Constipation
advertisement

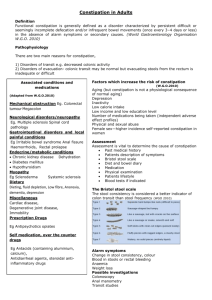
Constipation By: Dr. Shahram Ala (Pharm.D, BCPS) Constipation is a symptom, not a disease Some causes: IBS, Diabetes Mellitus, Hypothyroidism Patients definition & concept about constipation can be different Patients definition: Straining 52%, hard stools 44%, infrequent stool 32% Misconception: 62% believe that daily defecation is necessary to good digestive health What is the right number of daily or weekly bowel movements?! Clinical definition Any of two of following symptoms for at least 3 month (not necessarily consecutive) in a year Straining Hard or lumpy stool Sensation of incomplete evacuation Fewer than 3 defecation per week Causes of constipation ↓ fiber :(most common) ↓ liquid ( 8 glasses/d is needed for constipated) ↓ Exercise : bedridden, coma Ignoring urge to defecate Systemic: Hypothyroidism, DM, Uremia, pregnancy, hypercalcemia, Hypokalemia Neurological: Stroke, Parkinsonism, Multiple sclerosis Causes of constipation (Cont.) GI-related: IBS, Hemorrhoid, Anal fissure, Anorectal & Colorectal carcinoma ,obstruction Medication: Opiate, Anticholinergics, Al(OH)3 Iron, cholestyramine, Antihypertensive drugs (CCBs, diuretics), relaxants, chronic use of laxatives, Antiepileptics, progestron Uncertain: idiopathic chronic constipation Rate of empting: carbohydrate>protein>Lipid Fear, Pain Inhibit and exitation stimulate Clinical manifestation: Pale- Icteric-Anorexia-Headache-Abdominal pain, Diagnosis Good history is enough for most cases (Duration, frequency, Consistency, blood in the stool, weight loss, Diet, Exercise, Toilet habits, Laxative use (what), other drugs) Basic laboratory tests: CBC, Electrolytes, BS, BUN, Cr, TSH Structural: Barium enema, Sigmoidoscopy, Colonoscopy Treatment Treatment of underlying disease (Malignancies, Hypothyroidism,…) Alteration of lifestyle (Diet, Exercise, Liquids) Laxatives Acute constipation Glycerin suppository Sorbitol powder Bisacodyl Anthraquinones ( C-lax) Saline laxative (MOM) Tap-water enema If laxative treatment is required for > 1 week, refer to a physician Chronic constipation Most common in bedridden or geriatrics Choice: Psyllium (with enough liquids) Low doses of other laxatives: C-lax, MOM, Sorbitol, Lactulose Constipation in hospitalized patients May be related to general anesthesia or opiates Glycerin suppository Milk of magnesium Tap water enema Constipation in infants & children If constipation is a persistent problem: Consider neurological, metabolic or anatomical abnormalities If No: Approach as adults Drug classes Those causing water evacuation in 1-6 hr Caster oil, Saline cathartics, PEG lavage solutions Those causing soft or semi fluid stool in 6-8 hr C-lax, Bisacodyl Those causing softening of stool in 1-3 days Psyllium, Lactulose, Mineral oil, Decussate Bulks Psyllium, musillium Increase Volume of intestine Stimulate natural intestine peristaltic Anti Diarrhea & constipation Lasts 12-24 h (even 3 days) Drink freely water unless obstruction Emullients Docusate Na cap: 500mg Anionic surfactants Decrease stool surface tension, increase Fluide secration into intestine Lasts 1-3 days SE: GI cramp Lubricants Liquid Parafine Inhibition of fluide reabsorbtion from colon, Softener of stool, stimulate peristaltic Post MI, Post surgery lasts 6-8 h 15-45 ml PO, or rectal SE: Aspiration (neonate, Geriatrics, before sleep), malabsorbtion (lipid soluble Vit.), Anal pruritis, staining Stimulant laxatives Bisacodyl Stimulates mucosal nerve plexus of the colon (myentric) Intermittent use for constipation Oral: 6-8hr Supp: 15-60min Interactions: Milk, Antacids (EC) SE: Cramp, fluid and electrolyte imbalance, Contraindication: pregnancy, lactation, appendicitis Caster oil Usually for bowel preparation Active metabolite: Ricinoleic acid Onset: 1-3 hr Saline MOM, mgso4 Indications: Antacid (5-15 ml PRN), Laxatives (30-60 ml HS) Mg: Osmotic, Release cholecystokinin Onset: 3-6 hr Interactions: Quinolones, Tetracycline, Fe, EC drugs (bisacodyl, sulfasalazine) Breast-feeding: can be used CRF? Hyperosmotics Glycerin, Lactulose, mannitol, Sorbitol Lactulose: Acetic acid, Formic acid, Lactic acid Encephalopathy ( lasts :24-48 h) SE: flatulence, abdominal cramp, diarrhea, electrolyte imbalance Glycerin Is very safe and acceptable for intermittent basis particularly in infants Supp: 1g, 3g Onset: less than 30 min Mannitol Tap-water enema 200 ml results in a bowel movement within 0.5hr Soapsuds are no longer recommended (proctitis, colitis) Drugs for chronic idiopathic constipation Cisapride (also for Parkinson's disease) Erythromycin Summary Underlying causes of constipation should be considered Foundation of treatment is diet and psyllium Acute constipation may be treated with tapwater enema or glycerin suppository, if needed, oral sorbitol, low dose bisacodyl or C-Lax Approach for chronic constipation is use of psyllium and if needed, intermittent low-doses of other drugs