In this journal I will talk about antidepressants drug
advertisement
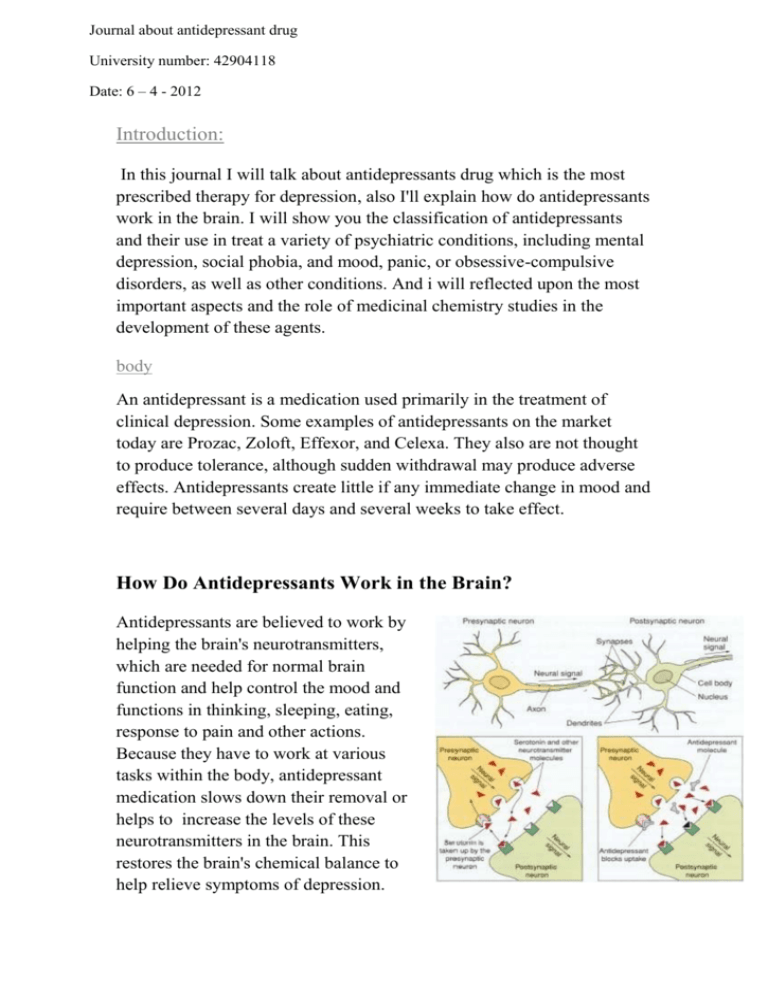
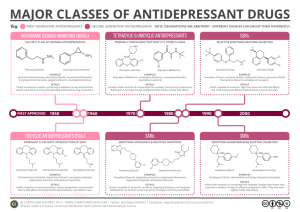
Journal about antidepressant drug University number: 42904118 Date: 6 – 4 - 2012 Introduction: In this journal I will talk about antidepressants drug which is the most prescribed therapy for depression, also I'll explain how do antidepressants work in the brain. I will show you the classification of antidepressants and their use in treat a variety of psychiatric conditions, including mental depression, social phobia, and mood, panic, or obsessive-compulsive disorders, as well as other conditions. And i will reflected upon the most important aspects and the role of medicinal chemistry studies in the development of these agents. body An antidepressant is a medication used primarily in the treatment of clinical depression. Some examples of antidepressants on the market today are Prozac, Zoloft, Effexor, and Celexa. They also are not thought to produce tolerance, although sudden withdrawal may produce adverse effects. Antidepressants create little if any immediate change in mood and require between several days and several weeks to take effect. How Do Antidepressants Work in the Brain? Antidepressants are believed to work by helping the brain's neurotransmitters, which are needed for normal brain function and help control the mood and functions in thinking, sleeping, eating, response to pain and other actions. Because they have to work at various tasks within the body, antidepressant medication slows down their removal or helps to increase the levels of these neurotransmitters in the brain. This restores the brain's chemical balance to help relieve symptoms of depression. Chemicals in the brain can return normal function to people suffering from extreme sadness, hopelessness and lack of interest in life, ill effects experienced by people with depression. The work of antidepressants has also been successful in the treatment of people with eating disorders, chronic pain and other disorders that often carry depression with them. classification of antidepressants Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors: Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are one of the oldest classes of antidepressants and are typically used when other antidepressants have not been effective. MAOIs prevent monoamine oxidase from breaking down the monoamines. This results in an increased amount of active monoamines in the brain. They are used less frequently because they often interact with certain foods and require strict dietary restrictions. MAOIs can also result in severe adverse reactions if taken with many other medicines, including some over-the-counter cough and cold remedies. MAOIs are mostly used for atypical depression. A newer type of MAOI called moclobemide is slightly different to the older MAOIs. It is considered to be a safer choice than the older MAOIs, as it requires fewer dietary restrictions and has fewer significant interactions with other medicines. Moclobemide is considered a secondline treatment for major depression. Tricyclic Antidepressants : The tricyclic antidepressants are the most effective drugs presently available for the treatment of depression. These act by block the absorption (reuptake) of the neurotransmitters serotonin and norepinephrine, making more