PROCESSES OF EVOLUTION SELF TEST JUNE 2009
advertisement

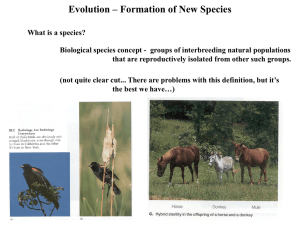
PROCESSES OF EVOLUTION SELF TEST. 1). Prezygotic isolating mechanisms include all of the following except a). hybrid sterility. b). courtship rituals. c). habitat separation. d). seasonal reproduction. 2). Which of the following is an example of mechanical isolation? a). Two species of birds live in the same habitat; one mates in spring and the other in summer. b). Two species of frogs have different mating calls. c). The flower structure of one species prevents the transfer of pollen from another species. d). One species of lizards inhabits the trees, and another species inhabits the ground cover. 3). __________________ isolating mechanisms include improper development of hybrids and failure of hybrids to become established in nature. a). Prezygotic b). Postzygotic c). Temporal d). Mechanical 4). Reproductive isolation and the evolution of species could occur through which of the following? a). founder effect b). reinforcement c). adaptation d). all of these 5). Speciation occurs most frequently in populations that are a). sympatric. b). undergoing disruptive selection. c). allopatric. d). not geographically separated. 6). The large number of Hawaiian Drosophila species has likely resulted from a). adaptive radiation. b). a single common ancestor. c). geographic isolation. d). all of these 7). The finch species of the Galápagos Islands are grouped according to their food sources; which of the following is not a finch food source? a). seeds b). carrion c). insects d). tree buds 8). Cichlid diversity can be attributed to a). adaptive radiation. b). new habitats and geographic isolation. c). a second set of jaws in the throat of the fish. d). All of the above contributed to cichlid diversity. 9). The hypothesis that evolution occurs in spurts, with great amounts of evolutionary change followed by periods of stasis, is a). punctuated equilibrium. b). allopatric speciation. c). gradualism. d). Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium. 10). Biological diversity through time has a). gradually increased. b). been constant. c). increased overall despite periodic drops. d). both increased and decreased with no overall change. LONGER QUESTIONS 1). In the figure, one interbreeding population has been divided, which results in two or more geographically isolated populations. Over time, these isolated populations can undergo little or no evolutionary change, can undergo speciation, or can become extinct. Explain under what conditions each scenario can occur: a). Population undergoes little or no evolutionary change. b). Population undergoes speciation. c). Population becomes extinct. APPLYING YOUR KNOWLEDGE 1). Outline the differences between allopatric speciation and sympatric speciation. Which is likely to occur more rapidly and why? 2). Polyploid animals are far less common than polyploid plants. Why do you think this might be so?