Mutations - RMC Science Home
advertisement
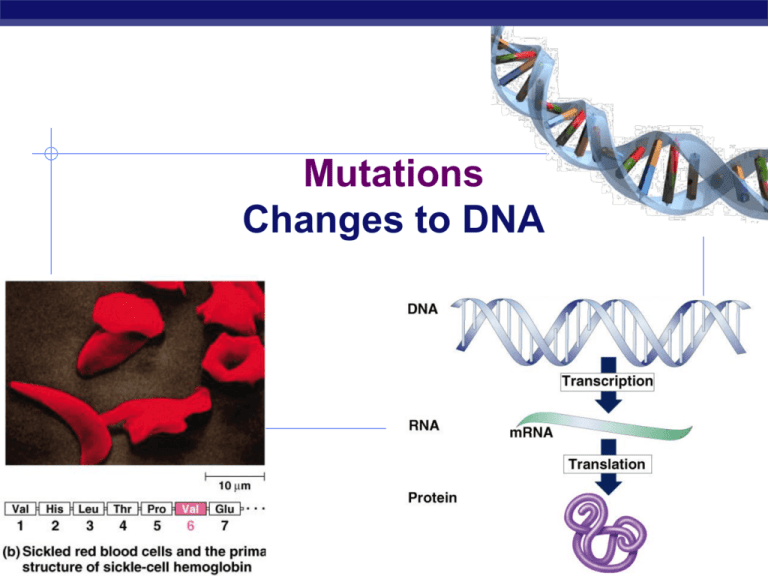
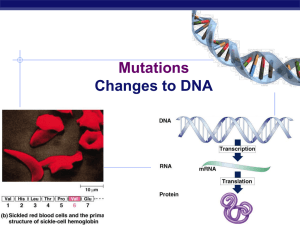
Mutations Changes to DNA Regents Biology 2009-2010 Mutations permanent change in a cell’s DNA sequence Includes changes in nucleotide sequence, alteration of gene position, gene loss, duplication, or insertion of foreign sequences Can be inherited if mutation is in gamete Most mutations have a negative effect Positive mutation? evolution Regents Biology Mutagen Any agent that causes changes in DNA Includes physical agents that damage DNA X-rays UV rays Cigarette tar Gamma rays carcinogens Regents Biology Mutant An organism carrying a gene that has mutated Regents Biology Mutations Changes to DNA are called mutations change the DNA changes the mRNA may change protein may change trait DNA mRNA protein trait Regents Biology TACGCACATTTACGTACG AUGCGUGUAAAUGCAUG aa aa aa aa aa aa aa Classes of Mutations 1. Gene level 2. Mutations include different point & frame-shift mutations Chromosome level Rearrangement of genes within or between chromosomes Regents Biology Gene Level Mutations Changes to the letters (A,C,T,G bases) in the DNA point mutation change to ONE letter (base) in the DNA may cause change to protein, may not frameshift mutation Regents Biology addition of a new letter (base) in the DNA sequence deletion of a letter (base) in the DNA both of these shift the DNA so it changes how the codons are read big changes to protein! Point Mutations One base change can change the meaning of the whole protein THEFATCATANDTHEREDRATRAN THEFATCARANDTHEREDRATRAN OR THEFATCATENDTHEREDRATRAN Regents Biology Does this change the sentence? A LITTLE! Point Mutations Missense mutation = changes amino acid AUGCGUGUAUACGCAUGCGAGUGA MetArgValTyrAlaCysGluStop AUGCGUGUAUACGUAUGCGAGUGA MetArgValTyrValCysGluStop Regents Biology Does this change the protein? DEPENDS… Sickle cell anemia Hemoglobin protein in red blood cells strikes 1 out of 400 African Americans limits activity, painful & may die young Normal round cells Misshapen sickle cells Only 1 out of 146 amino acids Regents Biology Point Mutations Silent mutation = no change to protein AUGCGUGUAUACGCAUGCGAGUGA MetArgValTyrAlaCysGluStop AUGCGUGUAUACGCUUGCGAGUGA MetArgValTyrAlaCysGluStop Regents Biology Does The this codechange has repeats the protein? in it! Why not? Point Mutations Nonsense mutation = change to STOP AUGCGUGUAUACGCAUGCGAGUGA MetArgValTyrAlaCysGluStop Really destroyed that protein! AUGCGUGUAUAAGCAUGCGAGUGA MetArgValStop Regents Biology Frameshift Mutations Add or delete one or more bases changes the meaning of the whole protein THEFATCATANDTHEREDRATRAN Does this change the sentence? A LOT! Delete Add one! one! THEFATCANTANDTHEREDRATRAN OR THEFATCAANDTHEREDRATRAN Regents Biology Frameshift Mutations Addition = add one or more bases AUGCGUGUAUACGCAUGCGAGUGA MetArgValTyrAlaCysGluStop AUGCGUGUAUACGUCAUGCGAGUGA MetArgValTyrValMetArgValA Regents Biology Does this change the protein? A LOT! Frameshift Mutations Deletion = lose one or more bases AUGCGUGUAUACGCAUGCGAGUGA MetArgValTyrAlaCysGluStop AUGCGUGUAUACGAUGCGAGUGA MetArgValTyrAspAlaSerGA Regents Biology Does this change the protein? A LOT! Cystic fibrosis Broken salt channel in cells strikes 1 in 2500 white births gene codes for a protein channel that allows salt to flow across cell membrane broken protein doesn’t work as channel doesn’t allow salt out of cell, so water doesn’t flow out either thicker & stickier mucus coating around cells mucus build-ups in lungs & causes bacterial infections destroys lung function without treatment children die before 5; Regents Biology with treatment can live past their late 20s Salt channel Effect on Lungs normal lungs airway salt channel salt normal mucus H 2O cells lining lungs cystic fibrosis salt H 2O transports salt through protein channel out of cell Osmosis problems! thick mucus mucus & bacteria build up = lung infections & damage Regents Biology Deletion leads to Cystic fibrosis deletion Loss of one amino acid! Regents Biology Chromosome Level Mutations Mutation involving a large segment of DNA 1. 2. 3. Translocation Inversion Deletions Regents Biology Chromosome Level Mutations Translocation 1. Relocation of groups of base pairs from 1 chromosomes to another (usually occurs between homologous chromosomes) New proteins can result Eg. Some types of leukemia Transposable element – fragments of DNA that continue to move from 1 chromosomes to another (can disrupt Regents Biology transcription Chromosome Level Mutations Translocation Inversion 1. 2. 3. A sequence of DNA is inverted (reversed) ABC → CBA Can disrupt base pairing Deletions Regents Biology Chromosome Level Mutations Translocation Inversion Deletions 1. 2. 3. Involve loss of chromosomal material Eg. Cancer – results of mutation in genetic sequence Regents Biology Not to ask questions is a mutation! Regents Biology