SJB Cells and Tissues Revised 4/28/2014 Page of 3 Name: Per
advertisement

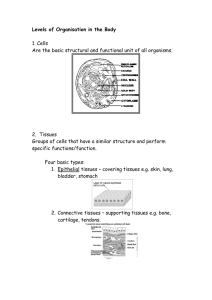
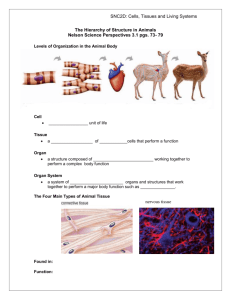
SJB Cells and Tissues Revised 3/17/2016 Page 1 of 3 Name: _______________________________________ Per. _____ Date: _________________ Learning Target: Investigating Cells and Tissues Activity I Can… Describe how specialized cells work together to form tissues that perform basic life functions for multicellular organisms. I Will… View a Discovery Education video segment on cells and tissues View various cell and tissue samples under the microscope Infer how cell structure influences the function of the tissue the cells form Work cooperatively to describe the functions of the four basic types of tissues in the human body. Learning Check √: Completion of Investigating Cells and Tissues Activity Packet In the Discovery Education video segment “Specialized Cells and Tissues” [4:26 min.], you saw examples of skin cells and tissues, muscle tissues, nervous tissue, and blood cells; in this activity you will view pictures of microscopic slides of these cells and tissues. There is no need to start with Slide 1 since all the specimens will eventually be viewed. Copies of the four slides have been placed at each table. Work through the slides until you have viewed all the specimens. Slide 1: Motor Neuron. Nervous tissue is one of the four basic types of tissue in the human body. What is the function of nervous tissue? ___________________________________________ How does the structure of the neuron relate to its function? ___________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ Where do you think nervous tissue is located in the body? Give at least three locations: ______________________ ______________________ Draw the motor neuron you viewed: ______________________ SJB Cells and Tissues Revised 3/17/2016 Page 2 of 3 Slide 2: Mammal Blood Smear. Blood cells working together are classified as a connective tissue. There are many different types of blood cells. There are some that can be categorized as red blood cells that carry oxygen and some as the white blood cells that protect the body. Red blood cells are small biconcave disks without a nucleus (they lose it as they mature and migrate out of the bone marrow). White blood cells are larger, come in different types and have a blue nucleus. Look at the picture of a microscopic human blood smear. Which type are there more of; red or white blood cells? ________________________________ Why do you think there are so many of one category of blood cell and much fewer of the other type? Hint: Think about the function. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Why do you think blood is considered a connective tissue? _____________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ Name at least three other examples of connective tissues in the body: (Refer to your text or notes) ___________________ _________________ _________________ Slide 3: Human Skin. Skin is an epithelial tissue that along with other accessory structures forms the largest organ in our body. The cells that make up skin are several layers deep. Why does skin need so many layers of cells? _____________________________________________________________________________ What is the function of epithelial tissues? ___________________________________________ There is an old saying “…only skin deep…” what do you think that saying means? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ SJB Cells and Tissues Revised 3/17/2016 Page 3 of 3 Slide 4: Cardiac and Striated Muscle. Be sure to view both types of muscle on the slide. What is the function of muscular tissue? ____________________________________________ Where is cardiac muscle found in the body? _________________________________________ Striated muscle is sometimes called “skeletal” muscle. Where is skeletal muscle found in the body? ______________________________________________________________________________ Do you notice any structural differences between cardiac and striated/skeletal muscle? Identify the differences and explain their significance in terms of relating structure to function. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Conclusion question: All the cells making up the tissues that you viewed today all started from a single zygote cell, then a small mass of identical cells, and then a blastocyst. How did these cells change so much? Explain the processes that took place. (Hint: I am determined you will answer this correctly, even if your answer is a little different than others.) ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ EXTRA CREDIT: Look at the Slide 5 the picture taken from tissue of the stomach. Explain (fully) why the stomach is classified as an organ: ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________