Pre-AP Strategies: Lodi Unified School District Pathways
advertisement

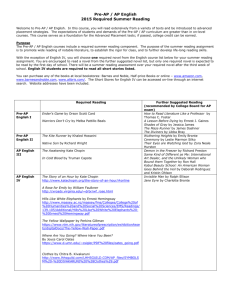
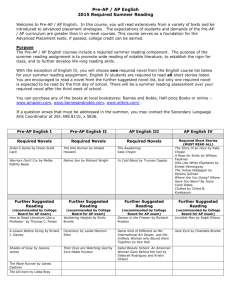
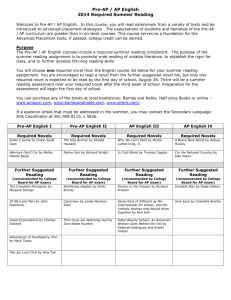
Lodi Unified School District Advanced Placement Pathways INTRODUCTION TO PRE-AP STRATEGIES 1 What is Pre-AP? Pre-AP is a set of content-specific strategies designed to: – Build rigorous curricula – Promote access to AP for all students – Introduce skills, concepts, and assessment methods to prepare students for success when they take AP and other challenging courses 2 What is Pre-AP? (con’t) – A instructional process to strengthen the curriculum and increase the academic challenge for all students – An inclusive program for encouraging more students to access higher learning – A tool for working together in the same direction – A new way of thinking and approaching the classroom 3 Who should be considered for AP Pathways? • GATE identified students • AVID identified students • Underrepresented student subgroups • Student/Parent/Guardian choice/request • Teacher/Counselor/Administrator choice/request 4 Pre-AP Strategies in Social Science History (US, European) Government Economics Human Geography Psychology a study of change over time 5 Pre-AP Strategies in Social Science (Con’t) Students should be able to recognize and understand: • Cause and effect relationships • Multiple causations • Trends, themes, and interactions • The importance of BOTH change and continuity is shaping human events 6 Pre-AP Strategies for Social Science Primary Source Analysis Strategies – APPARTS: Author, Place and time, Prior Knowledge, Audience, Reason, The main idea, Significance 7 G-Persia • • • • • • • G—Geographic P-- Political E—Economic R—Religious S—Social I—Intellectual A--Artistic 8 C-GRIPES • • • • • • • C—Cultural G—Geographic R—Religious I—Intellectual P—Political E—Economic S--Social 9 SPRITE • • • • • • S—SOCIAL P—Political R—Religious I—Intellectual T—Technological E—Economic 10 SPEC • • • • S—SOCIAL P—P0litical E—Economic C--Cultural 11 SOAPSTone • • • • • • S—Speaker O—Occasion A—Audience P—Purpose S—Subject T--Tone 12 OPTIC • • • • • O—Overview P—Parts T—Title I—Interrelationships C—draw a Conclusion 13 BART • • • • B—BIAS A—Attribution R—Reliability T--Tone 14 Strategies for going from Main Idea to Details Big Picture Strategy Creating Guiding Questions Working from Essential-Thematic Questions 15 Strategies for going from Details to Main Idea 1. Conceptual Identifications 2. Using Subheadings 3. Generating main ideas from a reading 4. Half-page solutions (note-taking strategy) 16 Strategies for Synthesizing Information 1. Categorization 2. Generalization 3. Evaluation 17 Assessment Strategies 1. Multiple Choice—test-taking strategies • Tips 2. Designing effective questions • Improving Student Writing • Focus on Thesis 18 Assessment Strategies 3. 4. 5. 6. (con’t) Writing supporting paragraphs Writing effective conclusions Construction/use of Rubrics Frequent and appropriate use of past AP exams as models and skill-building strategies 19 Pre-AP Mathematics Pre-AP Strategies in Mathematics and Statistics 20 Pre-Ap Mathematics • • • • • Posing Questions Reflection After-class Debriefing Classroom Illustration(s) Use of Circular Objects 21 Teaching from a Conceptual “Big Picture” view of Mathematics • • • • Identifying and Generating Patterns What’s the Rule? Deducing Relationships Looking below the surface— Identifying common structures • Sequencing Problems 22 Teaching from a Conceptual “Big Picture” view of Mathematics (con’t) • Talking Mathematically—Class Discussions • Providing Summaries • Indicating Agreement • Retelling Problems • Assembling Clues 23 Math Assessments • • • • Formative Summative Short Answer Tests Use of past AP Tests 24 Pre-AP Science Pre-AP Strategies in