3.NBT Tasks - 3
advertisement

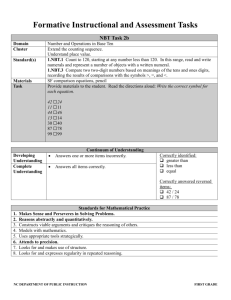
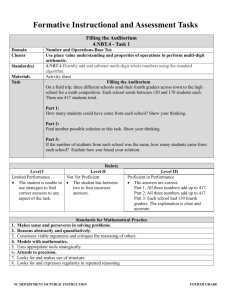
Formative Instructional and Assessment Tasks Cafeteria Lunch Orders 3.NBT.1– Task 1 Domain Cluster Standard(s) Materials Task Number and Operations in Base Ten Use place value understanding and properties of operations to perform multi-digit arithmetic. 3.NBT.1 Use place value understanding to round whole numbers to the nearest 10 or 100. Cafeteria Lunch Orders handout, paper, pencils Distribute the Cafeteria Lunch Orders handout to teachers. Read: The cafeteria organized student lunch orders on this chart. Ask: o On what day was the number of hot lunches about the same as the number of cold lunches? Explain your solution using pictures, numbers, or words. o On what day was the number of cold lunches about 20 more than the number of hot lunches? Explain your solution using pictures, numbers, or words. o About how many hot lunches need to be ordered this week? Explain your solution using pictures, numbers, or words. Level I Limited Performance Student’s response is incorrect, incomplete, or off task. Rubric Level II Not Yet Proficient Student does 1-2 of the following: Student states that on Wednesday the numbers of hot lunches and cold lunches were about the same. Student states that on Friday about 20 more cold lunches were ordered that hot lunches. Depending on how student rounds, he/she finds that between 1400-1420 lunches need to be ordered. Some solutions are explained. NC DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC INSTRUCTION Level III Proficient in Performance Student states that on Wednesday the numbers of hot lunches and cold lunches were about the same. Student states that on Friday about 20 more cold lunches were ordered that hot lunches. Depending on how student rounds, he/she finds that between 1400-1420 lunches need to be ordered. All solutions are explained using pictures, numbers, or words. THIRD GRADE Formative Instructional and Assessment Tasks 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Standards for Mathematical Practice Makes sense and perseveres in solving problems. Reasons abstractly and quantitatively. Constructs viable arguments and critiques the reasoning of others. Models with mathematics. Uses appropriate tools strategically. Attends to precision. Looks for and makes use of structure. Looks for and expresses regularity in repeated reasoning. NC DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC INSTRUCTION THIRD GRADE Formative Instructional and Assessment Tasks Cafeteria Lunch Orders The cafeteria organized student lunch orders on this chart. NUMBER OF CAFETERIA LUNCH ORDERS Day Monday Hot Lunches 248 Cold Lunches 257 Tuesday 362 143 Wednesday 292 288 Thursday 301 226 Friday 217 239 Use information from the chart to answer each question. 1. On what day was the number of hot lunches about the same as the number of cold lunches? Explain your solution using pictures, numbers, or words. 2. On what day was the number of cold lunches about 20 more than the number of hot lunches? Explain your solution using pictures, numbers, or words. 3. About how many hot lunches need to be ordered this week? Explain your solution using pictures, numbers, or words. NC DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC INSTRUCTION THIRD GRADE Formative Instructional and Assessment Tasks Comparing Heights 3.NBT.1– Task 2 Domain Cluster Standard(s) Materials Task Number and Operations in Base Ten Use place value understanding and properties of operations to perform multi-digit arithmetic. 3.NBT.1 Use place value understanding to round whole numbers to the nearest 10 or 100. Comparing Heights handouts, paper, pencils, calculators (optional) Distribute copies of the Comparing Heights handout. Read: Neil and Jerome were comparing their heights to see who is taller. Neil measured his height and said “I am 59 inches. 59 rounds to 100 so I am about 100 inches tall.” Jerome measured his height and said, “I am 65 inches. 65 rounds to 70 so I am about 70 inches tall. You’re taller, Neil.” Ask: 1. What is wrong with the boys’ reasoning? 2. How could the boys correctly use rounding to compare their heights? 3. What are two examples of ways you could use rounding in your life? Level I Limited Performance Student’s response is incorrect, incomplete, or off task. