Modeling Mendel*s Law
advertisement

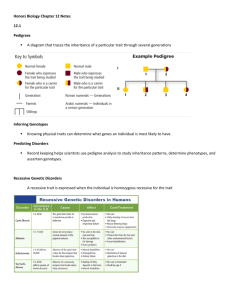
Mendelian Heredity CH12 pg 267 Sexual Reproduction • Combining of a sperm cell and an egg cell from two individuals • The offspring of this "cross" will have characteristics from both "parents“ – hybrid Self – Pollination Contrasting traits, easy to grow and reproduce Heterozygous 3:1 Ratio Characters vs Traits Mendel’s Laws of Heredity • Law of Dominance - One factor (trait) in a pair may mask the effect of the other. Mendel’s Laws of Heredity • Law of Segregation - The two traits for a characteristic separate during the formation of eggs and sperm. Mendel’s Laws of Heredity • Law of Independent Assortment - The traits for different characteristics are distributed to reproductive cells independently. pg272 Using Punnett Squares • Punnett Square – Model that predicts the likely outcomes of a genetic cross with the alleles taken from the parents – Shows all the genotypes that could result from a given cross How to for Punnett Square • Capital letter – Dominant trait – Letter represents trait (B for brown) – Dominant always written first in sequence (Bb) • Lower case letter – recessive trait – same letter as dominant trait (b for blond) Monohybrid Cross • Contrasting traits (purple vs white flower) • Homozygous Cross (PP or pp) • Heterozygous Cross (Pp) – Paternal alleles across the top – Maternal alleles down the left side Monohybrid Cross • Phenotype • Genotype Using Probability • Likelihood that a specific event will occur • Probability = # of one kind of possible outcomes total # of all possible outcomes • Probability of a specific allele in a gamete • Represented as a fraction or ratio Probability in a Heterozygous Cross • Flipping a coin/ possible alleles • Both parents have Pp, How do you know? P P p p Using a Pedigree • Several generations • Determine genetic disorders or diseases that can be inherited • Pedigrees can help answers questions about the three factors of inheritance – Sex-linked Genes – Dominant or Recessive – Heterozygous or Homozygous Many Genes, Many Alleles • Polygenic Inheritance – Several genes affect characteristic – Relative greenness or brownness, blue eyes are recessive Many Genes, Many Alleles • Incomplete Dominance – Intermediate between traits – Snapdragon (red and white = pink) Many Genes, Many Alleles • Multiple Alleles – 3 or more possible alleles, only to alleles for a gene can be present – Complex dominance – Blood types and Labrador coat color ABO blood groups Many Genes, Many Alleles • Codominance – Both Alleles for the same gene are fully expressed Genes affected by the Environment • Nutrients and temperature • Personality and behavior Genes Linked Within Chromosome • Genes that are close together are less likely to be separated than genes that are far apart