HRS Block 1 Cell Struc_Func_GoogleDoc
advertisement

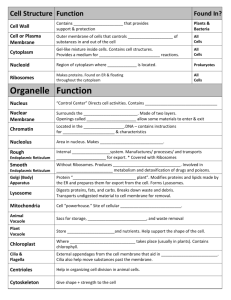
Cell Organelles Structure and Function Example: Mr. Boandl • Structure o o Made of bone wrapped in tons of muscle Tall, 6 feet 1 inch • Function o TO GIVE JACOB DOLIN THE MOTORCYCLE!!!!! Picture of Chuck Norris • Location -Whitehall High, D104 Chuck Norris on his 15th birthday. Chuck Norris last year. Cell Membrane • Structure: -double layer of phospholipids -includes wide variety of proteins • Function: -isolates cell's contents from the external environment -regulates flow into and out of cell -allows interaction with other cells Picture of Cell Membrane • Location: -outside cell (encloses cell) & inside cell wall -plants and animals Cell Wall • Structure: • the cell wall is made of cellulose and cellulose like material. • cellulose is an insoluable carbohydrate compsed of glucose subunits. • Function:protects the cell from it's enviroment and keeps certain substances out. • supports the cell and keeps it up so the plant will stand up straight. Picture of Cell Wall • Location:around the outside of a cell. • only in plants (and picture) Cytoplasm • Structure: o includes water, salts, and an assortment of organic molecules o also contains organelles • Function: o keeps organelles in place Picture of Cytoplasm • Location: o everywhere but the nucleus o plants and animals Nucleus • Structure: nucleolus: synthesize ribosomes nuclear pore: allow selective exchange of materials help control the flow of information chromatin: consist of uncondense DNA, granular material nuclear envelope: seperate nuclear material from the cytoplasm • Function: - membrane bound container for chromosomes -contain the cell genetic material (DNA) - regulate/ control the flow of protein and RNA Picture of nucleus • Location: Nucleolus • Structure: a) consists of ribosomal RNA & has ribosomes in synthesis. b) proteins & DNA • Function: a) makes & synthesizes ribosomes b) any ribosome can be used to synthesize thousands of proteins made by a cell Hi drew!! Picture of Nucleolus • Location: dark stain in middle of nucleus Ribosome • Structure: • composed of proteins and RNA • can be single or strung along messanger RNA (very small) • Function: • provides the site of protein synthesis • assembles the proteins that are essential for the cell Fun Fact!! Ribosomes do not have membranes. Picture of Ribosomes • Location: • made in the nucleolus and is in the cytoplasm or on the ER • in both plant and animal cells Microtubules and Microfilaments • Structure: • Function: Picture of Microtubules and Microfilaments • Location: (and picture) Smooth Endoplasmic reticulum • Structure: 1. Part of the Endoplasmic Reticulum 2. Outer part of the ER 3. Contains no ribosomes • Function: 1. In your liver, it contains enzymes that detoxify harmful drugs in metabolic byproducts. 2. In some cells it synthesizes other types of lipids such as the steroid hormones testosterone and estrogen. Picture of Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum 1.Location: outside the ER which is on the outside of the nucleus. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum • Structure: a. has ribosomes on the outside b. Series of inter-conneted channels in the cytoplasm • Function: a. the ribosomes synthesize proteins, including membrane proteins. b. Synthesizes itself and lipids. Picture of Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum • Location: a. found in the cytoplasm b. outside the nuclear envelope Golgi Apparatus • Structure: o Specialized set of membraneous sacs o Looks like a set of hollow pancakes • Function: o Seperates protiens and lipids recieved from the ER according to their destinations o Modifies some molecules o Packages these materials int vesicles that are then transported to other parts of the cell or to the plasma membrane for export. Picture of Golgi Apparatus • Location: o Floats around in the cytoplasm o It is in both animal and plant cells Lysosome • Structure: • Function Picture of Lysosome • Location: (and picture) Mitochondria • Structure: o o o 1-5 micrometers in diameter(round, oval, or tubular). Surrounded by a double membrane Have their own DNA • Function o o Convert the energy of sugar into ATP for use by the cell Break down of sugar is initiated without the use of oxygen but by enzymes in the fluid portion of the cytoplasm Picture of Mitochondria • Location: o All eukaryotic cell, including plants o Within the cytoplasm fun fact:Mitochondrial energy production is necessary for strength, stamina, and thought Chloroplast • Structure: 1-5 micrometers in length surrounded by a double membrane • Function Sites of photosynthesis in plants and photosynthetic protists Transfers sunlight into glucose Picture of Chloroplast • Location: In the cytoplasm, within the cell membrane and the cell wall Found only in plant cells Vacuole • : Fluid filled sacs. Surrounded by a single membrane Some food vacuoles formed during phagosytosis are only temporary, while many cells contain permanant ones • Function o Regulation balenfce of cells water content o a dump site for hazerdous waste o Stores sugars/ amino acid not immediatly needed by the cell o help cell maintain structure by turgor pressure o o o Picture of Vacuole • Location: o Found at the ends/tips of cells.