Structures and Weights PDR ()
advertisement

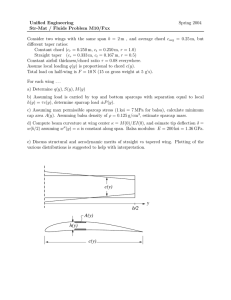
Structures Preliminary Design Review #1 Patrick Dempsey October 12, Bridget Fitzpatrick 2000 Heather Garber Keith Hout Jong Soo Mok Basic Layout of Wing Spar -located at the 1/4 chord Sparcaps -spruce -1/8” x 1/8” x 6.6’ Shearweb -balsa -1.5” x 1/16” x 6.6’ Ribs -balsa -spaced every 3 inches from tip -include lightening holes Added balsa at leading and trailing edge Geometric Layout of rib Typical rib section Geometric Layout of Wing -Stringers -None at this time -Many model planes do not have them -Would add weight -Wing covering- Monokote -Helps with twisting -Forms the skin Geometric Layout of Wing Sample of strut layout from NACA report 143 Code Code run using preliminary size of aircraft, load factor, and a chosen spar size -Wing loading -Schrenk’s approximation (Raymer) -Shear force -Moment -Find centroids -Moments of inertia -Normal stress My xx Iz WING LOADING Trapezoidal approximation 2y 1 q ( y ) q (0) 1 b q ( 0) w * 3.75 b Elliptical approximation q( y ) 4S 2y 1 ^ 2 b * pi b SHEAR FORCE MOMENT Normal STRESS Material Properties Material Balsa Plywood Spruce Monokote (oz/sqin) Epoxy (oz/sqin) CA glue (oz/joint) Young's Modulus (ksi) Stress Density (yield) (lbf/ft^3) (psi) 625 11 1725 800 37 4000 1500 34 8600 0.0021 0.007 0.0068 Table taken from Spring ’99 AAE 451 report (Team WTA) Further Testing -Test maximum shear stress of balsa using three point load test -Torsional test of wing with and without monokote Structure -Fuselage - balsa -Tapered box -Modeled as truss structure -Sheet on floor to hold equipment -Horizontal/Vertical tail – balsa -Modeled as a flat plate -May have to add a spruce spar due to the size of tail Landing Gear -Tail dragger configuration -Front wheels placed in front of center of gravity and to ensure propeller clearance -Spaced horizontally to avoid lateral tip over Center of Gravity Estimate -Center of Gravity -Within 5-10% static margin in front of aerodynamic center -Moment Balance -Find the weight and moment arm of every component Questions?