Kinds and Locations of Volcanic Activity Shield Volcanoes: Hawaii
advertisement

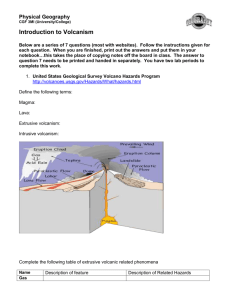
Volcanoes Overview • • • • • Magma Sources and Types Kinds and Locations of Volcanic Activity Hazards Related to Volcanoes Issues in Predicting Volcanic Eruptions Present and Future Volcanic Hazards in the United States Magma Source • Areas Where Magma Forms (need heat!) – – – – – – – Upper mantle: asthenosphere depths of ~ 50 to 250 km High temps (800-1100 C), medium pressure Rocks melt, or partially melt Divergent plate boundaries Above subduction zones Hot spots Plate tectonics: Asthenosphere is where melting occurs Source: http://www.geol.umd.edu/~jmerck/gal04/GEOL388/lectures/02.html Wahalua Visitors’ Center Aflame in Hawaii Source: Photograph by J.D. Griggs, USGS Photo Library, Denver, CO. Ruins of the Visitors’ Center After Lava Cooled Source: Photograph by J.D. Griggs, USGS Photo Library, Denver, CO. Magma Types • Composition: – Magmas: >Fe, Mg (mafic) vs >SiO2 (felsic) • Dependent on tectonic setting (1) Ocean spreading ridges and hot spots: Mafic rocks (basalt) (2) Continental rifts: felsic (rhyolite, andesite) (3) Subduction zones: mafic + felsic Mafic: Basalt Ultramafic: Peridotite Source: http://www.tmm.utexas.edu/npl/mineralogy/Blowups/Olivine_in_peridotite_xenolith.htm Felsic-mafic: andesite Source: http://www.otago.ac.nz/geology/features/rocks-minerals/rocks.html Felsic: Rhyolite Source: http://resourcescommittee.house.gov/subcommittees/emr/usgsweb/photogallery/ Magma properties • Volcanic Gases: CO2, SO2 • Pressure builds up as magmas rises to surface – Felsic (more SiO2): viscous + thick = explosive – Mafic (less SiO2): fluid, gases escape *What kind of volcano is safest to live by? Lava Flows on Kilauea in Hawaii Source: Photograph courtesy of USGS Photo Library, Denver, CO. Hawaiian Lavas: mafic basalts Source: Courtesy of Carla W. Montgomery. Volcanic Breccia (felsic) Source: Courtesy of Carla W. Montgomery. Kinds and Locations of Volcanic Activity • Individual Volcanoes–Locations • Seafloor Spreading Ridges, Fissure Eruptions • Shield Volcanoes • Volcanic Domes • Cinder Cones • Composite Volcanoes Volcanoes of the World Source:After R. Decker and B. Decker, Volcanoes, 1981, W.H. Freeman and Company, New York, NY. “Hot Spots” Around the World Source: Modified after map in online text This Dynamic Earth, U.S. Geological Survey. Kinds and Locations of Volcanic Activity • Shield Volcanoes: Hawaii – Mafic lavas, low, flat, ‘shields’ • Volcanic Domes • Cinder Cones • Composite Volcanoes Low-Angle View of Mauna Loa Source: Photograph courtesy of USGS Photo Library, Denver, CO. Satellite View of Hawaii Source: Photograph courtesy of USGS Photo Library, Denver, CO. Kinds and Locations of Volcanic Activity • Shield Volcanoes: Hawaii – Mafic lavas, low, flat, ‘shields’ • Volcanic Domes: Mt. St. Helens – Rhyolite, andesitic lavas. – Thick, viscous lavas (domes) • Cinder Cones • Composite Volcanoes Dome Formation, Mount St. Helens Source: Photograph courtesy of USGS Photo Library, Denver, CO. Kinds and Locations of Volcanic Activity • Shield Volcanoes: Hawaii • Volcanic Domes: Mt. St. Helens – Rhyolite, andesitic lavas. – Thick, viscous lavas (domes) • Cinder Cones: common – Release of gas pressure (pop bottle) – Produces pyroclastics • Composite Volcanoes Paricutín Volcano Erupting Source: Photograph courtesy of USGS Photo Library, Denver, CO. Paricutín Showing Form of Cinder Cones Source: Photograph by K. Segerstrom, courtesy of USGS Photo Library, Denver, CO. Kinds and Locations