uoslo-feb09 - Computer Engineering Research Group
advertisement

MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Data-centric Networking Through
Adaptive Content-based Routing
Hans-Arno Jacobsen
Bell University Laboratory Chair
http://www.padres.msrg.utoronto.ca
Middleware Systems Research Group
University of Toronto
University of Oslo, February 2009
Querying the Future
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Amazon to Chapters to You ....
Monday, October 10th in Cyberspace
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Thursday, November 15th,
in Toronto
Your book “...”
is available
at ....
$10 off
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
Business Process Example
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Loan Application Processing
Store in
DB
…
Reject
Credit
check 2
Credit
check
Check
score
Check
score 2
Approve
else
else
…
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
Send to
officer
Large-scale Business Processes
Vendor
Goods
selection
Goods delivery
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Dispatch B
Packaging
Pick-up goods
Out-stock B
FedEx
Delivery
Sale
prediction
Sale
Manufactory
Confirm
features
Sign
Contract
Fill out-stock
bill
Control
Fill dispatch
bill
Material
Out-stock B
Make plan
Out
Take
Assign
Target price
Finance
Check stock
Determinate
plan
Raw
materials
Execute
plan
Audit
Process
control
Raw
Pay
Credit card
Check
Check dealer
Check credit
Approval
Approval
Signature
Confirm
Monitoring
Feature
selection
Print receipt
Statistic
Marketing
Process
Check order
Design
Prototype
Warehouse
Fill order
Determinate
plan
CCC
administrate
Pick up
Requirement
collection
Feedback
Strategy
Design
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
Monitor
Validate
Affirm order
Chart
Marketing
Manufactory
University of Oslo, February 2009
Order
Payment
What is the Common Denominator?
Many applications are driven by asynchronous state
transitions.
Something happens, … an appropriate reaction is expected
and required.
Asynchronous state transitions represent events.
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
A process is triggered, a request submitted, …
Many applications require event management and
processing capabilities to run effectively.
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
In Terms of the Examples
These applications are driven by events
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Information matching the query is found and indexed
Person walks by a bookstore
Loan request is submitted online
Abstractly speaking events are disseminated and filtered
against queries
events
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
queries
University of Oslo, February 2009
What Event Processing Support is
Required ?
De-coupling and loose coupling
Fine-grained event filtering
In-network event processing
Composite event detection
Event correlation
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Many Applications are Event-based
Supply chain and logistics
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Workflows, business processes
and job scheduling
A
E
F
B
C
D
Event-Based
Light
Service oriented architectures
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
RFID and sensor networks
Agenda
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
What is the right abstractions?
My point of view
The PADRES project
Some details & results
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
What Abstractions Do Not Work?
Databases
Take this
cum gran salis
Data streams
Great for managing historic data
But what about future data
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Great for managing structured streams of tuples
But what about un-structured, multi-typed, sporadic events
from many sources
Rule-based expert systems
Great for inference and reasoning
But what about managing large numbers of fined-grained
filters in distributed envrionments
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
What Abstractions Enable Event
Processing?
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
The afore-mentioned points can best be
addressed by
The content-based publish/subscribe model
Realized by content-based message routing
Events are conveyed as publications.
Event listening, filtering and correlating is
based on content-based subscriptions
managed by the pub/sub system.
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
Publish/Subscribe 101
Not all publish/subscribe is equal
Publish/Subscribe models and evolution
Channel-based
Topic-based
OMG Data Dissemination Service (partially), …
Content-based
WS Notifications, OMG Data Dissemination Service …
Type-based
OMG CORBA Event Service, …
The PADRES ESB (see below), …
State-based
Subject Spaces
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Content-based Publish/Subscribe
TSX
Stock markets
NASDAQ
NYSE
Publisher
Publisher
Publications
Broker(s)
Subscriptions:
IBM > 85
ORCL < 10
JNJ > 60
Notification
Notification
Subscriptions
Subscriber
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
Subscriber
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
The Content-based Pub/Sub Model
Language and data model
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Boolean functions over predicates
Subscriptions are conjunctions of predicates
Publications are sets of attribute-value pairs
Matching semantic
A subscription matches if all its predicates match
Example
Treestructured
data
Graphstructured
data
Un-structured
data
Regular
languages
Relational
model
Subscription
XPath
RDF Query
Keywords
Regular
expressions
SQL
Publication
XML
RSS feeds
Text, documents
Sentences over
some alphabet
DBs, i.e., tables
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
That’s Like Data Base Querying !!
publication
subscriptions
data tuples
sets of tuples
sets of tuples
Query and subscription are very similar.
Data tuples and publication are very similar.
However, the two problem statements are inverse.
