Microscope Notes
advertisement

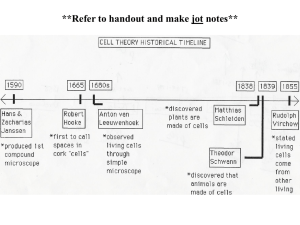
Microscope and Cell Theory Notes I. MICROSCOPE A. Field of View: Lighted area when looking through the eyepiece 1. Low power (40x) (total magnification is 40x = objective magnification x eyepiece magnification) 4 mm = 4000 Mm 2. Medium power (100x) 2 mm – 2000 Mm *As magnification increases, our field of view decreases. *Mm (micrometer) 1000 Mm = 1 mm B. Resolution: ability to distinguish 2 objects as separate = clarity * fine adjustment is responsible for resolution C. “Depth of View” – ability to focus 1 plane (or dimension) at a time Blurry Top thread very clear CELLS Cells are the structural, functional, reproductive units of life II. History: A. In 1600s, Anton van Leeuwenhoek, a Dutch lens grinder, built a microscope and was the 1st to observe tiny living organisms. B. In 1665, Robert Hooke, looked at cork under the microscope and reported the existence of cells. (Hooke coined the term “cells” because the tiny dark pores reminded him of the cells where monks slept in their dorms) C. In 1838 & 1839, botanist Matthias Schleiden, and zoologist Theodore Schwann originated the Cell Theory: 1. All organisms are made up of 1 or more cells, and 2. Cells are the fundamental units of lifethe smallest things that can be called “living” Pioneers of Cell Biology “I made a microscope. Check it out. Stuff looks wicked close-up.” Anton Van Leeuwenhoek 1632-1723 “Totally. This one time? I sliced up a piece of cork? Looked like it was made of a bunch of little empty rooms. Like cells monks live in. We should totally call them that. Cells.” “Plants are made of cells” “We“We cancan put put all these all these other other guys’ guys’ research research intointo oneone theory.” theory.” “Animals are made of cells” “Cells only come from other cells. They can’t come from nonliving stuff. Ever.” Rudolf Virchow Schleiden The Cell Theory Schwann 1. All living things are composed of cells 2. Cells are basic unit of structure and function in living things 3. All cells come from other cells. D. In 1855, Rudolf Virchow added a 3rd statement: 3. Cells arise only by division of other cells (Virchow discovered that cells divide forming new cells) III. Why do organisms need cells? A. Cells are miniature life-support chambers that maintain a special environment. B. Homeostasis – maintenance of conditions within specified limits. C. Many organisms are unicellular (consisting of only 1 cell) --However cell size is limited. D. Because of size constraints, large organisms such as animals and plants are multi-cellular. * Each cell of a multi-cellular organism make a specialized contribution to the body as a whole = division of labor. IV. Types of Cells A. Prokaryotic (pro = before; karyon = nucleus) 1. No nucleus 2. Are bacterial cells (Monera) 3. Believed to have evolved earlier than eukaryotic cells 4. Have a rigid cell wall B. Eukaryotic (eu = good, true) 1. Contains a nucleus! 2. Make up the bodies of all organisms other than bacteria: (include Algae, Fungi, Protists, Plants, & Animals!) V. Cell Parts A. Cell Membrane (ALL CELLS have one) 1. Phospholipids—main structural molecule of cell membrane a. Phosphate head • Polar (+ end, - end) • Hydrophilic (“water-loving”) b. Two Fatty acid tails • nonpolar • Hydrophobic (”water-fearing”) 2. In H2O, phospholipids form a LIPID BILAYER B. Fluid Mosaic Model (of cell membrane) 1. The idea that cell membrane is a fluid, shifting bilayer containing (besides phospholipids) a. b. Cholesterol—keeps membrane fluid Proteins with diff. jobs--examples Move things across membrane carry “markers” to ID cell Fluid Mosaic link