Key Supreme Court Cases
advertisement

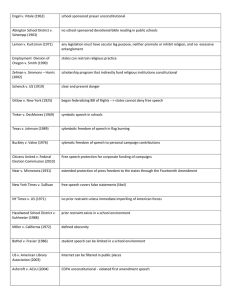
Key Supreme Court Cases Cases on Federalism • Marbury v. Madison (1803): judicial review, strong S.C. • McCulloch v. Maryland (1819): court has implied powers, necessary and proper clause, expands power of fed gov’t • Ableman v. Booth (1859): state courts can not contradict fed courts • US v. Nixon (1974): President is not above the law Cases on Discrimination, Race • Dred Scott v. Sandford (1857): Blacks, free or slave, are not citizens; slavery can not be outlawed in w territories • Plessy v. Ferguson (1896): segregated facilities are okayseparate but equal • Korematsu v. US (1944): Americans of Japanese descent can be interned • Brown v. Board of Education (1954) segregated schools violate 14th amend. Overturns Plessy • Regents of UC v. Bakke (1978) race-based set asides violate Equal Protection Clause. Some race usage may be employed in admission decisions Birth Control and Abortion • Griswold c. Connecticut (1965) married couples are entitled to contraception. Establishes right to privacy • Roe v. Wade (1973) abortion is a constitutional right, thus prohibitions against it in the 1st tri are prohibited • Planned Parenthood v. Casey (1992) Restrictions on abortion are allowed, though it affirms Roe • Gonzales v. Carhart (2007) Congress can prohibit a specific abortion procedure Search and Seizure • Mapp v. Ohio (1961) evidence gained by search/seizure that violates Const, is inadmissible in court • Katz v. US (1967) evidence from the wiretapping of a public phone w/o a warrant is inadmissible • Vemonia School District v. Acton (1995) schools may implement random drug testing Right to an Attorney • Gideon v. Wainwright (1963) those charged w/ a serious offense are entitled to an attorney and state must pay • Escobedo v. Illinois (1964) person in police custody has a right to speak to an atty • Miranda v. Arizona (1966) Police must advise people of their right to remain silent, to have an atty. Interrogation must stops if suspect wishes to remain silence • In re Gualt (1967) Juveniles charged w/ a crime are protected by due process Freedom of Speech • Schenck v. US (1919) “Clear and Present Danger” speech is not protected by the 1st amend • Near v. Minnesota (1931) Rejects prior restraints on publishing, censorships is unconstitutional except in rare situations • Chaplinsky v. NH (1942) established the ‘fighting words doctrine: that some words are not protected by 1st amendment • Tinker v. Des Moines schools (1969) Wearing armbands is a legitimate form of protest, even on school grounds Other Landmark Cases • Fletcher v. Peck (1810) 1st time SC struck down a state law as unconstitutional • Dartmouth College v. Woodward (1819) extended contract rights to corporations • Gibbons v. Ogden (18240 Power to regulate interstate commerce is granted to Congress