4/9 Daily Catalyst Pg. 39 Active Transport
advertisement

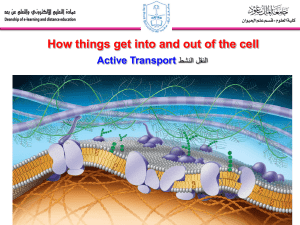
4/1 Daily Catalyst Pg. 44 Active Transport 1. Explain the differences between plant and animal cells and tonicity. 2. Since glucose is too big to cross the cell membrane and if water is not moving, what is another way for glucose to enter the cell? 4/1 Daily Catalyst Pg. 44 Active Transport Quiz #10 TODAY Cell and Transport test on Wednesday Review day on Tuesday M.C. on cells and transport Tutoring available Spring Break review packet due Tuesday, April 7th 4/1 Daily Catalyst Pg. 44 Active Transport Daily Catalyst Class Business Active transport notes Lab work time Quiz #10 4/1 Objective Today, we will compare and contrast active and passive transport. Passive vs. Active Transport Passive Transport Osmosis Movement of water Passive No energy High to low Across the membrane Diffusion Movement of molecules Passive No energy High to low Across the membrane Label the following cells are isotonic, hypertonic, or hypotonic 1 2 3 Passive vs. Active Transport Key point #1: Active Transport the movement of molecules from low to high concentration Requires ENERGY ATP Concentration Gradient Key Point #2: The movement of molecules against the concentration gradient. Active Transport Example: the Sodium-Potassium pump Active Transport 2 types: Endocytosis Key point #3: Endocytosis: Molecules brought into the cells. EN=IN Vesicles Molecules are brought into the cell and the membrane pinches off, creating a vesicle. Key Point #4: A vesicle is made of phospholipids Exocytosis Key point #5: Exocytosis: Molecules exit the cell EXO=EXIT Exocytosis The vesicle fuses with the membrane and ejects the contents to the outside of the cell. Exocytosis and endocytosis are examples of active transport and require ATP. Video Clip http://www.dnatube.com/video/358/Endocytosis What type of transport? Exocytosis What type of transport? Endocytosis Tell me what you know? What kind of solution (hypotonic, isotonic, or hypertonic) does the cell shrink in? Hypertonic What type of transport? Active transport Lab Work Time Directions: With your lab group, complete day 3 instructions. Be sure to measure final mass, take observations, and record results. You will work on the charts on your own time. Time: 15 minutes Noise: 2 (with group) Quiz #10 Directions: Silently and independently complete quiz #10. Turn your quiz into the basket and begin working on your spring break packet or lab report. Time: 10 minutes Noise: 0 (SILENT)