Science 25 Pre-AP Science Strategies • • • Individualized Instruction Electronic Communication Technology Tools in Education 26 Pre-AP Science Strategies (con’t) Applying Technology in the Classroom Observation and Analyses Small Group Collaborative learning Multimedia Quizzes/Tests The Calculator-Computer Connection 27 Pre-AP Science Strategies (con’t) • Using Computers in the Science Classroom Integrating Power point Concept mapping Drawing a Concept Map • Using Spreadsheets to Analyze Experimental data 28 Pre-AP Science Strategies (con’t) • Creating a Live Web Page • Linking the Graphic Calculator to the Computer • Use of Scientific and Graphing Calculators • Scaffolding Science Lessons/Labs for various Grade Levels 29 Pre-AP Science Strategies (con’t) • Improving Reading Comprehension PACA—Predicting and Confirming Activity QAR--Question/Answer Relationship K-W-L 30 Pre-AP Science Strategies (con’t) • I-N-S-E-R-T: Interactive Notation System for Effective Reading and Thinking • Spider (Web) Map • Continuum Scale (Time Line) • Series of Events Chain 31 Pre- AP Science Strategies (con’t) • • • • • • Fishbone Map Concept map Human Interaction Outline Problem/Solution Outline Cycle Use of past AP Exams 32 Pre-AP English English Pre-AP Strategies 33 English teachers who utilize Pre-AP strategies at any grade level must: • Introduce literary terminology and definitions. • Model the application of terminology to the reading of the work. • Structure activities to ask students to explore a work and independently recognize the elements of style, use of literary techniques, etc. 34 Pre-AP English Strategies (con’t) • Structure close critical reading experiences • Select passage from works that illustrate an author’s style, technique, etc. • Teach students to write a prose-analysis essay • Provide historical background of a work of literature when necessary. 35 Pre-AP English Strategies (con’t) • Levels of Questioning • SOAPSTone: S—Subject O—Occasion A—Audience P—Purpose S—Speaker T--Tone 36 Pre-AP English Strategies (con’t) • Literary Analysis Strategies SIFT—Symbol, Images, Figures of Speech, Tone and Theme • Dante’s fourfold Method: Analyzing Symbol and Allegory • Aristotelian Theory of Criticism 37 Pre-AP English Strategies (con’t) LEAD: Analysis of Diction L—Low or informal diction E—Elevated language or formal diction A—Abstract and concrete diction D—Denotation and connotation 38 Pre-AP English Strategies (con’t) • Advanced Syntactical strategies • Syntax Analysis Worksheet • Introduction and analysis of Archetypes • DIDLS: Diction, Images, Details, Language, Sentence Structure 39 Pre-AP English Strategies (con’t) • TP-CASTT: Title, Paraphrase, Connotation, Attitude, Shifts Title (again) Theme 40 Metacognitive Strategies • Thinking Notes • Reading Aloud • Thinking Aloud 41 Pre-AP English Strategies (con’t) Ladders of Questions Reading Journals Reading Strategies Annotating Texts Discussion Methods Fishbowl Discussions Timed Discussions 42 Pre-AP English Strategies (con’t) Reading Conferences Bulletin Board Threaded Discussions Literature Circles Using Graphic Organizers 43 Pre-AP English Strategies (con’t) • SMELL: Sender-receiver relationship Message Emotional strategies Logical Strategies Language 44 Pre-AP English Strategies (con’t) • TWIST: Tone Word Choice Imagery and detail Style Theme 45 Pre-AP English Strategies (con’t) • Assessment Strategies PAMDISS: Writing Strategy— Purpose, Audience, Mode, Diction, Images/Concrete Details, Syntax, Structure 46 Pre-AP English Strategies (con’t) • Self-Evaluation and Revision: The Four Bases of Effective Writing • Peer Editing • Teacher-Made Scoring Guides and Rubrics • Use of AP Exam Student Samples 47 Pre-AP English Strategies (con’t) • Modification of AP Exam questions to meet classroom objectives • Use of Past AP Exams 48