Definition
advertisement

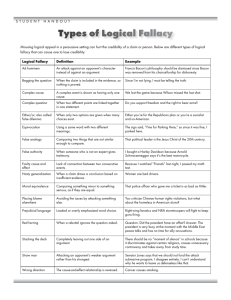
AP LANGUAGE & COMPOSITION Fall 2015 Terms Synecdoche Definition: a figure of speech that employs the use of a part for the whole, or the whole for the part Examples: Jack bought a new set of wheels. The Confederates have eyes in Lincoln's government. Colloquial Definition: the characteristic of writing that seeks the effect of informal spoken language as distinct from formal or literary English Example: "If you really want to hear about it, the first thing you'll probably want to know is where I was born, and what my lousy childhood was like, and how my parents were occupied and all before they had me, and all that David Copperfield kind of crap, but I don't feel like going into it, if you want to know the truth." (The Catcher in the Rye by J.D. Salinger) Litotes Definition: a figure of understatement in which an affirmative is expressed by a negation of the contrary or opposite Examples: A few unannounced quizzes are not inconceivable. I'm not forgetful that you served me well.–John Milton Metonymy Definition: a figure of speech in which one word or phrase is substituted for another with which it is closely associated Examples: Wall Street welcomes the reduction in interest rates. In Shakespeare's time, the crown was anti-Catholic. Paradox Definition: an assertion seemingly opposed to common sense because it contains a contradiction, but that may yet have some truth in it Examples: “What a pity that youth must be wasted on the young.”—George Bernard Shaw “I can resist anything but temptation .”— Oscar Wilde “Great fiction is a kind of lie that tells the truth, but it's impossible to lie about lies and end up with anything besides more lies. “(Laura Miller, “Why We Haven’t Seen a Great 9/11 Novel, Salon.com, 14 Sept. 2011) Euphemism Definition: the use of a word or phrase that is less direct, but that is also less distasteful or less offensive than another Examples: She missed class because her grandmother passed away last week. Many people are opposed to the government’s using enhanced interrogation techniques on prisoners. Hyperbole Definition: an extravagant exaggeration of fact, used either for serious or comic effect Examples: Ten thousand oceans cannot wash away my guilt. "I have seen this river so wide it had only one bank.“— Mark Twain Allusion Definition: a brief or casual reference to a famous person, historical event, place, or work of art Examples: Since my elementary-school days, math has always been my Achilles heel. "I have met my Waterloo," the mountain climber said after returning from a failed attempt to conquer Everest. Irony Definition: an expression of something which is contrary to the intended meaning; the words say one thing but mean another Examples: "What a beautiful day," Maxine said, opening her umbrella. “Yet Brutus says he was ambitious; And Brutus is an honourable man.”—Marc Antony in Shakespeare’s Julius Caesar Apostrophe Definition: a sudden turn from the general audience to address a specific group or person or personified abstraction absent or present Examples: “For Brutus, as you know, was Caesar's angel. Judge, O you gods, how dearly Caesar loved him.”— Marc Antony in Shakespeare’s Julius Caesar “Death be not proud, though some have called thee Mighty and dreadfull, for, thou art not soe,”—John Donne Ethos Definition: Appeal attempts to persuade by calling attention to the writer’s/ speaker’s character. Ethos does not concern the veracity of the argument, only its appeal. Examples: I am a husband, a father, and a taxpayer. I’ve served faithfully for 20 years on the school board. I deserve your vote for city council. “I would agree with St. Augustine that ‘an unjust law is no law at all.’” –MLK, “Letter from Birmingham Jail” Damning with Faint Praise Definition: The argument "attacks" a position by complimenting or praising the opponent or the opponent's argument. However, the praise is misdirected or unenthusiastic. Some common forms of faint praise might include calling an opponent's position "well intentioned," "a fine ideal," or "based on legitimate concerns." They might include saying that the opponent "makes some good points," or "shouldn't be blamed." From an early episode of Frasier: Frasier: Niles, you're a good brother and a credit to the psychiatric profession. Niles: You're a good brother too. That’s an interesting outfit you are wearing. Deductive Reasoning Definition: Deductive reasoning draws specific conclusions