Chemical Bonding
advertisement

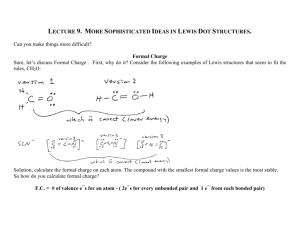
*A Chemical Bond is a mutual electrical attraction between the nuclei of one atom and the valence electrons of another atom. *This attraction binds the atoms together. a. Metallic bonding – “metal to metal” • Results from the attraction between metal atoms and the surrounding sea of electrons b. Ionic bonding – “nonmetal to metal” • Results from the electrical attraction between large number of cations and anions. It involves the transfer of electrons from one atom to another c. Covalent bonding – “nonmetal to nonmetal” • Results from the sharing of electron pairs between two atoms * * Many atoms transfer electrons and other atoms accept them. This creates cations (positive ions) and anions (negative ions). sodium atom Na sodium ion - Na+1 Na chlorine atom Cl chlorine ion – Cl-1 Cl Ionic bonding is the electrostatic attraction between positive cations and negative anions. This is the strongest bond type. *In many cases electrons do not completely transfer from one atom to another. The electrons between atoms are shared -like a “tug of war” *Consider two hydrogen atoms: Hydrogen Hydrogen H H The two hydrogen atoms SHARE the 2 electrons equally, giving each atom 2 electrons H:H the electron orbitals overlap or “share” electrons When electrons are shared equally the bond is called a nonpolar or pure covalent bond * *A polar covalent bond is when the electrons between two atoms are NOT shared equally. It is an unequal tug-ofwar. *Each Atom donates one electron to be shared to give each a stable, filled outer energy level * But sometimes, the two electrons are shared UNEQUALLY…one atom “tugs” harder on the shared electron pair (in this case the Cl is stronger). This creates an uneven distribution of charge. The H will have a partial positive charge ( ) and the Cl will have a partial negative charge ( ). * Since this bond has two “poles” – a positive pole and a negative pole – it is called a Polar Covalent Bond H Cl *We use electronegativities to determine whether we have an ionic, polar or non-polar bond *An electronegativity value is a number ranging from 0.0 to 4.0 that shows the tendency of an atom to attract electrons towards itself. The electronegativity values for the elements are found on an “electronegativity chart”, which looks like the periodic table. The numbers on the chart are the electronegativity values for that element. The HIGHER the number, the STRONGER the attraction for the electrons. * *How do we determine what type of bond will occur between two atoms? *The DIFFERENCE between their electronegativity values (EN) will tell us: electronegativity bond difference ( type EN) 1.7 and higher ionic 0.3 – 1.7 polar 0.0 – 0.3 non-polar *What type of bond will occur between Iodine (EN= 2.7) and the following elements: cesium (EN=0.8), iron (EN=1.8) and sulfur (EN=2.5) Bond between Iodine and Electronegativity difference cesium 2.7 – 0.8 = 1.9 iron 2.7 – 1.8 = 0.9 sulfur 2.7 – 2.5 = 0.2 Bond Type More negative atom * Bonding between: EN difference Bond Type Na and Cl S and O Ca and Br P and H Si and Cl S and Br 1.7 and greater 0.3 – 1.7 0.0 – 0.3 IONIC Polar Non-Polar More negative atom *What if the electronegativity difference is 0.3 or 1.7? What type of bond is it? *The cut-off numbers are guidelines, not definite delineation points. It is more of a gradual change from one bond type to another. Sodium and chlorine ionic bond Sulfur and oxygen polar covalent S O *Calcium and Bromine *Phosphorus and hydrogen *Silicon and chlorine *Sulfur and bromine