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
About future
About past
query
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Content-based Message Routing
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
[class,=,stock],[symbol,=,YHOO]
A1 [class,=,stock],[symbol,=,YHOO],[price,>,20.0]
S1
S1
P1
[class, stock],[symbol, YHOO],[price,25.0]
[class, stock],[symbol, YHOO],[price,45.0]
[class, stock],[symbol, MSFT],[price, 55.0]
P2
S2
A2
S2 [class,=,stock],[price,>,40.0]
[class,=,stock],[symbol,=,MSFT],[price,>,50.0]
Event-Based
Content Routing
Flexible
Decoupled
Declarative
Responsive
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
Publication Space
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Sub intersecting Adv
height
Pub matching Sub
height
90
75
70
70
20 25
20
weight
Adv: [height > 70],[weight > 25]
Sub: [height > 75],[weight > 20]
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
32
weight
Sub: [height > 75],[weight > 20]
Pub: [height , 90],[weight , 32]
University of Oslo, February 2009
ToPSS - The Toronto Publish/Subscribe System
Family [2000 – present]
ToPSS
Matching algorithms
Language expressiveness
vs. efficient matching
Routing protocols
Network architectures &
scalability
A-ToPSS CS-ToPSS
(matching)
(approximate) (composite subs)
S-ToPSS
L-ToPSS Rb-ToPSS
(semantic)
X-ToPSS
(XML matching)
(location-based)
Higher level abstractions
Workflow execution
Monitoring
(subject spaces)
M-ToPSS P2P-ToPSS LB-ToPSS
(mobile)
(peer-to-peer)
Federated-ToPSS
Historic-ToPSS
(historic data)
JS-ToPSS
(job scheduling)
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
(rule-based)
persistent-ToPSS
(federation of ToPSS brokers)
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
University of Oslo, February 2009
(load balancing)
Ad hoc-ToPSS
(ad hoc networking)
FT-ToPSS
(fault tolerance)
BPEL-ToPSS
(BPEL execution)
PADRES Data-centric Event Bus
First generation of students, when I looked away
http://padres.msrg.utoronto.ca
Peng Alex David aRno Eli Serge
PADRES is Publish/subscribe Applied to Distributed
Resource Scheduling
PAdres is Distributed REsource Scheduling
http://www.padres.msrg.utoronto.ca
Acknowledgements
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
University of Oslo, February 2009
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
PADRES Architecture
Business Process Management and Business Activity Monitoring
start
Deploy
Control
Redirect
Application
Events
7
add
remove
halt
resume
6
4
3
Visualize
Update
Monitor
...
Business Process Execution
Business Events
Content-based Routing (Publish/Subscribe)
Clients (publisher/subscriber)
Complex Events
Content-based Router
PADRES ESB
Computers
Computers
Laptops
Server Database
Network and
System Events
Server
Computers
Switch
Server Farm
Workstation
Switch
Database
Server
Computing, Storage, and Networking Resources
21
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
Laptops
2016/3/21
Event Management
Framework
PADRES Event Bus
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Consists of pub/sub message brokers
Content-based publish/subscribe interface
Content-based message routing
Store-and-forward message queuing
Comprised of a federation of brokers deployed as
overlay
Offers a slim client library for applications
Soon available under an open (source) license model
and as Apache Poloka incubation project
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
PADRES Event Broker
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
S
P
B
Matching
Engine
+
Routing B
Table
Publications
dest1
B
input
queue
B
subscription
dest
temperature > 37 dest2
temperature > 40 dest3
output output
queue queue
B dest3
dest2
temperature = 36
38
42
S
P
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
P
= publisher
S
= subscriber
Event Broker Architecture
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
PADRES Broker
Input Queue
Output Queues
Matcher
SRT
If sub intersects
Send to
[class,=,foo],[attr,>,17]
B1
Sub
Pub
PRT
Pub
If pub matches
Send to
[class,=,foo],[attr,>,20]
B2
Queue Handler
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
Sub
Queue Handler
University of Oslo, February 2009
Post Processor
Forwarder
Pre Processor
Pub/Sub Messages
Adv
Sub
Innovative PADRES Features
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Historic
Access
Composite
Events
E
F
B
C
D
Security
Robustness
Load
Balancing
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
Management
A
University of Oslo, February 2009
Limitations of Acyclic Overlays
Sensitive to
Congestion
Imbalanced workloads
Broker failures
Overlay changes
P
Broker
Publisher
Subscriber
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
General Overlay Network
Robust
Flexible
Self-healing
Adaptive
P
PP
P
Publisher
Subscriber
Congested Link
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Challenges with General Overlays
Subscriptions route
in loops
Brokers receive
duplicate
subscriptions
Multiple copies of
message maybe
created
Same problem for
publications
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
S
Adv 1
University of Oslo, February 2009
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
X
S
1
2
3
4
S
5
6
Adv 2
Number of Redundant Messages
Number of Dropped Messages
16000
14000
Average Connect Degree = 5
12000
Average Connect Degree = 10
10000
8000
6000
4000
2000
0
50
100
Number of Nodes
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
500
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Content-based Routing in
General Overlays