from general principles or premises. Unlike inductive reasoning, which always involves uncertainty, the conclusions from deductive inference are certain provided the premises are true. Scientists use inductive reasoning to formulate hypothesis and theories, and deductive reasoning when applying them to specific situations. Examples: If there are a red ball and a blue ball in a bag, and each color ball is drawn one-half of the time, we come to believe that each color ball has a one-half probability of being drawn at any one time. If you work hard, then you will succeed, and if you succeed, then you therefore, if you work hard, you will be happy. will be happy; False Analogy Definition: A false analogy occurs when the two objects or events being compared are relevantly dissimilar. Examples: Guns are like hammers – they’re both tools with metal parts that could be used to kill someone. And yet it would be ridiculous to restrict the purchase of hammers – so restrictions on purchasing guns are equally ridiculous. Education cannot prepare men and women for marriage. Trying to educate them for marriage is like trying to teach them to swim without allowing them to go into the water. It can’t be done. Inductive Reasoning Definition: Inductive reasoning, or induction, is reasoning from a specific case or cases and deriving a general rule. It draws inferences or conclusions from observations. Scientists use inductive reasoning to formulate hypothesis and theories, and deductive reasoning when applying them to specific situations. Examples: All known planets travel about the sun in ellipitical orbits; therefore, all planets travel about the sun in ellipitical orbits. Johnny has chocolate smeared on his face and hands and crumbs on his shirt, and he is the only one in the kitchen standing next to the open cookie jar. Conclusion: Johnny has been eating cookies out of the cookie jar. Logos Definition: Logos is appeal based on logic or reason. This can be achieved through facts, statistics, logical analogies, expert testimony, definitions, etc. Examples: Notably, since stabilizing in mid-2009, real household spending in the United States has grown in the range of 1 to 2 percent at annual rates, a relatively modest pace. Households' caution is understandable. Importantly, the painfully slow recovery in the labor market has restrained growth in labor income, raised uncertainty about job security and prospects, and damped confidence. Pathos Definition: Pathos is appeal based on emotion, usually using emotionally loaded or connotative language, vivid descriptions, and narration of emotional events. Examples: "Our hearts are broken by their sudden passing. Our hearts are broken -– and yet, our hearts also have reason for fullness.” President Obama in his eulogy for the Tuscon shooting victims “Like a boil that can never be cured so long as it is covered up but must be opened with all its ugliness to the natural medicines of air and light, injustice must be exposed, with all the tension its exposure creates, to the light of human conscience and the air of national opinion before it can be cured.” MLK, “Letter from Birmingham Jail” Syllogism Definition: A form of deductive reasoning consisting of a major premise, a minor premise, and a conclusion. Example: -All humans are mortal .(major premise) -I am a human. (minor premise) -Therefore, I am mortal. (conclusion) -All dogs are mammals. (major premise) -All golden retrievers are dogs. (minor premise) -Therefore, all golden retrievers are mammals. (conclusion) Argument ad hominem Definition: Attacking the opponent rather than the opponent’s argument. Examples: "You can't believe Jack when he says the proposed policy would help the economy. He doesn't even have a job.” ”They [British voters] know their Premier to be a neurotic, dysfunctional mediocrity; an insecure Stalinist who worships power but cannot take a decision; a moral and political coward who tries to fill the vacuum at the heart of his leadership with blustering rhetoric and adolescent bullying.” Non sequitur fallacy – “does not follow” Definition: A fallacy in which a conclusion does not follow logically from what preceded it. Drawing a conclusion from irrelevant evidence. Examples: If you loved me, you’d buy me a car. We can't figure out how any natural process could account for the complexity of the human cell or the bacterial flagellum or a donkey's eye or some other complex biological entity; therefore, an intelligent designer must have