of these chemicals available in the brain. This seems to help brain cells send and receive messages. These antidepressants also affect other chemical messengers, which can lead to a number of side effects. SAR •Antidepressants are characterized by lack of co-planarity in the tricyclic ring. • Various side chains are noted in the entire class of antidepressants that represent substituted ethyl and propyl amines. • the N-monomethyl derivatives are more potent and have a more rapid onset of activity than the corresponding N-disubstituted compounds. So we can increase the efficacy of some compound by convert Ndisubstituted to N-monomethyl derivatives. • Marked activity is observed for secondary methylamino derivative, while ethyl and propyl derivatives are less potent. • Tertiary amine antidepressants like imipramine are more effective inhibitors of serotonin uptake, useful in-patients with psychomotor agitation. Secondary amines like protriptyline are more effective inhibitors for nor-epinephrine uptake, useful in retarded depression, owing to a lower sedation and hypotension. So we can convert a compound from selective nor-epinephrine reuptake inhibitor to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and vice versa . Products : Aryl and aryloxyalkyl amine: Fluoxetine ( Prozac), paroxetine ( seroxat) , Sertraline ( Zoloft) Fluoxetine: Fluoxetine is in a class of medications called selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). It works by increasing the amount of serotonin, a natural substance in the brain that helps maintain mental balance. it is used to treat depression, obsessive-compulsive disorder , some eating disorders, and panic attacks. Also it used to relieve the symptoms of premenstrual dysphoric disorder, including mood swings, irritability, bloating, and breast tenderness. Selective norepinephrine uptake inhibitors: It is a type of drug that acts as a reuptake inhibitor for the neurotransmitters norepinephrine (noradrenaline) and epinephrine (adrenaline) by blocking the action of the norepinephrine transporter (NET). This in turn leads to increased extracellular concentrations of norepinephrine and epinephrine and therefore an increase in adrenergic neurotransmission. Nisoxetine Reboxetine Bupropion Selective serotonin uptake inhibitor and 5HT2A antagonist: trazodone hydrochloride. Trazodone also has anxiolytic and hypnotic effects. Trazodone has considerably less prominent anticholinergic (dry mouth, constipation, tachycardia) and sexual side effects than most of the tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) 5HT1A agonist and partial agonist: Buspirone Alpha 2 Antagonists: Mirtazapine Conclusion: Antidepressant drugs potentiate ether directly or indirectly the action of norepinephrine and / or serotonin in the brain. This, along with other evidence, led to biogenic amine theory, which proposes that depression is due to a deficiency of monoamines, such as norepinephrine and serotonin at certain key sites in the brain. After study SAR of antidepressant drugs we succeeded to increase the selectivity and reduce side effect in some compounds by modulation their structure for example: tertiary amine antidepressants more selective to serotonin uptake, while Secondary amines are more effective inhibitors for nor-epinephrine uptake and more useful due to less sedating and hypotensive effects.