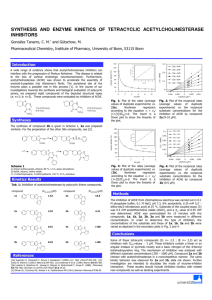
Organophosphates-B
advertisement

Pesticide Toxicology Week 2: Organophosphate Insecticides a. Acute toxicity Categories of Effects • Muscarinic – Mimic action of muscarine • Peripheral nervous system only – Smooth muscle, heart, exocrine glands • • • • Bronchoconstriction, salivation, lacrimation, perspiration Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, cramps Urination, defecation Bradycardia, miosis • Nicotinic – Mimic action of nicotine • • • • Neuromuscular junction of voluntary muscles Muscle weakness (including respiratory muscles) Twitching, cramps, pallor Elevated blood pressure, tachycardia • CNS symptoms – Confusion, restlessness, irritability, slurred speech, – Insomnia, emotional instability – Coma Time Course of Toxicity • Onset of symptoms – Minutes • Sarin, parathion, TEPP – Hours • EPN – Days • Chlorpyrifos • Abatement of symptoms – Slow onset tends to mean slow abatement – Acute symptoms rarely last more than a few days • Regeneration of AChE takes ~ 1 month – Ample opportunity for re-intoxication Chronic Effects of OPs: OPIDN • Organophosphate-induced delayed neuropathy (neurotoxicity) • Caused by subset of AChE-inhibiting OPs but not due to AChE inhibition • Delayed onset – – – – Symptoms begin 7-30 days after exposure Recovery continues up to 1 year Permanent effects Longest axons most vulnerable • Mechanism – Inhibition of neurotoxic esterase – Axonal damage – Death of neuron OPIDN: Organophosphorus ester-induced delayed neuropathy Leptophos (Phosvel™) • Dying back axonopathy • It is not due to inhibition of AChE (acetylcholinesterase) • Only compounds that can inhibit AChE cause it. – So it is presumably an esterase • May result from single exposure – Or from multiple smaller exposures • Irreversible • Rats and mice do not become paralyzed • Adult hens become paralyzed – Chicks do not. • Human children do become paralyzed • An estimated 100,000 people worldwide have been affected Leptophos: How Not to Identify a Neurotoxicant Case history on website deals more with the regulatory process than with toxicology. Chronic Effects of OPs: Reproductive Toxicity • Avian – Subset of OPs – Inhibition of AChE – Inhibition of kynurenine formamidase • Mammalian – No physical defects due to AChE inhibition – Human evidence for developmental CNS damage • Chlorpyrifos (Dursban) – Delayed neuropathy also causes erectile dysfunction Chronic Effects of OPs: Miscellaneous • Intermediate syndrome – Subset of insecticidal OPs – Onset delayed for several days – Not OPIDN – Recovery? • Long-term CNS effects – Epidemiological evidence – Documented by EEG after sarin exposure • Gulf War syndrome? Regulatory Aspects of OP Toxicity • What is the measure of toxicity – Symptoms – AChE inhibition – ChE inhibition Ecotoxicology • Chemical attributes – Persistence – Potential for bioaccumulation • Ecosystem effects – Secondary poisoning – Temporary changes in ecosystem – Permanent changes in ecosystem • Ecosystem simplification • Stressed ecosystems – Reproductive toxicology • Non-mammalian species – Evolutionary consequences of efforts at extermination Bioaccumulation and Persistence • OPs are – More water soluble than OCs – Less persistent • Days or months, not years – Malathion (outdoors) – Bioaccumulation is unlikely Secondary poisoning • May result from – Rapid lethality + residue • Fenthion used as avicide – LD50 » 5 mg/kg in birds » 250 mg/kg in rats – Weakened target • Cooper’s hawk in S America – Hard to detect • Small dead organisms disappear fast Temporary changes in ecosystem composition • Insecticides kill insects – Disrupts food supply for • • • • Insects Fish Mammals Birds • Agricultural applications occur during spring – primary breeding season • Single applications should be repairable Reproductive toxicity • Difficult to assay – Stage-specific – Species-specific • Historical Examples – Organochlorines • DDT thins birds’ eggshells • PCBs cause malformations • Dioxin-like chemicals cause GLEMEDS in trout – OPs • Malformations in birds – Sprayed on quail eggs – Site specific, not global • Local effects repairable if no other stresses occur Ecosystem Simplification • Elimination of already stressed species • Destruction of habitat – Herbicides – Large-scale agriculture – Monocultures – Lack of hedgerows Consequences of evolutionary pressures • Resistance – Degradation of chemical – Insensitivity to chemical – Blocking entry of chemical Other – Western corn rootworm • Dieldrin • Migration rate? – Crop rotation • Overwintering cycle • Egg laying behavior – Malaria control and mosquito behavior