put these parts together in the cell. Either/Or Fallacy Definition: Also known as false dilemma fallacy, this is a fallacy in argument that occurs when someone is asked to choose between two options when there are clearly other alternatives Examples: My country right or wrong. You either support the war or you support the terrorists. Sweeping Generalization Fallacy Definition: a fallacy which applies a general statement too broadly or uses some statement in an all-inclusive way without allowing for any exceptions, such as a stereotype Example: That fraternity got in trouble for hazing; all fraternities need to be banned for hazing. The apples on the top of the box look good. The entire box of apples must be good. Post Hoc, Ergo Prompter Hoc Fallacy a fallacy which infers a causal connection. In other words, just because one event happened before another doesn’t mean it caused the second event to happen. Definition: Examples: Most people die after being given last rites; therefore, priests kill people when they administer last rites. The baseball slugger didn’t wear his lucky socks, which caused him to go 0 for 4 and make two fielding errors. Argument Ad Populum Definition: The fallacy of attempting to win popular assent to a conclusion by arousing the feeling and enthusiasms of the multitude. Examples: True patriots will buy only Chevrolets! Taking the words “under God” out of the Pledge of Allegiance violates our Judeo-Christian heritage. Slippery Slope Fallacy a fallacy in which the arguer asserts that if we take even one step onto the "slippery slope," we will end up sliding all the way to the bottom without being able to stop Definition: Examples: First we'll ban assault rifles, then handguns, then rifles, then shotguns, then, eventually,�BB guns and finally squirt guns...and snowballs. (this one also includes reductio ad absurdum—taking it to the point of absurd) Animal experimentation reduces our respect for life. If we don't respect life, we are likely to be more and more tolerant of violent acts like rape and murder. Begging the Question Fallacy an argument which asks the reader to simply accept the conclusion without providing real evidence Definition: Examples: It is a decent, ethical thing to help another human being escape suffering through death. Paranormal phenomena exist because I have had experiences that can only be described as paranormal. Circular Reasoning an attempt to support a statement by simply repeating the statement in different or stronger terms. In this fallacy, the reason given is nothing more than a restatement of the conclusion that poses as the reason for the conclusion Definition: Examples: Richardson is the most successful mayor the town has ever had because he's the best mayor of our history. President Reagan was a great communicator because he had the knack of talking effectively to the people. Straw Man Fallacy an argument where the opponent's position is misrepresented and, instead of attacking the opponents position, the misrepresentation is attacked. Definition: Examples: We should have conscription. People don't want to enter the military because they find it an inconvenience. Supporting the Patriot Act is advocating the destruction of the civil rights of all Americans. Hasty Generalization Fallacy Definition: this fallacy is the opposite of a sweeping generalization as it infers a general rule from a specific case, jumping to a bold conclusion based on a limited sample of evidence Examples: The old man who lives next door yelled at me for walking through his lawn; he’s just a grouchy, mean old man. You can't speak French. I can't speak French. Petey Burch can't speak French. I must therefore conclude that French is too difficult a language to learn. Equivocation Fallacy when a key word or phrase in an argument is used with more than one meaning. It is an illegitimate switching of the meaning of a term during the reasoning. Definition: Examples: A feather is light. Therefore, a feather cannot be dark. I don’t approve of political jokes. I’ve seen too many of them get elected. Polysyndeton Definition: sentence style that uses many conjunctions to slow the rhythm or to suggest the continuity of the experience Examples: "He pulled the blue plastic tarp off of him and folded it and carried it out to the grocery cart and packed it and came back with their plates and some cornmeal cakes in a plastic bag and a plastic bottle of syrup." (Cormac McCarthy, The Road) "Let the whitefolks have their money and power and segregation and sarcasm and big houses and schools and lawns like carpets, and books, and mostly--mostly--let them have their whiteness.