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Maintain the same interface to pub/sub
clients
Develop content-based routing protocols for
Advertisement
Subscription
Publication
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
Advertisement Routing
Each advertisement forms a spanning
advertisement tree
Duplicate advertisements are discarded by
brokers
Each advertisement is assigned a unique tree
identifier (TID)
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
e.g., A: [class,=,stock]……[TID,=,adv_msg_id]
SRT (Subscription Routing Table)
A set of [advertisement, last hop] pairs
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
Subscription Routing I
Each subscription is augmented with a TIDpredicate with a variable
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
e.g., S: [class,=,stock] … [TID,=,$X]
The variable is bound to the TID of matching
advertisements
PRT (Publication Routing Table)
A set of
[subscription, { (TID, last hop of subscription), … } ] pairs
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
Subscription Routing II
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
S: [class,=,stock],[name,=,*],[price,>,50], [TID,=,$Z]
At Broker 1:
S
Adv1: [class,=,stock],[name,=,IBM],
[price,>,60],[TID,=,Adv1]
X
S
1
2
3
4
5
6
Adv2: [class,=,stock],[name,=,HP], Adv 1
[price,>,50],[TID,=,Adv2]
S matching Adv1:
[class,=,stock],[name,=,*],
[price,>,50],[TID,=,Adv1]
S matching Adv2:
[class,=,stock],[name,=,*],[price,>,50],
[TID,=,Adv2]
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
Adv 2
Publication Routing
Each publication is assigned the TID of its
inducing advertisement
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
e.g., P [class, stock]……[TID, adv_msg_id]
Publication routing protocols:
Fixed TID routing: a publication is routed to
subscribers along its advertisement tree.
Dynamic publication routing: a publication may
be routed to subscribers across branches of
different advertisement trees.
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
Fixed TID Routing
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
X Adv 1
P
Property 1: No
broker receives
duplicate publication
messages.
Adv 2
1
2
3
4
5
6
P
Sub
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
Dynamic Publication Routing
Publication’s TID can be
changed in transit.
``Best`` path algorithms
Property 2: Changing a
publication P’s TID while
in transit will not change
the set of subscribers
notified of P.
X Adv 1
Adv 2
1
2
3
4
5
6
P
Sub
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
University of Oslo, February 2009
Faster Matching with TIDs
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Subscriptions are augmented with TIDs only
once at the first broker.
Other brokers can route the subscription
based on the TID alone.
Similar argument applies to publication
routing.
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
Advantages
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Simple and powerful concept
Retain the publish/subscribe client interface
Speed up subscription and publication
propagation
Generate duplicated messages only at
advertisement level
Build multiple subscription routing paths for
publications
Route publications dynamically
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
Composite Subscription
Composite subscriptions (CS) are used for
event correlation, in network filtering, and the
detection of composite events (complex event).
AND
S5
AND
OR
S1
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
A composite event is the constellation of
events being detected by the composite
subscription.
OR
S2
S3
S4
Applications:
Business process management,
Business activity monitoring
CS={ {S1 OR S2} AND {S3 OR S4} AND S5 }
S are atomic subscriptions. I.e., they are
satisfied by a single, multi-attribute event.
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
Topology-based CS Routing
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Adv 3
Adv 2
2
1
7
S2
3
5
S1
4
CS’
S3
8
6
9
Adv 1
CS
CS={ {S1 AND S2} AND S3 }
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
Adaptive CS Routing
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
CSs may be split according to potential
publication traffic, bandwidth, latency etc.
Adv 2
Adv 2
2
1
Adv 1
2
3
1
CS={S1 AND S2} Adv 1
CS={S1 AND S2}
(b)
(a)
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
3
University of Oslo, February 2009
Adaptive CS Routing
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Adv 3
Adv 2
CS’
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
CS’
8
S3
S2
Adv 1
9
S1
CS
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
CS={{S1 AND S2} AND S3}
Evaluation
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
32 overlay brokers, 20 publishers, 30
subscribers, initially
20 machine vs. PlanetLab
Workload
http://research.msrg.utoronto.ca/Padres/DataSets
Yahoo!Finance stock quote traces
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
Dense Topology
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
On PlanetLab
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
University of Oslo, February 2009
Increased Publication Rate
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
With Broker Failures
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Composite Event Detection
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Conclusions
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
The right abstraction for event processing is
content-based publish/subscribe.
