 1 The positive ion is always written first in a chemical formula. Remember it is the metals on the left side of the periodic table that like to be positive when they become ions. Example: Sodium chloride NaCl Example: Calcium chloride CaCl2 Rule 2 The negative ion is written in the second “half” of the formula. Non-metals that have become negative ions change their name to ending with (–ide.) Example: Sodium chloride NaCl Example: magnesium oxide MgO Rule 3 Subscripts are used to indicate how many of each ion are needed in the formula to create a neutral compound. Reminder neutral means having no charge value. Example: sodium chloride NaCl Example: calcium flouride CaF2 Example: aluminum sulfide Al2S3 Rule 4 Transition metals are located in the short columns of the Periodic Table. Because these metals often can have more than one possible charge Roman Numerals are used to indicate the charge on the metal. Example: tin IV chloride SnCl4 Example: Chromium VI sulfide CrS3 Rule 5 Polyatomic ions are located in an alphabetized list on the back of the Periodic Table. The endings -ate and –ite “mean” mixed with oxygen! If a polyatomic ion needs a subscript, the ion must be put in parentheses. Example: Aluminum hydroxide Al(OH)3 Example: Calcium acetate Ca(C2H3O2)2 Rule 6 Two non-metals will sometimes bond covalently. Because the charges make “no sense” Latin prefixes are used to indicate how many of each substance are found in the compound. Example: N2O4 Dinitrogen tetroxide Example: triphosphorus hexachloride P3Cl6 Lets Practice! Slide 13 Please write out the following formulas. Check charges you may need to use subscripts! Example: Potassium nitride Example: Calcium phosphate Example: Ammonium oxide Example: Gold III chloride Lets Practice! Slide 14 Please correctly name the following compounds. Don’t worry these formulas all correctly written with correct subscripts etc…. Example: SrCO3 Example: Ca(NO3)2 Example: CrO3 Example: N2Cl4 More practice………slide 15 Example: MnCl6 Example:CCl4 Example: (NH4)2S Example: K2CrO4 Example: Cr Br6 Example: MgC2O4 More practice…………slide 16 Example: CO2 Example: CaCO3 Example: K2SO4 Example: TiS Example: Li2SO3 Example: Sr2C Answers Slide 13 KNO3 Ca3(PO4)2 (NH4)2O AuCl3 Answers Slide 14 SO5 V2S5 Na2SO4 Fe2O3 N3S6 AlBr3 Answers Slide 15 Manganese VI chloride Monocarbon tetrachloride Ammonium sulfide Potassium chromate Chromium VI bromide Magnesium oxalate Answers Slide 16 Monocarbon dioxide Calcium carbonate Potassium sulfate Titanium II sulfide Lithium sulfite Strontium carbide