“ (Maya Angelou, I Know Why the Caged Bird Sings,) Anaphora Definition: a repetition of the same word or group of words at the beginnings of successive clauses Example: "I needed a drink, I needed a lot of life insurance, I needed a vacation, I needed a home in the country. What I had was a coat, a hat and a gun.“ (Raymond Chandler, Farewell, My Lovely) "Of all the gin joints in all the towns in all the world, she walks into mine.“ (Rick Blaine in Casablanca) Loose (Cumulative) Sentence Definition: A type of sentence in which the main idea (independent clause) comes first, followed by dependent grammatical units such as phrases and clauses. If a period were placed at the end of the independent clause, the clause would be a complete sentence. The effect can be to make a work seem informal, relaxed, and conversational. Examples: The hotel has greatly expanded its customer base through the addition of a fitness spa, extensive advertising, and weekend specials. He was willing to pay slightly higher taxes for the privilege of living in Canada, considering the free health care, the cheap tuition fees, the low crime rate, and the comprehensive social programs. Periodic Sentence The opposite of loose sentence, a sentence that presents its central meaning in a main clause at the end. This independent clause is preceded by phrases or clauses that cannot stand alone. The effect of a periodic sentence is to add emphasis, structural variety, and to build suspense. Definition: Examples: After a long, bumpy flight and multiple delays, I arrived at the San Diego airport. "And though I have the gift of prophecy, and understand all mysteries, and all knowledge; and though I have all faith, so that I could remove mountains, and have not charity, I am nothing.“ (The King James Bible, I Corinthians 13) Zeugma the (often faulty) ellipsis of a verb or a noun used to join two or more parts of a sentence. The meaning is mostly parallel Definition: Examples: Lust conquered shame, boldness fear, madness reason. As Virgil guided Dante through Inferno, the Sibyl Aeneas Avernus. Alexander conquered the world; I, Minneapolis. Tricolon three parallel elements of the same length occurring in a series Definition: Examples: "You are talking to a man who has laughed in the face of death, sneered at doom, and chuckled at catastrophe.“ (The Wizard of Oz, 1939) "Tell me and I forget. Teach me and I remember. Involve me and I learn." (attributed to Benjamin Franklin) Apposition placing side by side two coordinate elements, the second of which serves as an explanation or renaming of the first Definition: Examples: "This is a valley of ashes--a fantastic farm where ashes grow like wheat into ridges and hills and grotesque gardens…” (The Great Gatsby, F. Scott Fitzgerald) "Miniver Cheevy, child of scorn, grew lean while he assailed the seasons.“ (E.A. Robinson, "Miniver Cheevy") Parallel Structure a similarity of grammatical structure in a pair or series of related words, phrases, or clauses Definition: Examples: "It is by logic we prove, but by intuition we discover.” (Leonardo da Vinci) "Humanity has advanced, when it has advanced, not because it has been sober, responsible, and cautious, but because it has been playful, rebellious, and immature.” (Tom Robbins, author) Asyndeton Definition: the deliberate omission of conjunctions between a series of related clauses Examples: “Veni, vidi, vici.” (I came, I saw, I conquered) (Julius Caesar) “Dogs, undistinguishable in mire. Horses, scarcely better; splashed to their very blinkers. Foot passengers, jostling one another’s umbrellas in a general infection of ill-temper…” (from Bleak House, Charles Dickens) Syllepsis a kind of zeugma in which the clauses, which are usually added as a pun, do not stick to the sentence grammatically and ideologically. You can remember it as a union of incongruous elements. Syllepsis is mostly used to lend a comic or a satiric effect. Definition: Examples: “He carried a strobe light and the responsibility for the lives of his men.” (from The Things They Carried, Tim O’Brien) Cecily: “Oh, flowers are as common here, Miss Fairfax, as people are in London.” (from The Importance of Being Earnest, Oscar Wilde) The ink, like our pig, keeps running out of the pen. Periphrasis Definition: substitution of a descriptive word or phrase for a proper name or of a proper name for a quality associated with the name. Examples: “The big man upstairs hears your prayers.