3.4 Writing Formula, Complete and Net Ionic Equations
advertisement

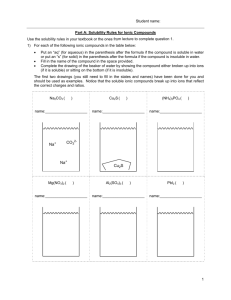
Objective: write a formula equation, complete ionic equation, and net ionic equation that represent a reaction We must be able to represent a reaction in three different ways: Formula Equation Total or Complete Ionic Equation Net Ionic Equation A balanced chemical equation in which all the reactants and products are given by their chemical formula. For Example: AgNO3(aq) + NaCl(aq) → AgCl(s) + NaNO3(aq) Soluble species are indicated by placing “(aq)” after the formula. Precipitates are indicated by placing “(s)” after the formula. This way of expressing the reaction is used whenever we want to indicate the chemical formula of the reactants and products. Ion Solubility Exceptions NO3– soluble none ClO4– soluble none Cl– soluble I– soluble except Ag+, Hg22+, *Pb2+ SO42- soluble except Ca2+, Ba2+, Sr2+, Hg2+, Pb2+, Ag+ CO32- insoluble except Group IA and NH4+ PO43- insoluble except Group IA and NH4+ OH– insoluble except Group IA, *Ca2+, Ba2+, Sr2+ S2- insoluble except Group IA, IIA and NH4+ Na+ soluble none K+ soluble none NH4+ soluble none except Ag+, Hg22+, *Pb2+ Shows all the soluble ionic species broken up into their respective ions. For Example: Ag+(aq)+ NO3-(aq)+ Na+(aq)+ Cl-(aq) → AgCl(s)+ Na+(aq)+ NO3-(aq) This method is not frequently used because it is cumbersome to write out. It is used to emphasize the situation which exists before and after the reaction. Spectator ions: Ions that remain unchanged during a reaction and do not participate in the reaction.They are present on both sides of the equation. The spectator ions in the above equation are NO3-(aq) and Na+(aq) NEVER write a total ionic equation until you have first written a balanced formula equation. If you proceed directly to a total ionic equation the result may be balanced but still may not represent the actual situation. Shows only the reacting species (species which are actively involved in the reaction…the one making the PPT) in the equation. The net ionic equation is formed by omitting the spectator ions from the total ionic equation. For Example: We had: then: AgNO3(aq) + NaCl(aq) → AgCl(s) + NaNO3(aq) Ag+(aq)+ NO3-(aq)+ Na+(aq)+ Cl-(aq) → AgCl(s)+ Na+(aq)+ NO3-(aq) Canceling out spectator ions, we get: Ag+(aq)+ Cl-(aq) → AgCl(s) Example: Write a formula equation, a total ionic equation, and a net ionic equation for the reaction which occurs when solutions of Al(NO3)3(aq) and MgS(aq) are mixed. 1) 2) 3) Write the formula, complete ionic, and net ionic equation for each of the following reactions: Aqueous nickel (II) chloride reacts with aqueous sodium hydroxide to give nickel (II) hydroxide and sodium chloride. Solid potassium metal reacts with water to give potassium hydroxide and hydrogen gas. Aqueous sodium hydroxide reacts with phosphoric acid to give water and sodium phosphate.