Diabetes Therapy and Problems for the Cardiologist. Quali difficolta
advertisement

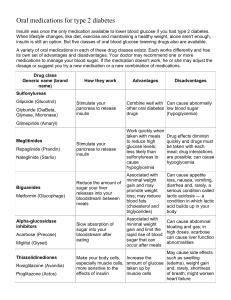
Diabetes Therapy and Problems for the Cardiologist. Quali difficolta pone la terapia diabetologica al cardiologo Mariell Jessup MD, FAHA, FACC, FESC Professor of Medicine University of Pennsylvania Philadelphia, Pennsylvania Disclosure: I have no conflicts with respect to this lecture ADA/EASD 2012 position statement The American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association of the Study of Diabetes (EASD) Metformin mechanism of action *effective only in the presence of insulin *major effect is to decrease hepatic glucose output, increases insulin-mediated glucose utilization in peripheral tissues (such as muscle and liver) *an anti-lipolytic effect that lowers serum free fatty acid concentrations, reducing substrate availability for gluconeogenesis Metformin advantages • Promotes weight loss or stabilization of weight • Lipid lowering activity, decreased triglycerides and free fatty acids • Less likely to cause hypoglycemia • Works well in combination Metformin adverse effects • Gastrointestinal: metallic taste in the mouth, mild anorexia, nausea, abdominal discomfort, and soft bowel movements or diarrhea • Reduces intestinal absorption of vitamin B12 in up to 30% of patients, and lowers serum vitamin B12 concentrations in 5 to 10% • Lactic acidosis: most important in renal failure, but heart failure and shock are always cited. – GFR < 60mL/min – Iodinated contrast ADA/EASD 2012 position statement The American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association of the Study of Diabetes (EASD) Sulfonylureas mechanism of action • increased responsiveness of beta cells to both glucose and non-glucose secretagogues (such as amino acids), resulting in more insulin being released at all blood glucose concentrations. • useful only in patients with some beta cell function. • Drugs in this class: Glipizide, glyburide (glibenclamide), gliclazide, and glimepiride Sulfonylureas adverse effects: hypoglycemia ■After exercise or a missed meal ■When the drug dose is too high ■With the use of longer-acting drugs (glyburide, chlorpropamide) ■In patients who are undernourished or abuse alcohol ■In patients with impaired renal or cardiac function or gastrointestinal disease ■With concurrent therapy with salicylates, sulfonamides, fibric acid derivatives (such as gemfibrozil), and warfarin ■After being in the hospital Increased risk after MI???? ADA/EASD 2012 position statement The American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association of the Study of Diabetes (EASD) Thiazolidinediones mechanism of action • bind to and activate peroxisome proliferatoractivated receptors (PPARs), which regulate gene expression in response to ligand binding • increase insulin sensitivity by acting on adipose, muscle, and liver to increase glucose utilization and decrease glucose production • drugs in this class: troglitazone, pioglitazone, and rosiglitazone. Thiazolidinediones effects and adverse events • Beneficial effects on :dyslipidemia, markers of inflammation, vascular smooth muscle proliferation, vascular reactivity, endothelial function, carotid intima media thickness, and progression of atherosclerosis on coronary intravascular ultrasound. • But…weight gain, fluid retention, heart failure, myocardial infarction, and fractures occur • RECORD trial (3.75 years follow-up) increased risk of HF (HR 2.24)in rosiglitazone combinations compared with metformin plus sulfonylurea. DPP-4 inhibitors mechanism of action • Drugs in this class: sitagliptin, saxagliptin, linagliptin, alogliptin, vildagliptin • Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4) is a ubiquitous enzyme expressed on the surface of most cell types that deactivates a variety of other bioactive peptides, including GIP and GLP-1; therefore, its inhibition could potentially affect glucose regulation through multiple effects DPP-4 inhibitors adverse events • well tolerated in short-term studies. • no effects on body weight or risk of hypoglycemia (in the absence of concomitant treatment with insulin or sulfonylureas • common side effects include: headache, nasopharyngitis, and upper respiratory tract infection • long-term safety with DPP-4 inhibitors has not been established. GLP-1 receptor agonists mechanism of actions • GLP-1-based therapies affect glucose control through several mechanisms: enhancement of glucose-dependent insulin secretion, slowed gastric emptying, regulation of postprandial glucagon, and reduction of food intake • Drugs in this class: xenatide, liraglutide, albiglutide, taspoglutide, lixisenatide GLP-1 receptor agonists effects and adverse events • potential benefit: weight loss • most common adverse events: – nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea – pancreatitis is serious Diabetes Therapy and Problems for the Cardiologist. • Since so many of our patients have diabetes, we must learn these new drugs • Huge controversy over the long-term cardiovascular effects of diabetic drugs • Edema is common with TZDs; lactic acidosis with metformin is probably not common • The GLP-1 agonists are potentially useful in HF.