“ “They do not escape Jim Crow; they merely encounter another, not less deadly variety.“ (James Baldwin, Nobody Knows My Name,) Imagery : lively descriptions which appeal to the five senses. Definition Example: “The dog stood up and growled like a lion, stiff-standing hackles, teeth uncovered as he lashed up his fury for the charge” (Hurston, Their Eyes Were Watching God) "When the others went swimming my son said he was going in, too. He pulled his dripping trunks from the line where they had hung all through the shower and wrung them out. Languidly, and with no thought of going in, I watched him, his hard little body, skinny and bare, saw him wince slightly as he pulled up around his vitals the small, soggy, icy garment. As he buckled the swollen belt, suddenly my groin felt the chill of death. (E.B. White, "Once More to the Lake," 1941) Metaphor a figure of speech in which one thing is compared to another by being spoken of as though it were that thing Definition: Examples: The question of federal aid to parochial schools is a bramble patch. David was a lion in battle. Oxymoron Definition: a figure of speech in which contradictory terms or ideas are combined Examples: "O brawling love! O loving hate! / O anything of nothing first create! / O heavy lightness, serious vanity! / Misshapen chaos of well-seeming forms! / Feather of lead, bright smoke, cold fire, sick health!" (Romeo, Act One from Romeo and Juliet) Jumbo shrimp Paralipsis Definition: drawing attention to something by pretending to pass over it. Examples: Mark Antony’s famous Friends, Romans, Countrymen speech – “Let the commons hear this testament,/Which (pardon me) I do not mean to read,/And they would go and kiss dead Caesar’s wounds…/have patience, gentle friends; I must not read it./It is not meet you know how Caesar lov’d you…/Tis good you know not that you are his heirs.” "The music, the service at the feast, The noble gifts for the great and small, The rich adornment of Theseus's palace . . . All these things I do not mention now." (Chaucer, "The Knight's Tale," The Canterbury Tales) Personification a figure of speech in which an inanimate object or abstract concept is endowed with human attributes. Definition: Examples: “And indeed there will be time/for the yellow smoke that slides along the street,/Rubbing its back upon the window panes.” (T.S. Eliot, “The Love Song of J. Alfred Prufock”) “A tree whose hungry mouth is prest/Against the earth’s sweetflowing breast." (Joyce Kilmer, “Trees”) Simile an explicit comparison of two things, usually with the word “as” or “like” Definition: Examples: He had a posture like a question mark. Like an arrow, the prosecutor went directly to the point. Symbol Definition: a person, place, action, or thing that represents something other than itself. Examples: The rose bush outside the prison in The Scarlet Letter The conch shell in Lord of the Flies Alliteration Definition: the repetition of initial or medial consonants in two or more adjacent words Examples: “A sable, silent, solemn forest stood.” (James Thomson, “The Castle of Indolence”) “Already American vessels had been searched, seized, and sunk.” (JFK, Profiles in Courage) Assonance Definition: the repetition of similar vowel sounds in the stressed syllables of adjacent words. Examples: “Tell this soul with sorrow laden if, within the distant Aidenn, It shall clasp a sainted maiden whom the angels name Lenore-Clasp a rare and radiant maiden whom the angels name Lenore.“ (“The Raven” by Edgar Allan Poe) “Whales in the wake like capes and Alps.” (from “Ballad of the Long-Legged Bait”, Dylan Thomas) Anadiplosis repetition of the last word of one clause at the beginning of the following clause. Definition: Examples: “The laughter had to be gross or it would turn to sobs, and to sob would be to realize, and to realize would be to despair. “ John Howard Griffin “Don’t you surrender! Suffering breeds character; character breeds faith; in the end faith will not disappoint. ..” Jesse Jackson Antanaclasis Definition: using the same word in two different meanings – repetition of a word in two different senses. Examples: “If we don’t hang together, we will hang separately.” Ben Franklin “Although we’re apart, you’re still a part of me.” from “On Blueberry Hill” Anthithesis Definition: the juxtaposition of contrasting ideas, often in parallel structure Examples: “That’s one small step for a man, one giant leap for mankind.” Neil Armstrong “Our knowledge separates as well as it unites; our orders disintegrate as well as bind; our art brings us together and sets us apart.” J. Robert Oppenheimer Chiasmus Definition: reversal or crossing of grammatical structures in successive phrases or clauses Examples: "You forget what you want to remember, and you remember what you want to forget." (Cormac McCarthy, The Road, 2006) “People the world over have always been more impressed by the power of our example than by the example of our power.” –Bill Clinton, 2008 DNC (this has anadiplosis, too!) Ellipsis Definition: deliberate omission of a word or words which are readily implied by the context. Examples: “Rape is the sexual sin of the mob, adultery of the bourgeoisie, and incest of the aristocracy.” –John Updike “The Master’s degree is awarded by seventy-four departments, and the Ph.D. by sixty.” Student example Epistrophe Definition: repetition of the same word or group of words at the end of successive cluases, the opposite of anaphora “I’ll have my bond! Speak not against my bond!/I have sworn an oath that I will have my bond!” Shylock in The Merchant of Venice, III.iii.3-4. Examples: “…We cannot learn from one another until we stop shouting at one another.” Richard Nixon Epanalepsis repetition at the end of a clause of the word that occurred at the beginning. Definition: Examples: “Blood hath brought blood, and blows have answer’d blows:/Strength match’d with strength, and power confronted with power.” King John, II.i.329-30. “Possessing what we still were unpossessed by,/Possessed by what we now no more possessed.” –Robert Frost Inverted Syntax Definition: reversing the normal word order of a sentence Examples: “Never was seen so black a day as this:” Romeo and Juliet, V.iv “Size matters not, ... Look at me. Judge me by size, do you?” Yoda from Star Wars Rhetorical Question a question asked for rhetorical effect to emphasize a point, no answer being expected Definition: Examples: “Robert, is this any way to speak to your mother?” “…Was I an Irishman on that day that I boldly withstood our pride? or on the day that I hung down my head and wept in shame and silence over the humiliation of Great Britain?...” –Edmund Burke Polyptoton Definition: repetition of words derived from the same root. Examples: “But alas…the gate is narrow, the threshold high, few are chosen because few choose to be chosen.” – Aldous Huxley Please, Please Me. Title of a Beatles’ song Anecdote Definition: a short narrative account of an amusing, unusual, revealing or interesting account often intended to illustrate or support some point. Examples: Cary Grant is said to have been reluctant to reveal his age to the public, having played the youthful lover for more years than would have been appropriate. One day, while he was sorting out some business with his agent, a telegram arrived from a journalist who was desperate to learn how old the actor was. It read: HOW OLD CARY GRANT? Grant, who happened to open it himself, immediately cabled back: OLD CARY GRANT FINE. HOW YOU? Cause and Effect Definition: writing which explores the causes of some event or chronicles the effects of some phenomenon in society or nature Examples: Although demographic shifts, stepped-up world trade, unemployment, and especially the advance of technology all have had an effect on the shape of the job market, middle-level jobs have been disappearing ultimately as a result of the ways in which technological gains are being distributed. When a machine replaces a production worker, both the firm and consumers as a group benefit. The loss falls mainly on the worker who is displaced. If that loss is generalized to millions of high-paid workers, they suffer as a group, and the economy as a whole suffers a loss of worker purchasing power. Thus the lack of a mechanism to distribute some of the financial gains from technology to the work force comes back to haunt the entire economy. Chronological Ordering Definition: writing that presents ideas according to the time in which they occurred. Examples: In A Separate Peace, first it’s summer and the boys are having fun, then Finny falls, and it is winter, time for the carnival, and then there is the trial, and….” To bake a cake first you preheat the oven, then mix the batter, then flour your pan, followed by putting the mixture in the pan to bake…. Classification Definition: writing that breaks a large subject into