Circulatory System
advertisement

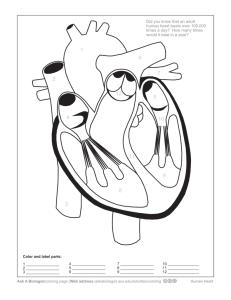
Circulatory and Respiratory System Vocabulary! 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Atrium Ventricle Pulmonary Circulation Systemic Circulation Valves Pacemaker Capillaries Veins 9. Arteries 10. Pharynx 11. Trachea 12. Bronchi 13. Alveoli 14. diaphragm The Circulatory System • The blood, heart, and blood vessels form the cardiovascular system • The lymph, lymph nodes, and lymph vessels form the lymphatic system • The Cardiovascular system and the lymphatic system make up the CIRCULATORY SYSTEM The Heart • A muscular organ that pumps blood through a network of blood vessels • Pumps on average more than 2.5 billion times in a lifetime • About the size of your fist • A tough, sac-like membrane surrounds the heart= pericardium Actual Images of the Human Heart Heart Coloring Page Anatomy of the Heart • The septum (a wall) divides the heart into two sides • Left side pumps blood to the lungs, right side pumps blood to the body • Each side of the heart is broken up into an upper and lower chamber • Upper Chamber=atrium • Lower Chamber= ventricle • Valves are flaps of tissue that open in one direction • The atrioventricular valve (Aortic Valve) on the right is a tricuspid valve • The mitral valve, or bicuspid valve is on the left Brain Pop! Heart Circulation in the Heart—Follow along on your coloring sheets! 1. Deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium 2. Right atrium sends deoxygenated blood into the right ventricle 3. Muscles of the right ventricle contract and force the blood into the pulmonary arteries (arteries send blood AWAY from the heart) 4. The pulmonary artery sends the blood to the lungs where the blood will pick up oxygen 5. The oxygenated blood returns to the left atrium of the heart 6. The oxygenated blood is then pumped into the left ventricle 7. Contraction of the muscular walls of the left ventricle force the blood into the largest blood vessel, the AORTA 8. From the AORTA blood is pumped into all parts of the body Heart Circulation Video Clip • 4 facts Circulatory Songs • #1 Mr. Parr • #2 Rap Control of the Heartbeat • The heart muscles force the heart to contract to move the blood from one chamber to another • The SINOATRIAL NODE (SA) is a group of specialized cells in the right atrium that initiate an electrical impulse (often called the pacemaker) • The electrical impulse reaches the ATRIOVENTRICULAR NODE in the septum causing the ventricles to contract a fraction of a second later than the atriums…. • With each beat, the respective heart valves close to keep blood from flowing backwards…“lub-dub” heart beat is the sound of the valves closing • If there is a defect or problem with a valve blood can go backwards and is heard as a ‘murmur’ Blood Vessels • ARTERIES are large, muscular vessels that carry blood away from the heart • Your ARTERIES stretch with each heartbeat (this is your ‘pulse’) • The force that blood exerts against the inside walls of a blood vessel= BLOOD PRESSURE • High blood pressure = HYPERTENSION Capillaries and Veins • Blood begins in the AORTA, the largest artery • From the AORTA, blood flows through smaller arteries, which then divide into smaller arterioles, and then even tinier capillaries. • Blood flows back to the heart going from capillaries, to venules, to veins, the VENA CAVA, to the heart Brain Pop Circulatory System! Circulatory System Coloring Crash Course Respiratory System •The RESPIRATORY SYSTEM exchanges gases with the cardiovascular system •The LUNGS are the site of the gas exchange between the atmosphere and the blood Respiratory Coloring Path of Air—Follow along on your coloring sheet! 1. Air is taken in through the mouth and nose, in the nose air is filtered through small hairs and mucous membranes which moisten and warm the air 2. The air then moves to the throat or PHARYNX 3. The EPIGLOTTIS is a small flap that covers the opening to the trachea (so you don’t swallow food) 4. Passing the pharynx, air goes into the TRACHEA (or windpipe) and is lined with cilia to trap particles 5. Air also passes the LARYNX (or voicebox) at this point 6. The Trachea breaks into 2 BRONCHI which lead to the 2 lungs 7. The bronchi branch into smaller and smaller tubes: BRONCHIOLES and finally ALVEOLI, tiny air sacs where the gas exchange occurs Video Clip—Path of Air Breathing • INSPIRATION=taking air into the lungs • When you breathe in, your DIAPHRAGM contracts and pushes up, expanding the lungs • When you breathe out—EXPIRATION--, your DIAPHRAGM relaxes • Breathing is controlled by your Nervous System and Brain • FUN FACT—you can’t suffocate yourself by holding your breath! Lab/Activity