Development - fog.ccsf.edu

Development
Learning objectives
• Ovulation and fertilization
• Implantation
• Embryonic and fetal development
• Labor and birth
• Postnatal development
Ovulation
Spikes in FSH and LH stimulate ovulation of a secondary oocyte
Secondary oocytes do not complete meiosis until fertilization
Ovulation of a secondary oocyte
Egg and sperm
Secondary oocyte has a layer of follicular cells and the protective zona pellucida
Acrosome of sperm contain enzymes for passing the corona radiata and zona pellucida
The acrosome on sperm requires about 7 hrs for activation
• Enzymes from the acrosome
– Disrupt the attachments between cells of the corona radiata and the zona pellucida
– Allows the sperm to reach the oocyte
Modern IVF techniques create significant ethical questions
• Combined with PCR, pre-implantation genetic diagnosis is possible for 8-cell embryos
• A single cell can be sampled
• What can be learned about an embryo from looking at its DNA?
• The union of the sperm and the egg that results in a cell with 46 chromosomes is called a(n):
A) embryo.
B) zygote.
C) fetus.
D) trophoblast.
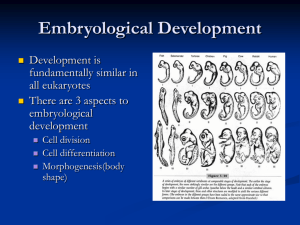
Fertilization until first cleavage
Identical and fraternal twins
Gastrulation allows formation of differential tissues from the inner cell mass
Gastrulation- forming of a gastrula- a primitive gut
Ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm are formed
Ectoderm, endoderm and mesoderm give rise do different tissues
• The inner cell mass of the blastocyst undergoes gastrulation, forming ectoderm, endoderm and mesoderm, which will ultimately give rise to all the tissues of the body
• When two secondary oocytes are released from the ovaries and are fertilized by different sperm cells, this is called:
• A) fraternal twins.
• B) identical twins.
• C) conjoined twins.
• D) clones.
Implantation
The embryo release human chorionic gonadotropin
Alerts the mother’s body to its presence, thereby sustaining the corpus luteum throughout pregnancy
The outermost layer of blastocyst cells give rise to the extraembryonic membranes- amniotic sac, umbilical cord and chorionic villi of the placenta
The placenta is the interface between fetal and maternal circulation
• allows the transfer of oxygen and nutrients from the mother’s blood to the fetus
• Prevents the mixing of fetal and maternal blood, allowing for differences in blood type between mother and child
Sexual development
• Male and female reproductive structures are formed from the same tissue
• Differentiated by the presence of absence of the SRY gene region of the Y chromosome
• A male has a genetic disease coded for on his
Y chromosome. Which parent passed on this trait?
• A) The mom
• B) The dad
• C) Either the mom or dad
• D) Neither parent: it is a spontaneous mutation
Because organs such as the lungs are not used in
utero, fetal circulation is arranged differently from the circulatory pathway of adults
Fetal development is most susceptible to birth-defect causing environmental insults between weeks 3 and 16
Growth of the fetus is allometric, and continues to be allometric until development is complete at adulthood
Labor is the painful process of birthing a baby, and consists of dilation, expulsion, and placental stages
Lactation cannot begin until a baby is delivered
• Colostrum and milk both contain antibodies which protect a baby against disease during its infancy
• Which of the following functions to maintain the corpus luteum and to stimulate it to continue to produce the hormone progesterone?
• A) Human chorionic gonadotropin
• B) Progesterone
• C) Estrogen
• D) Testosterone