Event processing & publish/subscribe are
interesting research areas.
ToPSS and PADRES explore many aspects
of these areas.
http://padres.msrg.utoronto.ca
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
Acknowledgements
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Graduate students, visitors, and PDFs currently
working on PADRES.
Partners from CA
Alex Cheung
Serge Mankovskii & Kirk Wilson
Chen Chen
Amer Farroukh
Patrick Lee
Guoli Li
Bala Maniymaran
Vinod Muthusamy
Reza Sherafat
Naweed Tajuddin
Chunyang Ye
Young Yoon
Plus many PADRES alumni
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
Partners from IBM
Phil Coultard & Allen Chan
Partners from Bell
Bell Systems & Technology
References
The DEBS Conference
http://www.debs.org
July 2009 at Vanderbilt U.
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Everything events Portal
http://www.event-based.org
The PADRES ESB project home
http://padres.msrg.utoronto.ca
An eQoSystem for declarative distributed applications with SLAs
http://research.msrg.utoronto.ca/Eqosystem/
The Micro-ToPSS event processing middleware for sensor networks
http://microToPSS.msrg.utoronto.ca/
Mobile-ToPSS – publish/subscribe for mobile and location-based applications
http://research.msrg.utoronto.ca/Mobile/
ToPSS - the Toronto Publish/Subscribe System Family Portal
http://www.ToPSS.biz (coming soon )
Quantifying events in software to increase modularity & customization in Cbased systems and software-based product lines
http://www.AspeCtC.net (ACC - the AspeCt-oriented C compiler)
The Middleware Systems Research Group
http://www.msrg.utoronto.ca
My web site
http://www.eecg.toronto.edu/~jacobsen
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
@ the University
of Toronto
Questions?
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
P ADRES
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
Benefits of Content-based
Publish/Subscribe
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Simplifies IT development and maintenance by
decoupling enterprise components
Supports sophisticated interactions among
components using expressive subscription
languages – going beyond the limits of topics
Allows fine-grained queries and event
management
Achieves scalability with in-network filtering
and processing
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
Faster Matching with TIDs
Subscriptions are
augmented with TIDs
only once at the first
broker.
Other brokers can route
the subscription based
on the TID alone.
Similar argument
applies to publication
routing.
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
S
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
X
S
S
Adv1 Adv2
1
2
3
4
5
6
Adv 1
University of Oslo, February 2009
Adv 2
Sparser Topology
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
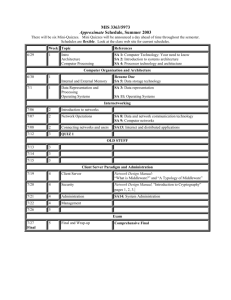
Effect of Subscriber Distance
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Distance
Fixed(ms)
Dynamic(ms)
Improvement
6 Hops
47.202
47.568
-0.78%
10 Hops
64.477
52.895
17.96%
12 Hops
74.416
60.598
18.57%
Max Diff
57.65%
27.39%
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
More Publishers
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Publication Burst
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
More Results
Faster matching
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
1926 publications cause 16997 times of matching
operations in the “Dense Topology” experiment.
About 89% of the matching operations can be saved if we
apply the TID-based faster matching.
Overhead of dynamic publication routing
Average CPU usage: 6.3% more than the Fixed routing
Average memory usage: 8.9% more than the Fixed routing
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
CS Routing Traffic
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Summary
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Minimize redundant traffic induced by cycles
Improve scalability and robustness of
pub/sub systems by offering routing path
alternatives
Enable flexible composite subscription
routing
Simplify solutions for failure recovery and
load balancing
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
Cost Model
Routing cost of CS
RCB(CS)) = Σi Tin*|P(CSBi)| +
Σi Tmatching*|P(CSBi)| +
Σi Tout_i*|P(CS)|
input
Selection factor (SF)
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
output
Rete s
SFA(S) = |σS P(A)| / |P(A)|
e.g., SFA(a = v) = 1 / (max - min)
Subscription cardinality
|P(S)| = Σi ri * SFAi (S)
|P(Sl)| + |P(Sr)|
if op = or
min (|P(Sl)| , |P(Sr)|)
if op = and
|P(CS)| =
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009
Fast Matching
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
1926 publications cause 16997 matching
operations in the “Dense Topology”
experiment.
89% of the matching operations can be
saved with TID-based fast matching.
Copyright © 2008 - Hans-Arno Jacobsen
University of Oslo, February 2009