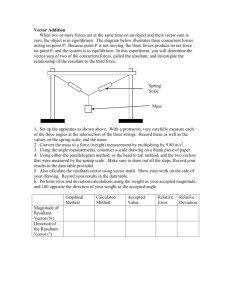
living with the lab
advertisement

living with the lab Introduction to Statics Statics is the branch of mechanics concerned with the analysis of loads (forces, torque/moment) on physical systems in static equilibrium . . . when in static equilibrium, a system is either at rest, or its center of mass moves at constant velocity. Wikipedia.org old railroad bridge (Leonard G. / Wikipedia) ENGR 122 living with the lab Units of Measure Most units of measure can be broken down into the basic units of length (L), mass (M) and time (t). physical quantity dimension SI system U.S. Customary system length area volume 2 living with the lab Units of Measure physical quantity L = length dimension M = mass SI system U.S. Customary system t=time 3 living with the lab Three Characteristics of a Force denotes a vector y 1. Magnitude (F) • • how hard you are pushing or pulling graphically represented by the length of the arrow 2. Direction (q) • q usually defined by an angle measured relative to a coordinate system 3. Point of Application x 4 living with the lab Components of a Force Forces can be split into components that align with a coordinate system. The force is the vector sum of the components. y q x defined relative to the +x axis in this case 5 living with the lab Resultants How can we find the net effect of two or more forces that act on a body? Generally . . . Geometric Solution: If all applied forces are arranged head to tail, a vector drawn from the tail of the first vector to the head of the last vector represents the resultant of all the forces. 6 living with the lab Class Problem: Two ants are hitched to a beetle and pull with the forces shown: a. b. c. d. e. f. Find the x and y components of the force exerted by ant 1. Find the x and y components of the force exerted by ant 2. Find the x component of the resultant force of the ants. Find the y component of the resultant force of the ants. Find the resultant force of the ants. What angle does the resultant force make with the x-axis? 7