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Rubric Level II Not Yet Proficient Student does 1-2 of the following: Student recognizes that Neil rounded to the nearest hundred and Jerome rounded to the nearest ten. Student states that both boys should have rounded to the same place for a more accurate comparison. Student determines 1-2 ways that rounding could be used in his/her life. Level III Proficient in Performance Student recognizes that Neil rounded to the nearest hundred and Jerome rounded to the nearest ten. Student states that both boys should have rounded to the same place for a more accurate comparison (i.e, round to the nearest ten since rounding to the nearest hundred does not lead to a realistic height). Student determines two ways that rounding can be used in his/her life. Standards for Mathematical Practice Makes sense and perseveres in solving problems. Reasons abstractly and quantitatively. Constructs viable arguments and critiques the reasoning of others. Models with mathematics. Uses appropriate tools strategically. Attends to precision. Looks for and makes use of structure. Looks for and expresses regularity in repeated reasoning. NC DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC INSTRUCTION THIRD GRADE Formative Instructional and Assessment Tasks Comparing Heights Neil and Jerome were comparing their heights. Neil measured his height and said, “I am 59 inches. 59 rounds to 100 so I am about 100 inches tall.” Jerome measured his height and said, “I am 65 inches. 65 rounds to 70 so I am about 70 inches tall. You’re taller, Neil.” 1. What is wrong with the boys’ reasoning? 2. How could the boys correctly use rounding to compare their heights? 3. What are two examples of ways you could use rounding in your life? NC DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC INSTRUCTION THIRD GRADE Formative Instructional and Assessment Tasks All About Rounding 3.NBT.1– Task 3 Domain Cluster Standard(s) Materials Task Number and Operations in Base Ten Use place value understanding and properties of operations to perform multi-digit arithmetic. 3.NBT.1 Use place value understanding to round whole numbers to the nearest 10 or 100. paper, pencils, calculators (optional), handout (optional) Part 1: Ask: How many different numbers will round to 300 when rounding to the nearest hundred? How many different numbers will round to 300 when rounding to the nearest ten? How can you prove that you found all possible numbers? Extension Activity: Will knowing the amount of numbers that round to 300 help you know the amount of numbers that round to 400? 500? Explain. Part 2: Read: How does rounding help you solve addition and subtraction problems? Give an example of a real world addition or subtraction problem that can be solved using rounding. Be sure to show how you would solve the problem. Level I Limited Performance Student’s response is incorrect, incomplete, or off task. Rubric Level II Not Yet Proficient Student does 1-2 of the following: Student identifies some (but not all) numbers that round to 300. Student explains how rounding helps solve addition and subtraction problems. Student gives a real world addition or subtraction problem that requires rounding to solve. Student provides some justification. Level III Proficient in Performance Student accurately completes part 1 of task (100; 10). Student explains how rounding helps solve addition and subtraction problems. Student gives example of a real world problem that can be solved using rounding. Student provides clear justification and reasoning for all parts of task. *Level IV: Student accurately completes Extension Activity. Student recognizes that there are 100 numbers that will round to 400 (or 500) when rounding to the nearest hundred. Student recognizes that there are 10 numbers that round to 400 (or 500) when rounding to the nearest ten. NC DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC INSTRUCTION THIRD GRADE Formative Instructional and Assessment Tasks 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Standards for Mathematical Practice Makes sense and perseveres in solving problems. Reasons abstractly and quantitatively. Constructs viable arguments and critiques the reasoning of others. Models with mathematics. Uses appropriate tools strategically. Attends to precision. Looks for and makes use of structure. Looks for and expresses regularity in repeated reasoning. NC DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC INSTRUCTION THIRD GRADE Formative Instructional and Assessment Tasks All About Rounding Part I: How many different numbers will round to 300 when rounding to the nearest hundred? How many different numbers will round to 300 when rounding to the nearest ten? How can you prove that you found all possible numbers? Part II: How does rounding help you solve addition and subtraction problems? Give an example of a real world addition or subtraction problem that can be solved using rounding. Be sure to show how you would solve the problem. NC DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC INSTRUCTION THIRD GRADE Formative Instructional and Assessment Tasks Compatible Numbers 3.NBT.2 – Task 1 Domain Cluster Standard(s) Materials Task Number and Operations in Base Ten Use place value understanding and properties of operations to perform multi-digit arithmetic. 