Female Reproductive System Notes
advertisement

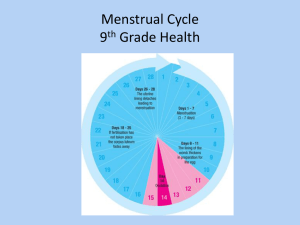
Female Reproductive System Functions • 1. Produce female sex hormone – estrogen and progesterone (Estrogen promotes secondary sex characteristics ) • 2. Storage and production of eggs – female sex cell Secondary Sex Characteristics • • • • Development of breasts Broadening of the pelvis Soft and smooth skin Deposition of fat in the thighs and buttocks • Development of pubic hair • Sex drive • Ovulation • Menstruation Some Vocabulary… • 1. Ovaries – female sex glands that store reproductive cell- ova (eggs) AND produce female sex hormones – estrogen and progesterone. • 2. Uterus – hollow, muscular, pear-shaped organ that nourishes and protects fetus • 3. Fallopian Tubes – pair of tubes with fingerlike projections that draw in the egg (ovum) Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Fallopian Tubes Uterus Cervix Ovaries Vagina Hymen Female Reproductive System To put it in perspective… More Vocab… 5. Cervix – opening of the uterus 6. Vagina – muscular, elastic passageway that extends from the uterus to the outside of the body The Hymen • Thin membrane that stretches across the opening of the vagina • May not be present in some females • Myth: because a girl does not have a hymen, it does not mean she is no longer a virgin Fertilization • If sperm is present in the fallopian tubes, the sperm cell and ovum may unite, causing fertilization. • This produces a zygote. • When zygote leaves the fallopian tube, it enters the uterus and implants itself in the uterine wall. • Wall thickens with blood to nourish, remains until pregnancy. What is ovulation? • Ovulation – process of releasing a mature ovum into the fallopian tube each month. Ovulation (releasing of Ovum) Menstruation • 1. Menstruation is the shedding of the uterine lining – or endometrium • 2. When females mature and go through puberty, the uterus prepares each month for possible pregnancy by increasing bloodflow to the endometrium causing the walls to thicken. • 3. If no fertilization takes place, endometrium deteriorates and becomes menstrual flow. Menstruation • Most females begin their menstrual cycle between ages of 10-15. • Hormones control menstrual cycle • However, stress, illness, low body weight, and poor nutrition can impact the cycle. • Menstruation occurs from the onset of puberty until menopause – end of a females productive years (usually 45-55 years old) Menstruation Cycle • Days 1-4: Lining of the uterus sloughs off and the dead tissue and blood leave the body Menstruation Cycle • Days 5-12: Lining of the uterus repairs itself and menstrual flow stops • Days 13-15: Ovulation occurs (release of egg from ovary) PREGNANCY MOST OFTEN OCCURS AT THIS TIME!!! • Days 16-25: The lining of the uterus again thickens Menstruation Cycle • Days 26-28: The lining breaks down and is about to leave the body. Reproductive Problems • 2. HPV – Human Papillomavirus – Also known as genital warts – Can lead to Cervical Cancer if not cured!! • 3. Uterine Cancer – Cancer of Uterus – most cases are among women who have gone through menopause • 4. Ovarian Cysts – Small fluid filled sacs that develop on Ovaries – Can rupture causing pain – Causes: Hormonal Imbalance, Irregular Cycles Reproductive Problems • 1. Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS) • caused by hormonal changes. • Occurs one to two weeks before menstruation. • Symptoms include anxiety, irritability, weight gain, depression, mood swings, and fatigue Reproductive Problems • 2. HPV – Human Papillomavirus – Also known as genital warts – Can lead to Cervical Cancer if not cured!! • 3. Uterine Cancer – Cancer of Uterus – most cases are among women who have gone through menopause • 4. Ovarian Cysts – Small fluid filled sacs that develop on Ovaries – Can rupture causing pain – Causes: Hormonal Imbalance, Irregular Cycles Problems of the Female Reproductive System • Toxic shock syndrome (TSS) - a rare bacteriacaused illness occurring mostly in menstruating women who use high absorbency tampons. Breast Cancer A disease in which malignant tumors grow in breast tissue. Risk factors for breast cancer – Being older than 50 – Family history of breast cancer – Starting menstruation before age 12 – Having no pregnancies – Having a first child born after age 30 – Beginning menopause after age 50 – Being obese – High percentage of body fat – High fat diet – Having cancer in one breast Maintaining Health • Bathe Regularly – shower daily, change tampons every few hours during menstrual period • Regular Checkups – Will include a test known as a Pap smear (detect cancerous cells on cervix) Also, a mammogram to test for breast cancer • Practice Abstinence – refraining from sexual activity until marriage. Maintaining Health • Perform Self Exam – – Massage each breast in a circular fashion – Check for lumps or abnormalities – See a doctor if you detect anything! Breast Self-Exam