File - Se civil engineering
advertisement

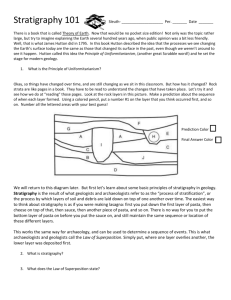
Stratigraphy The study of the origin, relationship and extent of rock layers (Strata). Lithostratigraphy Each layer is a different rock type. Chronostratigraphy Each layer is a different age. Biostratigraphy Each layer contains a different fossil assemblage. Lithostratigraphic Units Member A Formation A Member B Member C Group A Member D Formation B Member E Member F Formation C Member G Member H Member I Member J Supergroup Formation D Member K Member L Member M Member N Group B Formation E Member O Member P Member Q Member R Formation F Member S Member T Supergroup | Group | Formation | Member | Bed Principles (Laws) of Stratigraphy Principle of… • Original Horizontality • Superposition • Lateral Continuity • Cross Cutting Relationships • Inclusions • Faunal Succession Walther’s Law Nicholas Steno Danish physician Principles of Stratigraphy 1. Original Horizontality sediments are deposited at the earth’s surface in flat layers 1. Principle of Original Horizontality Principles of Stratigraphy 2. Superposition The oldest rocks are found on the bottom and the youngest rocks on the top. youngest oldest 2. Principle of Superposition Youngest Strata Oldest Strata Principles of Stratigraphy Principles of Stratigraphy 3. Lateral Continuity A bed will extend laterally until: 1. Pinches out. 2. Abuts against older rock. 3. Truncated by erosion. 4. Cut by fault. 3. Principle of Lateral Continuity Lateral Continuity Principles of Stratigraphy 4. Cross-Cutting Relationships Rock that are cut by another geologic feature are older than the feature that cuts them. Igneous Intrusion Fault Erosion Charles Lyell 4. Principle of Cross Cutting Relationships Principles of Stratigraphy 5. Rule of Inclusions If pieces of rock A are included in rock B, rock A formed before rock B. B A 5. Principle of Inclusions Principles of Stratigraphy 6. Faunal Succession Systematic sequence of fossils with time. Extinct fossils do not reappear in younger rocks. http://www.geo.utexas.edu/courses/401/