3.NBT.2 Fluently add and subtract within 1000 using strategies and algorithms based on place value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between addition and subtraction. Ms. Snyder’s Game Board (teacher copy), document reader/overhead projector, paper, pencils, handout (optional) Part 1: Display Ms. Snyder’s Game Board. Read: Ms. Snyder is playing a game with her class. In order to win round 1 of the game, the class must find two numbers on Ms. Snyder’s game board whose sum is exactly 1,000. Which two numbers will win the game? What strategy did you use to find the two numbers with a sum of 1,000? Write a list of steps that will help students follow your strategy. Part 2: Display Ms. Snyder’s Game Board. Read: In order to win round 2 of the game, the class must find three numbers on Ms. Snyder’s game board whose sum is exactly 1,000. Which three numbers will win the game? How is your strategy for round 2 different from what you did in round 1? Write a list of steps that will help students follow your strategy for round 2. Part 3: Create your own game board that has a set of two numbers whose sum is exactly 1,000 and a set of three numbers whose sum is 1,000. See if a friend can find each set of numbers whose sum is 1,000. Level I Limited Performance Student’s response is incorrect, incomplete, or off task. Rubric Level II Not Yet Proficient Student does 1-3 of the following: Student identifies that the sum of 463 and 537 is 1,000. Student identifies that the sum of 124, 376, and 500 is 1,000. Student generates a game board with a set of two numbers whose sum is 1,000 and a set of three numbers whose sum is 1,000. NC DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC INSTRUCTION Level III Proficient in Performance Student identifies that the sum of 463 and 537 is 1,000. Student identifies that the sum of 124, 376, and 500 is 1,000. Student clearly explains strategies for finding sums. Student generates a game board with a set of two numbers whose sum is 1,000 and a set of three numbers whose sum is 1,000. THIRD GRADE Formative Instructional and Assessment Tasks 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Standards for Mathematical Practice Makes sense and perseveres in solving problems. Reasons abstractly and quantitatively. Constructs viable arguments and critiques the reasoning of others. Models with mathematics. Uses appropriate tools strategically. Attends to precision. Looks for and makes use of structure. Looks for and expresses regularity in repeated reasoning. Ms. Snyder’s Game Board 500 236 376 463 145 537 743 856 124 NC DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC INSTRUCTION THIRD GRADE Formative Instructional and Assessment Tasks Compatible Numbers Ms. Snyder’s Game Board 500 236 376 463 145 537 743 856 124 Part I: Ms. Snyder is playing a game with her class. In order to win round 1 of the game, the class must find two numbers on Ms. Snyder’s game board whose sum is exactly 1,000. Which two numbers will win the game? What strategy did you use to find the two numbers with a sum of 1,000? Write a list of steps that will help students follow your strategy. NC DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC INSTRUCTION THIRD GRADE Formative Instructional and Assessment Tasks Part II: In order to win round 2 of the game, the class must find three numbers on Ms. Snyder’s game board whose sum is exactly 1,000. Which three numbers will win the game? How is your strategy for round 2 different from what you did in round 1? Write a list of steps that will help students follow your strategy for round 2. Part III: Create your own game board that has a set of two numbers whose sum is exactly 1,000 and a set of three numbers whose sum is 1,000. See if a friend can find each set of numbers whose sum is 1,000. NC DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC INSTRUCTION THIRD GRADE Formative Instructional and Assessment Tasks Toys For Us 3.NBT.2– Task 2 Domain Cluster Standard(s) Materials Task Number and Operations in Base Ten Use place value understanding and properties of operations to perform multi-digit arithmetic. 