Cell Parts
advertisement

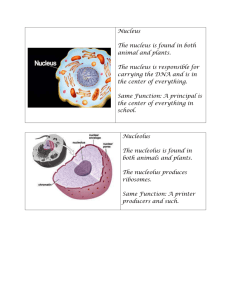
CH. 3 CELLS CYTOSKELETON Gives the cell shape, structure and helps it move Made of: Microfilaments Intermediate filaments Microtubules CYTOPLASM The “goo” that surrounds the nucleus Keeps everything in place Organelles are suspended in cytoplasm RIBOSOMES Ribosomes are the site of Ribosomes •Structure-spheres composed of RNA and protein •Function-site of protein synthesis •Free ribosomes make proteins that remain inside the cell •Attached ribosomes make proteins that become part of the cell or are exported from the cell THESE RIBOSOMES A R E AT TA C H E D T O W H AT ORGANELLE THESE ARE FREE RIBOSOMES (IN THE CYTOSOL). Nucleus Found in what type of cell Nucleus Function: 1. Control headquarters for the cell. AKA… the ________ 2. Structure: • Where is the nucleus found • Contains the genetic material-chromosomes- made of DNA & proteins • Surrounded by a double membrane-nuclear envelope/membrane • Inside is a nucleolus that makes ribosomes ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM ROUGH Structure: Network of membranes near nucleus Why is it considered rough Function: Transports proteins that were made by the attached ribosomes through the cell to the golgi. ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM SMOOTH Structure: Network of folded membranes throughout cell Why is it considered smooth Function: Makes lipids and breaks down toxic substances. GOLGI APPARATUS Location In the cytoplasm Structure Closely stacked, flattened membrane sacs Function Stores, packages, and transports products inside for use outside Vesicles (a bit of the golgi pinches for transport of stored materials). VESICLE Small sac in the cell Usually full of liquid Golgi Apparatus LYSOSOME (NOT FOUND IN PLANTS) StructureSaclike What does the lysosome contain FunctionDigests food particles Digests old organelles MITOCHONDRIA (FOUND IN ALL EUKARYOTIC CELLS) StructureOval Inside is a complex matrix of folded membranes. To increase surface area. FunctionChanges energy stored in food into a more useful form Mitochondria produces what important energy storing molecule CENTRIOLE Made of protein Found in animal cells Help pull apart cells in mitosis What kind of cell is this VACUOLE Location cytoplasm Structure sac of fluid surrounded by a membrane Function Sites of storage of water, ions and some nutrients. Plants: allows plants to maintain turgor pressure, holds water to prevent wilting. What would be the role of the large central vacuole in osmosis CHLOROPLAST. Where is the Chloroplast found Structure Double phospholipid bilayer. Inner layer Stacks = grana Non stacked area = stroma Function Capturing radiant energy and converting it to chemical energy. CELL WALL Location surrounding Plant cells Structure contains polysaccharide cellulose Function Provides structure and support for plant cells ____________ are found only in Plant cells. They take in light energy and store it in carbohydrates during photosynthesis. Note the cell wall and central vacuole in this diagram of a plant cell. They are also found only in plant cells. The function of the vacuole is Why is the cell wall important to the plant cell