Mental Models & Metaphors
advertisement

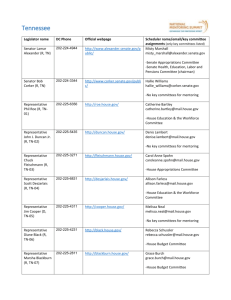
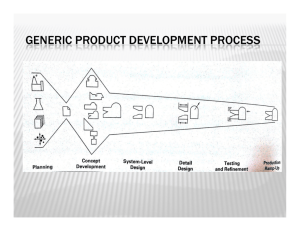
Lecture 4 Allocation and Detailed Design ISE 105 Spring 2006 Notes & Course Materials www.engr.sjsu.edu/kcorker Kevin.Corker@sjsu.edu Kevin Corker San Jose State University 3/8/05 K.M. Corker, Ph.D. Industrial & Systems Engineering System Definition Matrix Scope Needs Objt Bound Criteria Params Var Constrnt Review Scope & Bound In System Definition K.M. Corker, Ph.D. Industrial & Systems Engineering Example: Domestic Energy • Needs: – – – – N1: Adequate Supply of refined energy N2: Adequate Supply of energy reserves N3: Efficient Utilization of energy N4: Clean environment K.M. Corker, Ph.D. Industrial & Systems Engineering Objectives • Adequate Gasoline supply • Adequate Oil supply – Improve US refining capacity • Develop energy reserves – Improve US access to reserves • Utilize energy efficiently – Change energy utilization distribution (reduce transportation energy costs) • Develop New energy sources – Bio-diesel • Develop New Energy forms – Strong-Force electrodynamics • Change standard of living • Clean Environment K.M. Corker, Ph.D. Industrial & Systems Engineering World Poverty Map (39 components of poverty) K.M. Corker, Ph.D. Industrial & Systems Engineering Criteria • • • • • • • Supply/demand Relationship Number and volume of reserves Energy Efficiency Metrics Number and effectiveness of new sources Number and effectiveness of new forms Demographics of live-style Demographics of Environment K.M. Corker, Ph.D. Industrial & Systems Engineering K.M. Corker, Ph.D. Industrial & Systems Engineering Parameters & Variables (those elements of a system which if changed would have a significant effect on the identified needs) • A1: Types of refined energy (gas, oil, home heat, J12 jet fuel…) • A2: new energy sources (nuclear, solar, wind, geothermal…) • A3: Types of existing reserves tapped for development (natural gas, crude, cola, uranium…) • A4: Distribution and use of energy (transportation, industry, homes, offices…) • A5 Foreign energy purchased • A6 Contribution to pollution • A7 Demand • A8 Restrictions (taxes, rationing,) K.M. Corker, Ph.D. Industrial & Systems Engineering Constraints • • • • • • • • • • C1: Safety C2: Supply and Reserve availability C3: Source location (ANWAR) C4: Reasonable Costs (% GDP) C5: Low Pollution C6: Technological (energy available but no known method for distribution) C7: Funding C8: Government Regulations and policies C9: Time available C10: Standard of living variables K.M. Corker, Ph.D. Industrial & Systems Engineering System Definition (iteration 2) • Provide a Scope and Bound Matrix for your system • Provide specific needs, objectives, criteria, parameter/variables, and constraints • Due Monday 3/13/06 K.M. Corker, Ph.D. Industrial & Systems Engineering Allocation • You have identified preliminary needs and objectives for your systems • You have identified the technical requirements of (at least) two alternatives to meet those needs • We now need to assign or allocate subsystems to meet those needs K.M. Corker, Ph.D. Industrial & Systems Engineering Allocation and Evaluation • Subsystems packaging or work breakdown structures assign some part of the total system function to subsystems • Describe the achievement of a functional need broken down into functional subsystems for each of the alternative design approaches • The functional subsystems can then be evaluated for your alternative system designs K.M. Corker, Ph.D. Industrial & Systems Engineering ICOM Leading to Functional Decomposition K.M. Corker, Ph.D. Industrial & Systems Engineering Tree Structure K.M. Corker, Ph.D. Industrial & Systems Engineering Coffee Example K.M. Corker, Ph.D. Industrial & Systems Engineering Technical Performance Measures • Provide Specific Functional Requirements for each function and subfunction that is measurable – Bandwidth – Reliability requirements – Speed – Operability requirements … K.M. Corker, Ph.D. Industrial & Systems Engineering Allocation of Mission Specification Requirements • Each functional unit will contribute to meeting the over-all “design-to” specification • The customer priority and the unit costs can be used to guide establishment of design-to specification • Tradeoffs – Between different subfuncitons within a design or – Between functions in alternative designs K.M. Corker, Ph.D. Industrial & Systems Engineering Maximum Weight for Wearable Computer Max Cost for Sub Function Element Trade Space Cost Weight Cost Trade-off Function Max Weight Allowable Weight K.M. Corker, Ph.D. Industrial & Systems Engineering Preliminary Design Review Assignment Due 3/15/06 • Provide a System Function Allocation graph for each of two alternative designs for your system– take this the ICOM subsystem functional level • Determine a set of Technical Performance Metrics/Measures for each sub function • Make an allocation graph for two subsystems that you consider critical for two TPMs that you consider critical K.M. Corker, Ph.D. Industrial & Systems Engineering Detailed Design • You have developed (two) alternatives for a system • You have begun tradeoff analyses by identifying TPMs and allocating function and TPMs • At this point you would make a determination of which design best meets the TPMs • This is a complex evaluation process requiring modeling tools– so we will defer a description of that that decision making process until after we have spoken about models K.M. Corker, Ph.D. Industrial & Systems Engineering Detailed Design (Top Down & Bottom Up Tensions) • Describe in Detail: 1. Subsystems, units, assemblies, people, software, logistic support for your system(s) & address interrelationships 2. Specification of Performance, physical characteristics, power requirements, maintenance, information requirements for all systems 3. Identify and cost out COTS (commercial off the shelf elements) 4. Develop Systems Models 1. K.M. Corker, Ph.D. Engineering , prototype or service test model Industrial & Systems Engineering System Lifecycle Concurrent System Design & Development Production Process System Utilization Development/OPS Maintenance & Support Capability Development/OPS Retirement & System Disposal K.M. Corker, Ph.D. Industrial & Systems Engineering