3.NBT.2 Fluently add and subtract within 1000 using strategies and algorithms based on place value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between addition and subtraction. Toys for Us sales fliers, Toys for Us Recording Sheets, paper, pencils Part 1: Distribute Toys for Us fliers to students. Read: Congratulations! You just won a $1,000 gift card to Toys for Us. Look at the Toys for Us sales flier and make a list of what you will buy. Be sure to spend as close as possible to $1,000 without going over. Part 2: Read: Use your work from Part 1 to answer each question. • What was the total cost of your items? • How much money will be left on your gift card? • What strategies did you use to get as close to $1,000 as possible? • Is it possible to spend exactly $1,000? Explain. NC DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC INSTRUCTION THIRD GRADE Formative Instructional and Assessment Tasks Level I Limited Performance Student’s response is incorrect, incomplete, or off task. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Rubric Level II Not Yet Proficient Student does 1-4 of the following: Student selects a list of toys valued at or near $1,000. Student identifies the total cost of item on his/her list. Student identifies amount left on gift card. Problem solving strategies are clearly articulated. Student finds a list of items whose sum is exactly $1,000. Level III Proficient in Performance Student selects a list of toys valued at or near $1,000. Student identifies the total cost of item on his/her list. Student identifies amount left on gift card. Problem solving strategies are clearly articulated. Student finds a list of items whose sum is exactly $1,000. Standards for Mathematical Practice Makes sense and perseveres in solving problems. Reasons abstractly and quantitatively. Constructs viable arguments and critiques the reasoning of others. Models with mathematics. Uses appropriate tools strategically. Attends to precision. Looks for and makes use of structure. Looks for and expresses regularity in repeated reasoning. NC DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC INSTRUCTION THIRD GRADE Formative Instructional and Assessment Tasks Toys for Us trampoline $184 spy kit $51 mountain bike $240 science kit $46 scooter $449 MP3 player $152 roller blades $58 CD boom box $52 board game $19 electric guitar $210 puzzle $6 trumpet $180 hand-held game $72 basketball $15 gaming system $225 telescope $99 remote control car $39 snow cone machine $32 remote control airplane $44 ice cream maker $50 giant gumball machine $95 easy make oven $56 art set $47 frog tank with live frogs $34 make-up kit $31 ant farm $23 NC DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC INSTRUCTION THIRD GRADE Formative Instructional and Assessment Tasks Toys for Us Recording Sheet Congratulations! You just won a $1,000 gift card to Toys for US. Look at the Toys for Us flier and make a list of what you will buy. Be sure to spend as close as possible to $1,000 without going over. list of items you will purchase Use your list of items to answer each question. 1. What was the total cost of your items? 2. How much money will be left on your gift card? 3. What strategies did you use to get as close to $1,000 as possible? 4. Is it possible to spend exactly $1,000? Explain. NC DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC INSTRUCTION THIRD GRADE Formative Instructional and Assessment Tasks From 100 to 0 3.NBT.2 – Task 3 Domain Cluster Standard(s) Materials Task Number and Operations in Base Ten Use place value understanding and properties of operations to perform multi-digit arithmetic. 3.NBT.2 Fluently add and subtract within 1000 using strategies and algorithms based on place value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between addition and subtraction. Pencil and activity sheet or whiteboards and markers Austin and Matthew were playing a game called 100 to 0. To play the game, you roll a pair of dice to make a number. Example: If you roll a pair of dice a get 2 and 6 you could create the number 26 or 62. All players start with 100 at the beginning of the game. You subtract the number rolled from your number. To win, you have to end up with exactly 0. If you roll more than the number you need to have 0, you lose your turn. The list shows what each child rolled in the game. Which student won the game? Prove your answer. Level I Limited Performance Student’s response is incorrect, incomplete, or off task. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Rubric Level II Not Yet Proficient Student either: Is inaccurate in work. Goes over 100. Does not have an adequate explanation for the answer. Level III Proficient in Performance Student identifies Austin gets to 100 first. Student either subtracts from 100 accurately to find the number, or adds the numbers until reaching 100. Student clearly explains strategies for finding sums/differences. Standards for Mathematical Practice Makes sense and perseveres in solving problems. Reasons abstractly and quantitatively. Constructs viable arguments and critiques the reasoning of others. Models with mathematics. Uses appropriate tools strategically. Attends to precision. Looks for and makes use of structure. Looks for and expresses regularity in repeated reasoning. NC DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC INSTRUCTION THIRD GRADE Formative Instructional and Assessment Tasks From 100 to 0 Austin and Matthew were playing a game called 100 to 0. To play the game, you roll a pair of dice to make a number. (Example: If you roll a pair of dice a get 2 and 6 you could create the number 26 or 62.) All players start with 100 at the beginning of the game. You subtract the number rolled from your number. To win, you have to end up with exactly 0. If you roll more than the number you need to have 0, you lose your turn. The list shows what each child rolled in the game. Which student won the game? Prove your answer. Show how you found your answer. Numbers rolled on place value dice: Roll Roll 1 Roll 2 Roll 3 Roll 4 Roll 5 Roll 6 Roll 7 Roll 8 NC DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC INSTRUCTION Matthew 56 18 39 8 6 9 5 3 Austin 27 38 64 26 42 9 2 6 THIRD GRADE Formative Instructional and Assessment Tasks What’s the Best Deal? 3.NBT.3 – Task 1 Domain Cluster Standard(s) Materials Task Number and Operations in Base Ten Use place value understanding and properties of operations to perform multi-digit arithmetic. 3.NBT.3 Multiply one-digit whole numbers by multiples of 10 in the range 10–90 (e.g., 9 × 80, 5 × 60) using strategies based on place value and properties of operations. paper, pencils, copy of problem Display a copy of the problem on the board or document reader. Read: Max is trying to decide if he should go to Fast Foods, Green Groceries, or Super Store to buy biscuits for the school picnic. For $25, Max can buy: 60 five-packs of biscuits from Fast Foods. or 30 six-packs of biscuits from Green Groceries. or 40 eight-packs of biscuits from Super Store. Ask: Where should Max go to buy biscuits? Use pictures, numbers, words, or equations to explain your reasoning. Level I Limited Performance Student’s work is off-task, incomplete, or not accurate. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Rubric Level II Not Yet Proficient Student states that Max should shop at Super Store, but is unable to justify reasoning. OR Student has shown some justification of appropriate reasoning, but it does not lead to the correct answer. Level III Proficient in Performance Student states that Max should shop at Super Store. Student accurately justifies reasoning (i.e., For $25, Max will get the most biscuits at Super Store – 320 biscuits. He will only get 300 biscuits at Fast Foods or 180 biscuits at Green Groceries.) Standards for Mathematical Practice Makes sense and perseveres in solving problems. Reasons abstractly and quantitatively. Constructs viable arguments and critiques the reasoning of others. Models with mathematics. Uses appropriate tools strategically. Attends to precision. Looks for and makes use of structure. Looks for and expresses regularity in repeated reasoning. NC DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC INSTRUCTION THIRD GRADE Formative Instructional and Assessment Tasks What’s the Best Deal? Max is trying to decide if he should go to Fast Foods, Green Groceries, or Super Store to buy biscuits for the school picnic. For $25, Max can buy: 60 five-packs of biscuits from Fast Foods. or 30 six-packs of biscuits from Green Groceries. or 40 eight-packs of biscuits from Super Store. Where should Max go to buy biscuits? Use pictures, numbers, words, or equations to explain your reasoning. NC DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC INSTRUCTION THIRD GRADE Formative Instructional and Assessment Tasks Helping Hugh 3.NBT.3 – Task 2 Domain Cluster Standard(s) Materials Task Number and Operations in Base Ten Use place value understanding and properties of operations to perform multi-digit arithmetic. 