plate tectonics PP
advertisement

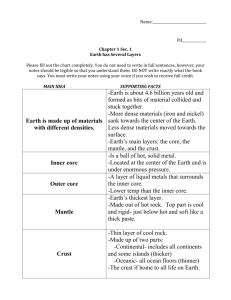
Bell work 9/17/15 1. Get out your Earth Layers foldable and sheet of notebook paper. 2. On the sheet of notebook paper answer the question. What are the differences between the three layers of the earth? Inside the Earth….Textbook page 393 The Core • made of nickle and iron • Outer core - liquid layer • Inner core - solid The Mantle: • Thickest layer between 6580%. • Takes up most of the Earth's mass @ 80% • 3 parts of the Mantle Lithosphere - Upper part of the mantle and the crust Asthenosphere - soft plastic like layer which tectonic plates move on. Mesosphere - lowest part of the mantle and is the densest The crust textbook page 392 Outer most and thinnest layer 2 types • Oceanic and Continental Oceanic crust - more dense Continental crust - less dense The Physical structure of Earth textbook pages 394-395 How do we know the Earth’s interior consistency???? Textbook page 398 seismic waves – vibrations caused by earthquakes Seismologists use readings from seismographs to calculate the density and thickness of each layer of the Earth. Intro. to Earthquakes by Frank Gregario tectonic plates – pieces of the lithosphere that move around on top of the asthenosphere Textbook page 396 • continental drift – hypothesis that the continents once formed a single landmass, broke up, and drifted to their present locations. • Textbook page 401 Textbook page 402 magnetic reversals and sea-floor spreading textbook page 403 sea-floor spreading – process by which new oceanic lithosphere forms as magma rises toward the surface and solidifies molten rock contains magnetic materials. magnetic materials align with the magnetic field of the Earth. molten rock cools and these materials are set in their direction. Earth’s magnetic field reverses magnetic materials align with the magnetic field of the Earth molten rock cools and these materials are set in this new direction. The Theory of Plate Tectonics textbook pages 404-405 plate tectonics – the theory that the Earth’s lithosphere is divided into tectonic plates that move around on top of the asthenosphere 3 possible causes of Plate tectonics textbook page 406 • What causes changes in density in the asthenosphere? – the circulation of thermal energy… as rock is heated, it expands, becomes less dense, and rises… as rock cools, it contracts, becomes denser, and sinks. How do the forces of plate tectonics cause rock deformation????? • compression • Tension compression can cause rocks to be pushed into mountain ranges as tectonic plates collide at convergent boundaries. tension can pull rocks apart as tectonic plates separate at divergent boundaries. folding textbook page 409 Faulting Strike-Slip How mountains are formed….. http://travel.nationalgeographic.com/travel/nationalparks/great-smoky-mountains-app/ How are mountains formed???? when tectonic plates undergo compression or tension • Folded mountains – rock layers are squeezed together and pushed upward • Fault-block – tension causes large blocks of the Earth’s crust to drop down relative to other blocks • Volcanic – rock that is melted in subduction zones forms magma then rises to the Earth’s surface and erupts. • uplift • subsidence • rift zone All photos and information for this power point was taken from the teacher’s edition of Holt Science & Technology, Tennessee grade 7. Except where noted……