Shoulder Girdle
advertisement

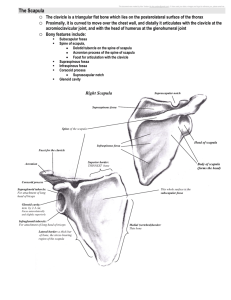
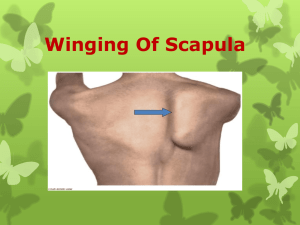
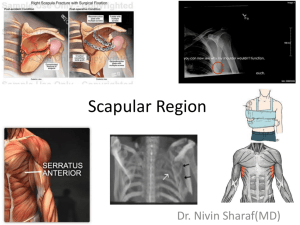
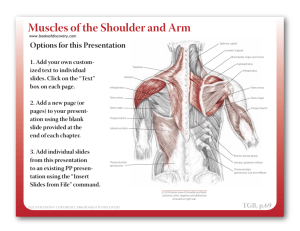
Shoulder Girdle Trapezius / Levator Scapulae / Rhomboids / Pectoralis Minor / Serratus Anterior / Sternocleidomastoid Trapezius The Trapezius is part of the group of muscles which control the shoulder girdle and is divided into parts; upper, middle and lower. Part 1: Upper fibres of the cervical vertebrae. This is the weakest part of the muscle and only provides minor elevation of the clavicle Part 2: The area commonly known as upper trapz. This is a strong elevator, rotator and retractor of the scapula Part 3: The mid-portion of the Trapzius. These fibres are mainly responsible for scapula retraction Part 4: The lower fibres of Trapezius. This part of the muscle assists in retraction and rotation. When all parts of the muscle work together they have the effect of simultaneously elevating and retracting the scapula. The Trapezius is used most commonly to fix the scapula to allow the Deltoid to move the Humerus. Origin Base of skull Ligaments cervical (upper) spine Spinous processes of Cervical 7 to Thoracic 12 vertibrae Insertion Posterior outer 1/3 of the clavicle Acromion process Spine of the scapula Actions Elevate the Scapula Retract the Scapula Upward rotation of the scapula Which nerve supplies the muscle? Cranial nerve Daily uses Shrugging the shoulders Overhead movements or the arm Levator Scapulae Shrugging the shoulders (scapula elevation) requires the use of levator scapulae and Trapezius. Fixation of the scapula by other muscles, allows the levator scapulae muscles to work together to aid cervical extension, or independently to laterally flex (side bend) the neck towards the side of the working muscle. Origin Transverse processes of C1-4 Insertion Medial border of the scapula above the level of the scapula spine Actions Scapula elevation Lateral flexion of the cervical spine (each side independently) Extension of the cervical spine (each side independently) Which nerves supply this muscle? Cervical nerve Dorsal scapular nerve Daily uses Shrugging shoulders Carrying a heavy shopping bag Rhomboids There are two rhomboid muscles - Rhomboid major is larger and positioned below rhomboid minor. Both muscles work together to retract the scapula (bring the shoulder blades together) and rotate the scapula. Chins and dips are excellent activities for developing these muscles. Origin Spinous processes of C7-T5 Insertion Medial border of the scapula, below the level of the spine of the scapula Actions Scapula retraction Rotation of the scapula downwards Which nerve makes it move? Dorsal scapular nerve Daily uses Pulling a draw open Pectoralis Minor The Pectoralis Minor muscle is the smallest of the two pectoral (chest) muscles. It works together with Serratus anterior which protracts and rotates upwards. When the two work together, pure protraction (without rotation) is produced. Origin Outer surface of ribs 3-5 Insertion Coracoid process of the scapula Actions Scapula protraction Rotation of the scapula downwards Innervation Medial pectoral nerve Daily uses Pushing a door open Serratus Anterior The Serratus anterior muscle is used in activities which draw the scapula forwards. It is used strongly in push-ups and bench presses. Winged scapula are an indicator of having a weak Serratus anterior. Origin Upper nine ribs at the side of the chest Insertion Costal aspect (side articulating with the ribs) of the medial border of the scapula Actions Scapula protraction Rotation of the scapula upwards Innervation Long thoracic nerve Daily uses Reaching up to open a high window Sternocleidomastoid Muscle The Sternocleidomastoid muscle is the big thick muscle in the neck and is easily seen at the front of the neck when rotating the head the other way. Origin Anterior surface of the upper sternum Inner part of the clavicle Insertion Mastoid process (behind the ear) Actions Contraction on both sides: Flexes the neck Contraction on one side only: Laterally flexes (side bends) to the same side and rotates to the other side Innervation Acessory XI nerve Daily uses Looking at the floor Looking over your shoulder Holding the phone between your ear and shoulder