categories for the purpose of analysis. Example: Paraphrasing is used for different purposes. Some paraphrases will be designated to support already existing evidence. Others will reinforce argumentation against evidence. Still others will help to develop existing arguments and provide back-up for any conclusion drawn in the course of writing. Depending on the function, paraphrases will be introduced in accordance with their unique context. Expository Definition: writing that provides information such as an explanation or directions. Examples: In 1997, 175,000 volunteers picked up three million pounds of garbage along the coasts of the United States. As a result, both people and sea animals can enjoy cleaner and safer environments. Glass bottles, lumber, and syringes are less of a threat to barefooted beachgoers. Fewer seabirds, fish, and crabs will die entangled in plastic can holders, fishing nets, and fishing line. People put trash in the oceans, but by volunteering their time to help clean up after themselves, people are also the solution to the problem. Order of Importance Definition: writing in which items are arranged from least important to most important (climactic order) or vice versa. A variation on this is psychological order, which grows from the idea that readers or listeners usually give most attention to what comes at the beginning and the end, and least attention to what is in the middle. Examples: After an extended absence from school, the first and most basic thing you need to do is make up the individual daily assignments that you missed. More importantly, ask the teacher questions about things you don’t understand before completing any quizzes. Reviewing and studying are then the best things you can do before taking the unit test. Parable Definition: a story or short narrative designed to reveal allegorically some religious principle, moral lesson, psychological reality, or general truth. Examples: Biblical parables such the prodigal son and the good Samaritan A scorpion was walking along the bank of a river, wondering how to get to the other side. Suddenly he saw a fox. He asked the fox to take him on his back across the river. "The fox said, 'No. If I do that, you'll sting me, and I'll drown.' "The scorpion assured him, 'If I did that, we'd both drown.' "The fox thought about it, finally agreed. So the scorpion climbed up on his back, and the fox began to swim. But halfway across the river, the scorpion stung him. "As the poison filled his veins, the fox turned to the scorpion and said, 'Why did you do that? Now you'll drown, too.' "'I couldn't help it,' said the scorpion. 'It's my nature.'" Parody Definition: a satiric imitation of a literary work, film, or of an author/person with the idea of ridiculing the author, his ideas, or work. Examples: Monty Python and the Holy Grail, which parodies King Arthur tales SNL skits like Tina Fey doing Sarah Palin Weird Al Yankovich’s songs, like “Eat It,” “Amish Paradise,” “Fat”, etc. Austin Powers movies Persuasion Definition: A form of argumentation; Persuasive writing attempts to convince the reader to take a specific action. Examples: “Sinners in the Hands of An Angry God” – Jonathan Edwards trying to get the congregation to change its sinful ways before they burn for eternity Marc Antony’s speech over Caesar’s body that begins “Friends, Romans, Countrymen, lend me your ears…” in which he incites them to revolt against the assassins Spatial Ordering Definition: In this pattern, items are arranged according to their physical position in space or relationships to one another. Examples: In describing items on a desk, I might describe items on the left first, then move gradually toward the right; The Eiffel Tower is divided into three sections. The lowest section of the tower contains entrance, a gift shop, and a restaurant. The middle section of the tower consists of stairs and elevators that lead to the top. The top section of the tower includes an observation deck with a spectacular view of Paris. RHETORIC Definition: the study and practice of effective communication; the ability to use language effectively, particularly in argument and persuasion Examples: Marc Antony’s speech over Caesar’s body in Julius Caesar, in which he incites the crowd to revolt and go to war against the assassins. Martin Luther King’s I Have a Dream speech (and other writings) in which he argues for equality and brotherhood SATIRE Definition: the use of irony, sarcasm, or ridicule to