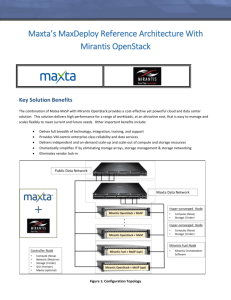
Deployment
advertisement

What if your OpenStack deployment succeeds? David J. Easter Product Line Manager, Mirantis OpenStack © MIRANTIS 2013 Agenda • Challenges • Prior to installation • Deployment • Post-deployment, Ongoing operations • Patching / Upgrade © MIRANTIS 2013 Challenges • Creating a production quality cloud is a complicated, error prone and manually repetitive process • There’s limited guidance on how to maintain and tune the cloud infrastructure for peak operations • Organizations are creating multiple private clouds and need a repeatable automated process. • Keeping up with the pace of community releases is a different world than traditional enterprise applications © MIRANTIS 2013 Prior to installation • Configuring the environment prior to deployment will take up most of your time • Obtaining hardware (servers, switches, etc.) • Configuring the network [this one is BIG] • Many times requires working across teams • Configuring the node servers where OpenStack will run © MIRANTIS 2013 How you can prepare • Pre-plan your HW requirements •How do you calculate how much hardware you need for your OpenStack cloud? • Which deployment mode you will use (HA or not?) • Choose the most suitable networking service (NovaNetwork: FlatDHCP, VLAN manager or Neutron: GRE, VLAN) • Plan a role (or roles) to be assigned to each node server • Prepare an addressing plan and network association • Prepare a logical network diagram © MIRANTIS 2013 Deployment • There are many choices • Which is right for you? © MIRANTIS 2013 Some factors to consider • Are you comfortable with O.S. level interfaces? • Can you get the responsiveness you need if you have questions or encounter issues? • Will the utility deploy what you want the way you want to deploy it? • Can you run it on your own HW initially? • How much automation do you require? • Can you install multiple clouds from the same utility? • Is the process easily repeatable? © MIRANTIS 2013 Post deployment • How do you test the new environment under real world business workloads? • Tempest is o.k. – exercises API • Additional tests are most likely necessary, esp. for HA & PaaS • As Ceilometer matures, a richer monitoring option may still be needed • Thresholds, actions • Leads to self-healing © MIRANTIS 2013 Ongoing operations • Programmatic interface needed for CRUD actions • Add nodes, remove nodes • Create / Delete entire clouds • Gather operational info (logs, health check, auditing) Delete Cloud Temp Production DevOps + 2 compute nodes OpenStack Control Plane Staging QA Cloud operations © MIRANTIS 2013 The OpenStack train keeps a rollin’ Folsom Grizzly Havana Icehouse • Is your organization able to do constant CI/CD • Stay in synch with bug/security updates & major releases • Cadence for release is every 6-8 weeks • Geometric rise in complexity if you’re managing your own unique fork © MIRANTIS 2013 Patching OpenStack • Ability to update components within current major version of a deployed OpenStack cluster • e.g. 2013.1.3 bug fix update OpenStack Control Plane © MIRANTIS 2013 Upgrade • Current method with least risk – parallel cloud • Migrate workloads • Does not require duplicate cloud footprint • Steal some capacity from Cloud 1 to build Cloud 2 • Continue to cannibalize Cloud 1 until Cloud 2 is complete Grizzly Havana OpenStack Control Plane © MIRANTIS 2013 Summary • Plan and set up the environment well in advance of the milestone to start deployment • Pick a deployment utility that makes the best use of your time and resources • Make sure you have tools in place to monitor, test and operate the cloud once deployed • Think ahead for how you will patch / upgrade © MIRANTIS 2013 Mirantis • Mirantis OpenStack • http://software.mirantis.com • Fuel community project • https://github.com/search?q=%40stackforge+fuel • Try out our Quick Start self-evaluation • Runs in VirtualBox on one machine • View a quick demo in our booth • Or online: http://youtu.be/dm0sVDgodHw © MIRANTIS 2013