File

Brooke Tucker
Forensics
Mr. Newman
12 January 2015
Pig Dissection Questions
Respiratory System and Endocrine System:
1.
Why is it necessary for the trachea to have rings of cartilage in its walls?
The cartilage rings in the trachea prevent it from collapsing.
2.
What is the purpose of the hormone thyroxine, which is produced by the thyroid gland?
Thyroxine’s main purpose is to stimulate oxygen consumption (metabolism) in the cells.
3.
Why do the lungs have a large number of blood vessels?
The lungs contain a large number of blood vessels so that oxygen from the lungs can be carried to the rest of the body by hemoglobin. Also so the body can exhale it’s carbon dioxide waste.
4.
Explain what must happen for the lungs to expand, allowing you to inhale.
In order for the lungs to expand; the diaphragm must contract, thus sucking air through the wind pipe into the lungs, while the surrounding muscles pull the rib cage up and out.
5.
Why is it necessary to close the opening of a puncture wound in the chest?
Puncture wounds to the chest must be closed so that oxygen and blood do not escape the body and to prevent lungs from collapsing or damaged.
Circulatory System:
1.
What is the purpose of the pericardial sac that surrounds the heart in mammals?
The purpose of the pericardial sac is to provide protection and support as well as lubrication to reduce friction in tissues surrounding the heart.
2.
Why do arteries have an interior ring of smooth muscle?
The interior ring of smooth muscle in arteries allows them to expand and contract as well as maintain and withstand blood pressure.
3.
Which arteries sometimes become blocked in a human and are then “bypassed” by using veins from the patient's legs?
The saphenous vein from the leg is used to bypass blocked arteries in the heart.
4.
What are the two major veins of the pig's heart that return deoxygenated blood from the body?
The two major veins that return deoxygenated blood to the heart are the superior and inferior venna cava.
5.
Why is pulmonary circulation bypassed in the unborn fetal pig, and how is it bypassed?
Pulmonary circulation is bypassed in the unborn piglet because the fetus does not breathe air in the womb. Therefore there is no gas exchanged happening in the lungs, so no oxygen to carry and no carbon dioxide to get rid of.
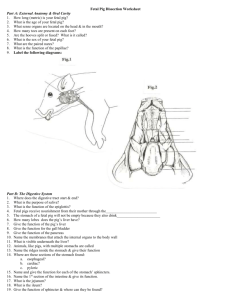
Digestive System:
1.
What are the main functions of the liver in mammals?
The main function of the liver in mammals is to digest food into its simplest form before it continues into the small intestine. It is responsible for producing the majority of the body’s cholesterol.
2.
What is the stomach muscle that controls the passage of food into the small intestine?
The pyloric sphincter controls the passage of food from the stomach to the small intestine.
3.
What is the purpose of the villi and microvilli of the small intestine?
Microvilli and villi increase surface space inside the small intestines for easier absorption of nutrients.
4.
What is the primary function of the large intestine?
The large intestine removes water and removes waste from the body.
5.
What is the purpose of rugae in the stomach lining, and what glands are found between them?
Rugae allows the stomach to expand as it fills then contract to its original state. The gastric pits, found between rugae folds, are openings to gastric glands which secrete gastric acid and protective mucus.
Urogenital System:
1.
If a mammal drinks large amounts of saltwater, what will this do to its urinary output?
When a mammal consumes a large amount of salt water the body becomes dehydrated trying to flush the salt from its system. The kidneys can be severely damaged or even fail from trying to filter out the salt.
2.
Why is there an advantage for female pigs to have long uterine horns and a small uterine body, whereas in humans the situation is reversed?
Long uterine horns in pigs allow for larger litters because females carry fetuses in the uterine horn whereas humans carry their young in the uterine body.
3.
Why is it important for the testes in pigs and other mammals to completely descend into the scrotum?
Undescended testes do not produce sperm because they must be cooler than body temperature.
4.
Explain the function of the nephrons in the pig kidneys.
Nephrons filter waste, excess fluids and toxins from blood.
5.
What is the unique difference between female egg production and male sperm production in mammals?
Females are born with all the eggs that they will cycle through in a life time, and eventually the cycle ends. Males on the other hand can potentially continue to generate and produce sperm throughout their entire lives after reaching sexual maturity.