Energy and Chemical Rnx - Liberty Union High School District
advertisement

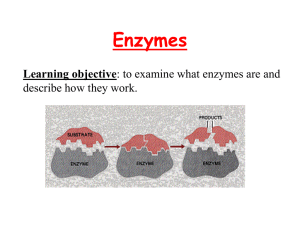
Energy and Chemical Rnx • All Chemical reactions either produce or take energy: Are exothermic or endothermic • In the body, ALL chemical reactions are collectively called your METABOLISM • There are 2 kinds of metabolic reactions • Anabolic or Catabolic • (Anabolism) (Catabolism) Anabolism or Anabolic reactions • **Energy storing, synthesis, (build up) RNX ie: Production of protein, fat, **Takes Energy to build up!!!! **Requires Energy input = ENDERGONIC/Endothermic Catabolism or Catabolic reactions **Energy releasing, decomposition, (break down RNX ie: protein to aa, starches to simple sugars. ** Gives off energy when breaking down molecules!!!! ** Produces Energy = EXERGONIC/Exothermic One Reaction feeds the other!!! Cyclic! Protiens RUN OUR LIFE • Proteins are a very diverse macromolecule and perform many functions within our body!! • 1. Provide Structure • EX: Keratin and Collagen • 2. Carry our Communication • • Ex: hormones, cell to cell signals, receptors, & reversibly binding proteins called, Ligands • 3. Membrane Transport • • EX: protein channels in PM, carriers that bind solutes, trigger nerve and muscle activity • 4. Catalysis ENZYMES • 5. Recognition and Protection • • EX: Glycoproteins in immune function, Antibodies, Clotting proteins Enzymes and Metabolism • • • • Enzymes are proteins that work as catalysts Substrate is what is acted upon by the enzyme Catalists facilitate molecular interactions!! (They help biochemical reactions to occur more rapidly under normal body temperatures) • Enzymes lower activation energy to push reactions involving substrates to go faster (with more energy, more completely) • Enzymes can help build substrates together or help break substrates apart. • Enzymes do not get consumed in the Reaction!! They are available for re-use !! They PUSH molecules together They PULL molecules apart • Sometimes enzymes have “helpers” called: • Cofactors (iron, copper, zinc, mg, ca) these cofactors stimulate proper folding • Coenzymes (NAD+)….electron acceptors that carry electrons from various metabolic pathways to others. Book • Supplement these notes with your own from the book on : • pages 69, Metabolism • Pages 77-80 Proteins • Pages 80-82 Enzymes