notes
advertisement

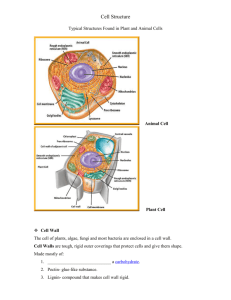
Period 1 ER • Is the site where liquid components of the cell membrane are assembled along with proteins and other materials that exported from the cell. • Network of tunnels throughout the cell. • Two kinds = Smooth & Rough (= bumpy because it has ribosomes attached) Golgi Apparatus • To modify , sort, and package proteins and other materials from the endoplasmic reticulum for storage in the cell or secretion outside the cell. • Located near the cell wall. • May also be called “Golgi Body.” Nucleus • Contains nearly all the cells DNA. • The coded instructions for making proteins and other important molecules • Molecules move through the nuclear pores to and from the rest of the cell • The nucleolus is where the assembly of ribosomes begins • Located anywhere in the cell. Mitochondria • Mitochondria are organelles that convert the chemical energy stored in food into compounds that are more convenient for the cell to use. • Its found in the eukaryotic cells, and plant cells. And is enclosed by two membrane. Chloroplast • Chloroplast collects energy form sunlight and turns it into chemical energy called photosynthesis • The chloroplast is located in plants and some insects. • Located by two membranes and inside the organelle are stacks of membranes which contains the green pigment chlorophyll Ribosomes • Ribosomes make protein. • Ribosomes are small particles of RNA and protein found throughout the cytoplasm and also attached to rough ER. Cytoskeleton • The Cytoskeleton is a network of protein filaments that helps the cell maintain its shape. Also involved in movement. • Microfilaments and microtubles make up the cytoskeleton. • Located near the nucleus. Lysosomes • The clean-up crew • Small organelles filled with enzymes • Breaks down proteins, carbs, and lipids into molecules for the cell to use • Can cause serious human illness Cilia • Cilia is used for both feeding and movement • Cilia is located outside of the cell, they surround the cell completely and are short • Examples: Found in unicellular organisms that live in both fresh and salt water (animal) Flagella • Used for movement • Whip-like structure • Located outside cell Vacuole • • • • • • Stores water, salt, proteins & carbohydrates Supports cell Found in some single celled organisms Helps with homeostasis Long and located centrally Always in plants & sometimes animals Period 3 ER • ER is shorter for Endoplasmic Reticulum. • ER is included in the, synthesis of proteins is called rough ER (has ribosomes & looks rough). Smoother ER contains collections of enzymes that perform special tasks. Movement of materials through cell. • Membrane; throughout cell Golgi Apparatus • The function of the Golgi apparatus is to modify, sort and package protein and other materials from the endoplasmic reticulum for storage in the cells or secretion outside the cell. • Wave appearance in the near the cell membrane (edge) of both animal and plant cells. Nucleus • • • • Contains the cells DNA Located in the middle of the cell Looks like a bouncy ball Chromatin (the granular material in the nucleus) surrounds the nucleolus Mitochondria • Mitochondria are organelles that convert the chemical energy stored in food into compounds that are more convenient for the cells to use • Found in the outer edge of the cell • Almost looks like a kidney Chloroplast • Mostly found in plant cells • Capture the energy from sun light and convert it into chemical energy (Photosynthesis) • Surrounded by Membranes Ribosomes • Ribosomes make protein. • Ribosomes are small particles of RNA and protein found throughout the cytoplasm and also attached to rough ER. Cytoskeleton • The Cytoskeleton is a network of protein filaments that helps the cell maintain its shape. Also involved in movement. • Microfilaments and microtubles make up the cytoskeleton. • Located near the nucleus. Lysosomes • • • • • Small organelles filled with enzymes They digest & break down lipids, carbs, etc. Removes junk that clutters cell Medium sized, like mitochondria If it fails, cell dies. Cilia • Short hairlike projection similar to a flagellum. • Produces movement in cells, found on the outside of the cell wall. • Propels cells rapidly through the water • Only in animal cells Flagella • Flagella are long whiplike projections that allow cell to move through their aquatic environments • It looks like a long tail on the backside of the cell • Only found in animal cells Vacuole • They store materials such as water, salt, proteins, and carbohydrates • They’re found in both plants and animals • Has a sack-like structure • Found near the middle of the cell • One of the biggest structures in the cell Period 5 ER • The internal membrane in the Eukaryotic cells • Endoplasmic Reticulum • Lipid component assemble, proteins and other materials exported • Wrapped around the nucleus • Two varieties: – Smooth – no ribosomes – Rough – has ribosomes embedded Golgi Apparatus • Modifies & sorts packaged proteins from the ER for storage • Looks like a stack of closely opposed membranes • Puts finishing touch on proteins Nucleus • Contains nearly all the cell’s DNA and with it the coded instructions for making proteins and other important molecules • Surrounded by nuclear envelope Mitochondria • Organelles that convert chemical energy stored in food into compounds that are more convenient for the cell to use • Enclosed by two membranes • In all eukaryotic cells (plant and animal) Chloroplast • • • • • Converts sun energy into chemical energy Biologically equivalent to a solar power plant Surrounded by membranes Only in plant cell Green Ribosomes • A small particle in the cell on which proteins are assembled • Made up of RNA and proteins • They produce proteins by following coded instructions from the nucleus • Each ribosome is a small machine Cytoskeleton • Network of protein filaments that help cell maintain shape • Also involved in movement Lysosomes • Part of cleaning crew and breaking down organelles • Free-roaming • Tay-sachs linked to lysosomes Cilia • Enables the cell to move • Its located outside the cell Flagella • Flagella's are long, whip like, projections that allow a cell to move. • Example: Animal protests that swim using the flagella are classified which are referred to the Zooflagellas. Vacuole • Store materials such as water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates in plants • Pressure of central vacuole helps the plant to support heavy leaves and flowers • Also found in single-cell organisms and some animals • Contractile vacuole work by pumping water out of a cell Period 6 ER • ER = Endoplasmic reticulum • Assembles proteins; like a hallway for the cell • Two varieties: – Smooth – Rough (= has ribosomes and therefore looks rough) Golgi Apparatus • Modifies, sorts and packages proteins Nucleus • Contains cell’s DNA • Composed of two membranes Mitochondria • Cell organelle that converts the chemical energy stored into food into usable energy • Has two membranes inside • Kidney bean shaped Chloroplast • Converts sunlight into chemical energy • Green in color • Only found in plant cells Ribosomes • Make protein (the main product/output of cell) • Found in cytoplasm or attached to rough ER • Very small Cytoskeleton • A network of protein filaments that helps the cell maintain its shape. • Involved in movement and supports the cell. • Inside and everywhere in the cell • Sandwich like form Lysosomes • Lysosomes are a clean up crew for the body • Made up of small chemicals called the enzymes • One function is to digest liquids and food Cilia • Short hair like projections similar to flagella • Cilia is used for feeding and movement Flagella • • • • Plural of flagellum Long whiplike projections allow cell to move Looks like a tiny tail Used by animal-like protists that use flagella to swim (usually having one or two) Vacuole • Cell organelle that stores materials such as water, salts, proteins and carbohydrates • It’s found in plants. And some animals and single celled organisms • It’s one of the biggest organelles