of Volcanic Activity • Shield Volcanoes: Hawaii • Volcanic Domes: inside Mt. St. Helens • Cinder Cones: common – Release of gas pressure (pop bottle) – Produces pyroclastics • Composite Volcanoes (stratovolcanoes) • Calderas Source: http://www.enchantedlearning.com/subjects/volcano/gifs/volcanodiagram.GIF Composite Volcano in the Aleutian Islands Source: Photograph by R.E. Wilcox, USGS Photo Library, Denver, CO. Hazards Related to Volcanoes • • • • • • • Lava Pyroclastics (rocks and lava) Lahars (mudflow of ash and water) Pyroclastic Flows–Nuées Ardentes Toxic Gases Steam Explosions Secondary Effects: Climate and Atmospheric Chemistry Formation of “Lava Trees” Near Kilauea Source: Photograph by J.D. Griggs, USGS Photo Library, Denver, CO. Map Showing Lava Filling Harbor in Iceland Source: Data from R. Decker and B. Decker, Volcanoes, Copyright © 1981 by W.H. Freeman and Company. Lava-Flow Control Efforts on Heimaey Harbor Source: Photograph courtesy of USGS Photo Library, Denver, CO. Pyroclastics Ejected During Eruptions Source: Data from U.S. Geological Survey. Hazards Related to Volcanoes • • • • • • • Lava Pyroclastics (rocks and lava) Lahars (mudflow of ash and water) Pyroclastic Flows–Nuées Ardentes Toxic Gases Steam Explosions Secondary Effects: Climate and Atmospheric Chemistry AftermathMt. St. Helens Eruption, 1980 Source: Photograph by M.M. Brugman, USGS Photo Library, Denver, CO. Ash and Rains Cause Structure Collapse Source: Photograph by R.P. Hoblitt, courtesy U.S. Geological Survey. Mudflow and Flood Damage from Mt. St. Helens Source: Photograph by C.D. Miller, USGS Photo Library, Denver, CO. Abacan River Mudflows, Philippines Source: Photograph by T.J. Casadervall, U.S. Geological Survey. Hazards Related to Volcanoes • • • • Lava Pyroclastics (rocks and lava) Lahars (mudflow of ash and water) Pyroclastic Flows–Nuées Ardentes – ‘Glowing cloud’ • Toxic Gases • Steam Explosions • Secondary Effects: Climate and Atmospheric Chemistry Pyroclastic Flow from Mount St. Helens Source: Photograph by P.W. Lipman, USGS Photo Library, Denver, CO. Nuée Ardente from Mont Pelée, 1902: *25,000 – 40,000 people died Source: Photograph by Underwood and Underwood, courtesy Library of Congress. Hazards Related to Volcanoes • • • • • • • Lava Pyroclastics (rocks and lava) Lahars (mudflow of ash and water) Pyroclastic Flows–Nuées Ardentes Toxic Gases Steam Explosions Secondary Effects: Climate and Atmospheric Chemistry Toxic gases: CO2? Cameroon, 1986 Source: http://wps.prenhall.com/wps/media/objects/476/488316/ch13.html Carbon Dioxide Cloud Over Lake Nyos, Cameroon Source: Photograph by M.L. Tuttle, USGS Photo Library, Denver, CO. Animal Carcasses From Deadly Cloud: 1700 people died Source: Photograph by M.L. Tuttle, USGS Photo Library, Denver, CO. Hazards Related to Volcanoes • • • • • • • Lava Pyroclastics (rocks and lava) Lahars (mudflow of ash and water) Pyroclastic Flows–Nuées Ardentes Toxic Gases Steam Explosions Secondary Effects: Climate and Atmospheric Chemistry Mt. Pinatubo Eruption, 1991 Source: Photograph by K. Jackson, U.S. Air Force. Source: http://eos.higp.hawaii.edu// Source: http://volcanoes.usgs.gov/Imgs/Jpg/Pinatubo/16112441-008_large.jpg The atmosphere: different levels Source: http://pubs.usgs.gov/publications/text/tectonics.html#anchor10693467 Stratospheric Aerosol, 1991: April 15 - May 25 Source: http://eos.higp.hawaii.edu// Stratospheric Aerosol, 1991: June 14 – July 26 Source: http://eos.higp.hawaii.edu// Stratospheric Aerosol, 1993: Feb. 13 – March 26 Source: http://eos.higp.hawaii.edu//