Active Transport, Exocytosis and Endocytosis
advertisement

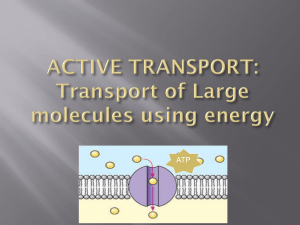
Quiz 1. Name and define the process shown by the denture cleanser experiment. 2. Name and define the process shown by the carrot experiment. 3. Define the following words. Semi-Permeable: Passive Transport: Active Transport: Learning Goals 1d. Differentiate between active and passive transport. 1e. Explain how large particles get into and out of cells (endocytosis/excotytosis) Active Transport • Active Transport – moving small particles • A process of transporting small particles that requires the cell to use energy • Usually involves the movement of particles from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. Active Transport . Active Transport • Specific proteins move small molecules from and area of lower concentration to higher concentration. • ATP - energy used from mitochondria Passive Transport • Passive Transport – moving small particles • Diffusion and osmosis are examples of passive transport. • Small particles move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. • Passive Transport is movement of particles across a cell membrane without the use of energy by the cell through channels made of protein. • Ex: sugar, oxygen, carbon dioxide What process is this? Explain. Passive Transport Transport Concepts Passive vs. Active Passive – no energy Active – needs energy Endocytosis vs. Exocytosis Exocytosis (moving larger molecules outside the cell) – Exocytosis • Exocytosis – moving large particles out of the cell • Exocytosis is an active-transport process • A vesicle forms around a large particle within the cell. • The vesicle carries the particle to the cell membrane. • The vesicle fuses with the cell membrane and releases the particle to the outside of the cell. OUTSIDE THE CELL OUTSIDE THE CELL OUTSIDE THE CELL SOLUTE CARRIER PROTEIN CARRIER PROTEIN CARRIER PROTEIN SOLUTE SOLUTE CYTOPLASM CYTOPLASM CYTOPLASM Endocytosis (moving larger molecules inside the cell) Endocytosis • Endocytosis – moving LARGE particles into the cell • Endocytosis is an active-transport process. • Cell surrounds a large particle, and encloses the particle in a vesicle to bring the particle into the cell • Vesicles are sacs formed from pieces of cell membrane. • Ex: bringing in protein OUTSIDE THE CELL OUTSIDE THE CELL OUTSIDE THE CELL SOLUTE CARRIER PROTEIN CARRIER PROTEIN CARRIER PROTEIN SOLUTE SOLUTE CYTOPLASM CYTOPLASM CYTOPLASM Cell Membrane AKA plasma membrane • The cell membrane contains proteins, lipids, and phospholipids. • Some of the proteins and lipids control the movement of materials into and out of the cell. Some of the proteins form passageways. Nutrients and water move into the cell, and wastes move out of the cell, through these protein passageways. Cell Membrane is made of molecules called phospholipids which consist of: • 1. a hydrophilic (water loving) head • 2. two hydrophobic (water hating) tails • Phospholipids get their name because the group of phosphate-bearing heads is combined with a fat, or lipid, molecule. In water they orient themselves so that their heads are exposed to the water and the hydrophobic tails are away from water. They cluster in a bilayer in which the tails of the phospholipids interact with themselves and exclude water, while the heads expose themselves to water.