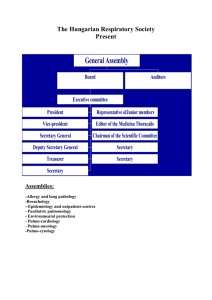
Offices in the Executive Branch
advertisement

Includes the White House Office Serves the President Must be approved by the Senate Any advice given to the President will usually be on issues related to their departments President will determine when they meet and how much to rely on their advise. The Executive Branch is shaped like a triangle. Top down: President depts hundreds of executive agencies Departments and agencies carry out government programs in 3 ways: 1. Develop procedures for putting new laws into practice 2. Administer day-to-day operations of government 3. Regulate or police various governmental activities This all helps shape government policy “Red Tape” – inefficiency caused by rules and regulations Each person has a designed function & must operate within a chain of command Assist in enforcing laws Federal FBI – handles violations of federal law Counterfeiting Bank Robbery Espionage & spying Kidnapping SBI – state – violations of state law Highway patrol Murder if suspect & body stay in state County – the county Local Police Spoils System – giving federal jobs to people that helped the winner – “To the Victor belong the Spoils” Government grew more and more incompetent as people who weren’t qualified filled positions (late 1800s) Americans demanded change (Progressives) Reformed system came about – called the Merit System Pendleton Act (1883) – instituted the Merit system where those most qualified get the jobs Jobs are divided into 2 categories Classified – jobs given based on exams & kept no matter who is president Unclassified – jobs filled by appointment as in the spoils system – Appointed positions Hatch Act (1939) Forbids civil servants from working in a campaign or participating in party politics Office of Personnel Management – administers tests and hires workers Merit System Protection Board – handles promotions based on merit political appointees Employment usually ends when the President leaves office 90% of national government employees are civil service workers Hiring is usually based on open, competitive examinations and merit. Before 1883, hiring was based on “who you knew” Top department jobs usually go to 15 Executive department heads – advisers Makes the president’s job easier by dividing the work Head of the Dept of Justice is the Attorney General. All other heads are have the title of secretary Department of Homeland Security – most recent addition – terrorism President Washington’s Cabinet – Department of State, Department of Treasury and Department of War State – Secretary of State – manages relations with other countries Treasury – Secretary of Treasury – manages the nations money Defense – Secretary of Defense – manages the military John Kerry Jack Lew Chuck Hagel Justice – Attorney General – legal affairs and the chief law enforcement officer in the US Interior – Secretary of the Interior – manages public lands and natural resources Agriculture – Secretary of Agriculture – designed to help farmers Eric Holder Sally Jewell Tom Vilsack Commerce – Secretary of Commerce – trade and promotes US business and tourism Labor – Secretary of Labor – deals with working conditions and wages Transportation – Secretary of Transportation – manages highways, railroads, airlines, and sea traffic Penny Pritzker Thomas E Perez Anthony Foxx Energy – Secretary of Energy – tries to find alternative sources of energy Health and Human Services – Secretary of HHS – well being and health of Americans Veterans Affairs – Secretary of Veterans Affairs – services for armed forces veterans Ernest Moniz Sylvia Matthews Burwell Robert McDonald Education – Secretary of Education – advice and funding for schools Housing and Urban Development (HUD) – Secretary of Housing and Urban Development – special needs and problems of cities Homeland Security – Secretary of Homeland Security – oversees America’s defenses against terrorist attacks Arne Duncan Julian Castro Jeh Johnson Not a part of any cabinet, but still have to report out to the President 3 types: Executive Agencies Government Corporations Regulatory Commissions Specialized areas of government President chooses the head of each agency Examples EPA – Environmental Protection Agency FDA – Food and Drug Administration CDC – Center for Disease Control and Prevention Others – NASA, FED, NSA, FDA DOES NOT REPORT TO THE PRESIDENT President appoints the head of regulatory commissions but only Congress can remove (impeach) Protects the public by making and enforcing rules for certain industries Ex. FCC, FAA Controls certain types of business Must be impartial with no political pressure Run by a board appointed by the President and approved by the Senate US Nuclear Regulatory Commission Similar to private corporations – but the government owns and runs them. General manager & board of directors runs each corporation They charge for services, but are not supposed to make a profit, all $ goes back into the business Examples Post Office Sallie Mae, Fannie Mae, and Freddie Mac President addresses Congress every year to discuss his/her goals and concerns Required by the Constitution “He shall from time to time give to Congress information of the State of the Union and recommend to their Consideration such measures as he shall judge necessary and expedient.” Article II, Section 3 Congress is in joint session – both houses are together to hear the President speak Includes the White House Office Serves the President Created by FDR – 1939 Assists the President in doing his job Includes over 2000 employees and $100 million budget Prepares reports, drafts bills, checks the work of various executive agencies Chief of Staff – decides what issues are brought to the President Press Secretary – provides reporters with news Office of Management & Budget – prepares the nation’s budget & makes reports to the President on the fiscal soundness of the nation National Security Council – provides for the safety of the nation – CIA – gathers information on other nations Core of EOP is the White House Office – 500 people who work for the President Chief of Staff – Denis McDonough Press Secretary – Jay Carney Senior Advisors to the President – Valerie Jarrett and Jennifer Palmieri Prepares the federal budget and helps the President monitor government spending Federal budget lays out the administrations plans and goals for the upcoming year Helps President coordinate the military and construct foreign policy. Includes the V.P., Sec. of State, Sec. of Defense, Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, and top commanders of each of the armed forces. Forms our nations foreign policies and principles of the U.S. Supervises the CIA. Contains three independent members or economists Advise the President about economic matters: employment in the U.S., tax policy, inflation, trade with other countries, etc. Not a part of any cabinet, but still have to report out to the President 3 types: Executive Agencies Government Corporations Regulatory Commissions Specialized areas of government President chooses the head of each agency Examples EPA – Environmental Protection Agency FDA – Food and Drug Administration CDC – Center for Disease Control and Prevention Others – NASA, FED, NSA, FDA DOES NOT REPORT TO THE PRESIDENT President appoints the head of regulatory commissions but only Congress can remove (impeach) Protects the public by making and enforcing rules for certain industries Ex. FCC, FAA Controls certain types of business Must be impartial with no political pressure Run by a board appointed by the President and approved by the Senate US Nuclear Regulatory Commission Similar to private corporations – but the government owns and runs them. General manager & board of directors runs each corporation They charge for services, but are not supposed to make a profit, all $ goes back into the business Examples Post Office Sallie Mae, Fannie Mae, and Freddie Mac
![August 20, 1986 SG/94/86 D-08 From: The Secretary General [*] To](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/007822023_2-1a5272e9a5af1caa9930908b70495ac3-300x300.png)