emphasize the vice, foolishness or weaknesses in humans, organizations, or social conventions. Examples: Gulliver's Travels, a satire of eighteenth-century British society, and “A Modest Proposal,” both by Jonathan Swift. most political cartoons in newspapers and magazines The Daily Show, The Colbert Report, skits on Saturday Night Live POINT OF VIEW Definition: the position from which a story is narrated; the narrator's viewpoint on events and characters. Examples: “In my younger and more vulnerable years my father gave me some advice that I’ve been turning over in my mind ever since. In consequence, I’m inclined to reserve all judgments, a habit that has opened up many curious natures to me and also made me the victim of not a few veteran bores.” from The Great Gatsby, told from Nick’s point of view. If the point of view were 3rd person omniscient, then the reader would know the thoughts and feelings of all of the characters in the story. If it’s 3rd person limited, the reader only knows the thoughts of one or two characters. ALLEGORY Definition: an extended metaphor or “conceit” that is sustained through whole sentences or even through a whole discourse in which objects, persons, and actions in a narrative, are equated with meanings that lie outside the narrative itself. The underlying meaning has moral, social, religious, or political significance, and characters often represent abstract ideas such as charity, greed, or envy. Examples: The Pandora woods in Avatar is an allegory for the Amazon rainforest. Also, the attempt to get the Na'vi to 'cooperate' carries overtones of the U.S. involvement in Iraq and Afghanistan.” (Owen Gleiberman, review of Avatar. Entertainment Weekly, Dec. 30, 2009). Lord of the Flies is an allegory, with the island representing Eden or paradise, each of the boys representing a type of government, the conch representing authority, and so on. TONE Definition: the writer's attitude toward the subject of the message. Elements that create tone include DIDLS. Examples: In his New York Times column (29 July 2011 ), Charles M. Blow conveys a bittersweet tone toward the Buffalo Soldiers and his grandfather in particular. Orwell’s tone in “Shooting an Elephant” is conflicted and resentful toward both the British Empire and the Burmese. TAUTOLOGY Definition: unnecessary repetition of an idea, in different words; to repeat the same thing in different words Examples: a good-looking beautiful woman a round circle a big giant a widow woman CACOPHONY (ka-kä-fə-nē) Definition: harsh or discordant sound, in writing created through use of sound devices like alliteration, assonance, consonance and onomatopoeia Examples: It created a cacophony of hacking coughs, bronchial rattles, asthmatic wheezes, consumptive croaks. (Angela’s Ashes) The cacophony of phlegmatic and tubercular lungs was punctuated here and there by a moan or a scream of someone terrified, thrashing in the throes of a nightmare. —Ronald Gearles, Undoing Time, 2001 EPITHET Definition: an adjective or adjectival phrase to characterize a person, thing, attribute, or quality; the use of a qualifying word or phrase to further describe something Examples: Ivan the Terrible The Artist formerly known as Prince Dwayne “The Rock” Johnson EXPLETIVE Definition: a figure of emphasis in which a single word or short phrase, usually interrupting normal speech, is used to lend emphasis to the words on either side of the expletive but adds nothing to the meaning Examples: "The strength of America's response, please understand, flows from the principles upon which we stand.“ -- Rudy Giuliani, 9/11 Speech to the United Nations General Assembly "The minimum wage, I might add, today is far less than it was in 1960 and 1970 in terms of purchasing power.“ -Ralph Nader, 2000 NAACP Address ANESIS (an'-e-sis ) Definition: the addition of a concluding sentence that diminishes the effect of what has been said previously. Examples: She had set more track records than any woman in the country. She had more stamina, skill, and perseverance than many of the best, but she had broken her leg and would not be competing this year. "This year's space budget is three times what it was in January 1961, and it is greater than the space budget of the previous eight years combined. That budget now stands at 5 billion, 400 million dollars a year -- a staggering sum, though somewhat less than we pay for cigarettes and cigars every year.“ --John F. Kennedy, Rice University Address on Space Exploration