Fetal Development
advertisement

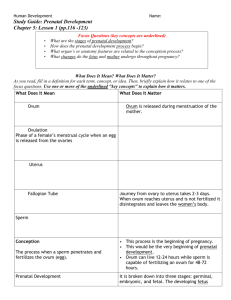
Developed by D. Ann Currie Ovary gives rise to oogonial cells. Cells develop into oocytes. Meiosis begins and stops before birth. Cell division resumes at puberty. Development of Graafian follicle. The female gamete are called Ovum. The ovum are considered fertile for about 12-24 hours after ovulation. Production of sperm First meiotic division: ◦ Primary spermatocyte replicates and divides. Second meiotic division: ◦ Secondary spermatocytes replicate and divide. Produce four spermatids. The male gamete are Sperm. The sperm can survive in the female reproductive tract for 48-72 hours. However they are believed to be healthy and highly fertile for only 24 hours. In a single ejaculation the male deposits approximately 200-500 million sperm in the vagina. Only hundreds of sperm actually reach the ampulla. Only one sperm fertilizes the ovum. Fertilization occurs: when the sperm and ovum unite. in the ampulla of the fallopian tube. Capacitation: ◦ Removal of plasma membrane and glycoprotein coat ◦ Loss of seminal plasma proteins Acrosomal reaction: ◦ Release of enzymes ◦ Allows entry through corona radiata Zone pellucida blocks additional sperm from entering Secondary oocyte completes second meiotic division ◦ Forms nucleus of ovum Nuclei of ovum and sperm unite Membranes disappear Chromosomes pair up At the moment of fertilization the sex of the zygote is determined. Female have XX (sex chromosomes) Male have XY ( sex chromosomes) Zygote moves through the fallopian tube towards the cavity of the uterus. Transportation takes 3 or more days. Rapid mitotic divisions called cleavage is occurring. 7-10days after fertilization the blastocyst implants. Most frequent site of attachment is the upper part of the posterior uterine wall. About 10-14 days after conception Primary germ layers: Ectoderm Mesoderm Endoderm Chorionic villi form spaces in decidua basalis Spaces fill with maternal blood. Chorionic villi differentiate: Syncytium: outer layer Cytotrophoblast: inner layer Anchoring villi form septa Nutrition Excretion Fetal respiration Production of fetal nutrients Production of hormones Large molecular compounds can not crossthe placenta Other see text Body stalk fuses with embryonic portion of the placenta Provides circulatory pathway from chorionic villa to the embryo Delivers oxygenated blood to the fetus: One Vein Returns waste material to maternal circulation: Two Arteries Amnion: Encloses the amniotic cavity The inner membrane that forms about the 2nd week of embryonic development Forms a fluid-filled sac that surrounds the embryo and later the fetus. Chorion: Is the outer membrane Becomes vascularized and forms the fetal portion of the placenta. Consists of 800-1200 ml by the end the pregnancy Surrounds, cushions, protects, the fetus and allows for fetal movement. Maintains body temperature of the fetus. Contains fetal urine and is a measurement of fetal kidney function. The fetus modifies the amniotic fluid through the processes of swallowing, urinating, and movement trough respiratory tract. Other see text. First 2 week after conception Cleavage Blastomeres form morula Blastocyst: - develops into embryonic disc and amnion Trophoblast: - develops into chorion Beginning at Day 15 through approximately the 8th week after conception. Week 9 after conception to birth Beginning development of GI tract Heart is developing Somites develop—beginning vertebrae Heart is beating and circulating blood Eyes and nose begin to form Arm and leg buds are present Eyelids are closed Tooth buds appear Fetal heart tones can be heard Genitals are well-differentiated Urine is produced Spontaneous movement occurs Lanugo begins to develop Blood vessels are clearly developed Active movements are present Fetus makes sucking motions Swallows amniotic fluid Produces meconium Subcutaneous brown fat appears Quickening is felt by mother Nipples appear over mammary glands Fetal heartbeat is heard by fetoscope Eyes are structurally complete Vernix caseosa covers skin Alveoli are beginning to form Rhythmic breathing movements Ability to partially control temperature Bones are fully developed but soft and flexible Variability seen on FHR monitor Increase in subcutaneous fat Lanugo begins to disappear Skin appears polished Lanugo has disappeared except in upper arms and shoulders Hair is now coarse and approximately 1 inch in length Fetus is flexed Fraternal: two ova and two sperm Identical: single fertilized ovum - Originate at different stages Umbilical Cord Fetal Heart Rate-110-160 BPM Ductus venosus Ductus arteriosus Foramen ovale