Study Guide
advertisement

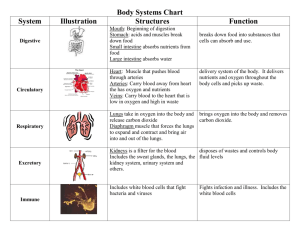
Human Body Systems Study Guide Genetics Key Vocabulary – characteristics, inherited, likeness, traits, organism Examples of inherited traits – hair color, eye color, right or left handed, tongue rolling, ear lobes attached or unattached……..these are things you are born with and you cannot change or improve with practice!! Examples of learned traits – playing a sport or instrument, speaking a language, becoming an artist….these are things you can change or improve with practice or classes!!! Cells and Tissues Key vocabulary – multicellular, unicellular Cells make up tissues. Tissues make up organs. You need to know what unicellular organisms look like, such as paramecium, amoeba, and bacteria. Hint: You need microscopes to see them!!!! You need to know what multicellular organisms look like, such as humans, dogs, cats, bugs, plants. Hint: If you can see it without a microscope, it is multcellular! Musculoskeletal System – Combination of the muscular system and the skeletal system Key vocabulary – ribs, cranium The main function of the skeleton is to support and protect the body structure. The main function of the muscles is to help the body move around. The Nervous System Key Vocabulary – brain, spinal cord, nerves The main function is to control all the systems of the body. It sends messages that tell each system what to do involuntarily. The Circulatory System Key vocabulary – arteries, veins, capilaries The main function is to move oxygen and nutrients through blood to cells and tissues around the body. It’s how blood circulates around the body! The Cardiovascular System Key vocabulary – heart, arteries, veins The main function is to pump the blood through the body using the heart muscle. The heart has four chambers that pump oxygenated blood into the arteries to go to the body. Veins carry used up, deoxygenated blood back to the heart. The Respiratory System Key vocabulary – lungs, diaphragm, oxygen, carbon dioxide The main function is to provide the blood with oxygen so that oxygen can be delivered to all parts of the body. The diaphragm is the muscle below the lungs that moves up and down to get the lungs to expand or contract. We breathe in oxygen, and breathe out carbon dioxide. The more oxygen we breathe in (faster breathing), the more oxygen that goes to our lungs and around our body. The circulatory system takes the blood with oxygen from our lungs to the rest of our body. The exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide occurs or happens in the lungs. The Digestive System Key Vocabulary – esophagus, stomach, small intestine, gallbladder, large intestine The main function is to digest food to take the nutrients out to help fuel the body. Process – mouth, to esophagus, to stomach where acid breaks it up using stomach acid, to the small intestine where the gallbladder releases bile to help break down fat, this is where the nutrients are taken out for your body to use, to the large intestine where the water is taken out The Excretory System Key Vocabulary – kidneys, liver, urinary bladder, skin The main function is to get rid of waste from the body. The kidneys remove waste from our body and put it in the bladder for us to get rid of. The liver breaks up proteins in our body using urea and uric acids. The skin gets rid of salt, extra water, and acids our body doesn’t need. ***All systems work together, interdependently, to sustain life!!!***