Mon. Jan. 14
Stat 100
Jan. 14
To Do
• Chapter 7, Try problems 1-5,10-15
• Answers are at course web site
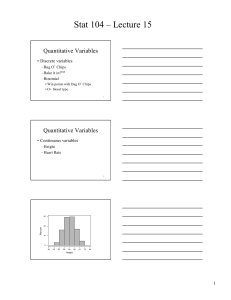
Histogram
• a type of bar chart that shows the distribution of a variable
• Vertical axis shows “how often”
• Horizontal axis shows values of the variable
Possible Shapes of
Numerical Data
• Skewed
• Symmetric
• Bell-Curve (most common type of symmetric)
CDs Owned
10
5
0
25
20
15
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500
CDS
Heights of Men in a Stat Class
20
10
0
60 70 height
80 90
Pennsylvania Cash 5 Picks for Five Years
Effect of Shape on Mean and Median
• For symmetric, mean and median about equal
• For skewed, mean and median will differ.
Thought Question
For 8 individuals, here are the times (seconds) it took to do a manual dexterity task.
9 , 16, 17, 18, 20, 22, 26, 32
How would you measure the variability among these eight numbers?
Possible measures of variation
• Range from low to high
• Range from lower to upper quartile (range of middle half)
• Standard deviation
Standard Deviation
• Measures variability
• Roughly, measures average difference between individuals and the mean.
• If all values are the same, Std. Dev. = 0
For time to complete task data in thought question
• St. Dev. = 6.9
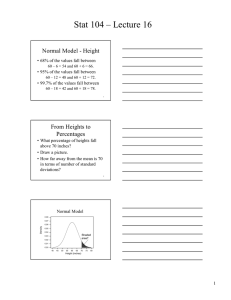
For Data with Bell-Curve Shape
• Nearly all (about 99.7%) of the data are within three standard deviations one way or the other from the mean.
Women’s Heights
• Mean = 65 inches, and SD =2.7 inches
• 3 standard deviations = 3×2.7 = about 8 inches
• Nearly all women’s height are within 8 inches of the mean.
• That is, most women are between 57 and 73 inches tall.