3.NBT.3 Multiply one-digit whole numbers by multiples of 10 in the range 10–90 (e.g., 9 × 80, 5 × 60) using strategies based on place value and properties of operations. Helping Hugh handout, paper, pencils, manipulatives Distribute copies of Helping Hugh handouts to each student. Draw students’ attention to the receipts on the handout. Read: Hugh works at his dad’s pet shop, but he keeps making mistakes! Look at Hugh’s receipts and decide why he is making so many mistakes. Write a note to Hugh that teaches him how to prevent his mistakes from happening again. Use drawings, charts, objects, words, numbers, or equations to help Hugh understand. Level I Limited Performance Student’s work is off-task, incomplete, or not accurate. Rubric Level II Not Yet Proficient Student identifies that Hugh is multiplying by a single digit, rather than a multiple of ten. However, student is unable to clearly teach Hugh how to fix his mistake. NC DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC INSTRUCTION Level III Proficient in Performance Student identifies that Hugh is multiplying by a single digit, rather than a multiple of ten (i.e., instead of multiplying 30x7, Hugh mistakenly multiplies 3x7). Student teaches Hugh an appropriate strategy for multiplying by a multiple of ten. THIRD GRADE Formative Instructional and Assessment Tasks 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Standards for Mathematical Practice Makes sense and perseveres in solving problems. Reasons abstractly and quantitatively. Constructs viable arguments and critiques the reasoning of others. Models with mathematics. Uses appropriate tools strategically. Attends to precision. Looks for and makes use of structure. Looks for and expresses regularity in repeated reasoning. NC DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC INSTRUCTION THIRD GRADE Formative Instructional and Assessment Tasks Helping Hugh Hugh works at his dad’s pet shop, but he keeps making mistakes! Look at Hugh’s receipts and decide why he is making so many mistakes. Write a note to Hugh that teaches him how to prevent his mistakes from happening again. Use drawings, charts, objects, words, numbers, or equations to help Hugh understand. NC DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC INSTRUCTION THIRD GRADE Formative Instructional and Assessment Tasks Earn That Bike 3.NBT.3 – Task 3 Domain Cluster Standard(s) Materials Task Number and Operations in Base Ten Use place value understanding and properties of operations to perform multi-digit arithmetic. 3.NBT.3 Multiply one-digit whole numbers by multiples of 10 in the range 10–90 (e.g., 9 × 80, 5 × 60) using strategies based on place value and properties of operations. Paper, pencils, copy of problem Elana makes $30 every time she helps her aunt watch her baby on a Saturday. Elana wants to purchase a new bike with the money she earns. The new bike is $240. How many weeks will she have to help her aunt to earn enough money to purchase a new bike? Use words, pictures, or equations to show how she can figure out how long it will take. Level I Limited Performance Student’s work is off-task, incomplete, or not accurate. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Rubric Level II Not Yet Proficient Student states 8 weeks but can not explain work. OR Student has shown some justification of appropriate reasoning, but it does not lead to the correct answer. Level III Proficient in Performance Student states that it will take 8 weeks. Student accurately explains: 3 x X = 24 or 30 x X = 240 and that 3 x 8= 24 or 30 x 8 = 240 Student explains how answer was computed in words, pictures or equations. Standards for Mathematical Practice Makes sense and perseveres in solving problems. Reasons abstractly and quantitatively. Constructs viable arguments and critiques the reasoning of others. Models with mathematics. Uses appropriate tools strategically. Attends to precision. Looks for and makes use of structure. Looks for and expresses regularity in repeated reasoning. NC DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC INSTRUCTION THIRD GRADE Formative Instructional and Assessment Tasks Earn That Bike Elana makes $30 every time she helps her aunt watch her baby on a Saturday. Elana wants to purchase a new bike with the money she earns. The new bike is $240. How many weeks will she have to help her aunt to earn enough money to purchase a new bike? Use words, pictures, or equations to show how she can figure out how long it will take. NC DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC INSTRUCTION THIRD GRADE