University Of Pennsylvania College of General

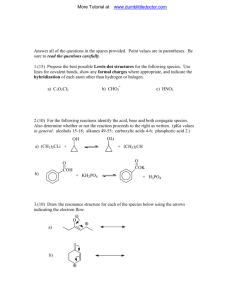
University Of Pennsylvania
College of General Studies
Professor William A. Price, Ph.D.
CHEM 241-601
Organic Chemistry , 9 th Edition
By T.W. Graham Solomons
From the Bark of the
Pacific Yew Tree
O
O O OH
O NH O
OH
O
Taxus brevifolia
OH O
O
O
O
O
Introduction:
Structure and Bonding
Atomic structure
Lewis Structures
Resonance
Structural Formulas
Acids and Bases
Nucleus is a Tiny Fraction of the Volume of an Atom
Orbitals are Probabilities
2s Orbital Has a Node
The p Orbital
p x
, p y
, p z
Electron Configurations
Lewis Dot Structure of
Methane carbon - 4 valence e hydrogen - 1 valence e
.
.
.
C
.
H.
1s 2 2s 2 2p 2 1s
Tetrahderal Geometry
Bonding Characteristics of
Period 2 Elements
“Saturated” with Hydrogen
All Have the Same Geometry
All Have 4 Regions of Electron Density
A Saturated Hydrocarbon
Nitromethane
Nitromethane has 2 Formal
Charges
Formal Charge = [Group #] - [# bonds] - [# non-bonding electrons]
CH
3
NO
2
H
H
H
C N
N = 5-4-0 = +1
O
O
O = 6-1-6 = -1
Both Resonance Structures
Contribute to the Actual Structure
CH
3
NO
2
H
H
H
C N
O H
H
H
C N
O
O O
2 Equivalent Resonance Structures
Resonance Rules
• Cannot break single (sigma) bonds
• Only electrons move, not atoms
3 possibilities:
– Lone pair of e to adjacent bond position
• Forms p bond
- p bond to adjacent atom
- p bond to adjacent bond position
Curved Arrow Formalism
Shows flow of electrons
H
H
H
C N
O
O
H
H
H
C N
Arrows depict electron pairs moving
O
O
Resonance Stabilization of Ions
Pos. charge is “delocalized”
H
C
H
C
H
C
H
H
H
C
H
C
H
C
H
H
H
C
H
C
H
C
H
H resonance hybrid
Bonding Pattens for C, N, and O sp3 sp2 sp tetrahedral geometry trigonal planar linear
C
C C
C
N N
N
O O
Common Cationic, Neutral and
Anionic Forms
Two Nonequivalent Resonance
Structures in Formaldehyde
Resonance in Acetate Anion
Resonance in [CH
2
NH
2
] +
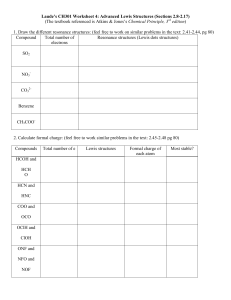
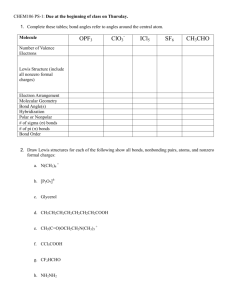
Propose Lewis Structures a) H
2
CO
2 b) O
3 c) N
2
O d) NH
3
O e) C
2
H
3
ClO f) C
2
H
5
NO
Problem
Draw [NO
2
] + and [NO
2
] . Which ion has a
“localized” charge and which has a
“delocalized” charge. Explain.
Drawing Structures
H
H
H
H
C
C
H
Butane, C
H
C
H
C
H
4
H
10
H
H
H
H
H
H
C
C
H
H
C
H
C
H
H
H
Methylpropane, C
4
H
10
CH
3
CH
2
CH
2
CH
3
CH
3
CH(CH
3
)CH
3
Octane Representations
C
8
H
18
is molecular formula but there are 18 possible structural isomers
H H H H H H
H
H
C
C
H H
C
C
C
C
H H H H
C
H
C
H
HH
Lewis structure
CH
3
CH
2
CH
2
CH
2
CH
3
(CH
2
CH
2
CH
2
CH
2
CH
3
)
6
CH
3 condensed structural formula
Condensed
Formulas
Line-Angle Structures are
Often Used as a Short-hand
H H H H H H
H
H
C
C
H H
C
C
H H
C
C
H H
C
H
C
H
HH
Lewis structure
Line-angle or "zig-zag" structures
Line-Angle Structures
H
H H
C
H
H
C
H
H
C
H
C
H
H
H
C
C
H
H
H
H
H
C
C
C
C
H
H
H
C
H
H
H
H
H
C
C
12
H
26
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
At the end of every line and at the intersection of any lines there is a carbon atom with 4 bonds. Hydrogen atoms are mentally supplied to fill the valency to 4.
H
H H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
Line-Angle structure
Superimposed on Lewis Structure
H
H H
C
H
H
C
H
H
C
H
C
H
H
H
C
C
H
H
H
H
H
C
C
C
C
H
H
H
C
H
H
H
H
H
C
H
H
Double Bonds are Shown
Depictions of trans 2-pentene
H
H
H
C
H
H
H
C C
C
C
H H
Lewis Structure
H
H
CH
3
H
C C
H
CH
2
CH
3 condensed structural formula line-angle or zig-zag structure
For Cyclic Structures, Draw the
Corresponding Polygon
Cyclohexane
H
H
H
H
C
C
H
H H
H
C
C
C
C
H
H
H
H
Some Steroids
HO
Cholesterol
C
27
H
44
O
O
Testosterone
C
19
H
26
O
2
OH
O
Adrogenic/Anabolic Steroids
CH
3
OH
CH
3
H
H H
Testosterone
O
CH
3
O
CH
3
H
H H
Androstenedione
Anabolic Steroids
O
CH
3
OH
H
H H H N
N
Nandralone Stanozolol
CH
3
H
CH
3
OH
CH
3
H H
Benzene can be drawn as one of two resonance structures
H H
H
C
C
C
H H
C
C
C
H
H
C
C
C
H H
C
C
C
H
H H
Some Line-Angle Structures