Sokhumi State University Shota Rustaveli State University
advertisement

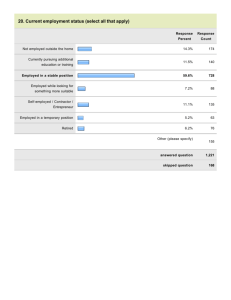
Modernization of Educational Process as a Mean to Satisfy the Requirements of Labour-market in the Field of Culture Management Georgian law about the Higher Education Parliament of Georgia Higher Education System Management Georgian government Prime-Minister of Georgia Ministry of Education and Science of Georgia National Center for Educational Accreditation Teaching University (Bachelor and Master programs) College (Bachelor programs) 60 20 College 7 12 40 4 4 15 Teaching University 28 University 0 State HEIs - 23 Private HEIs - 47 Bachelor’s Degree 240 ECTS Higher Education Cycles University (Bachelor, Master and Doctoral programs) Certified medical specialists (veterinary) educational program and residency Master’s Degree 120 ECTS 300-360 ECTS Degree of Certified Specialist (professional higher educational program) 120-180 ECTS Doctoral Degree 180 ECTS Undergraduate programs – 411 Graduate Programs - 77 2008 29.8 53.6 16.5 2007 31.8 54.9 2006 29.9 56.5 0.1 Employed (hired) 13.3 0 Self-employed 13.6 0 Unemployed Not stated 0 20 40 60 80 100 Employees by kind of activity Agriculture Mining and quarrying Manufacturing 0.3 1.1 4.9 4.2 53.4 2007 9.9 1.1 4.2 1 2 3.8 7.3 3.5 2.6 0.2 Electricity,gas & water supply Construction Wholesale and retail trade Hotels & restaurants 0.2 4.7 1.1 3.1 55.3 2006 9.6 1 4.5 0.8 1.5 4.5 7.6 3 2.4 0.1 Transport, storage and communications Financial intermediation Real estate and business activities Public administration and defence Education 0.3 5.1 1.32.5 54.3 2005 10.8 0.9 4 0.8 1.5 4.7 7.5 3.3 2.2 0.2 Health and social work Other community Private house economy 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% 90% 100% Exterritorial organiaztions and bodies 41.4 27.6 25.3 3.5 13.6 8.9 7.3 15.6 6.3 7.7 2.6 0 2006 Primary 41.1 40 0.2 Basic 27 16.7 2.5 8 2007 Secondary Primary vocational Secondary vocational 4.3 0.4 Higher Without education 2008 Employed by level of sex (%) Male Female 38.4 43.9 Primary 43.3 43 38.4 36.8 Basic 28.1 25.7 27 24.9 26.7 27.4 Secondary Primary vocational 18.7 18.3 16.4 Secondary vocational 10.2 6.9 2.9 2006 7 7.5 0.2 2.2 7.5 0.2 2007 Higher 5.4 1.9 0.2 2008 8.6 7.7 7.5 4.1 3 8.6 5.1 0.2 Without education 2006 3.1 3.2 0.5 0.2 2007 2008 <20 17.3 20-24 25-29 30-34 35-39 18.4 40-44 45-49 50-54 12.4 12.1 11.2 8.9 2.1 10.2 7.3 6.6 4.8 4.1 0.5 4.2 3 1.3 2007 32.3 1.3 2008 18.5 18 17.7 17 16.4 16.7 27.7 8.7 9.2 8.4 6.2 2.3 2006 65+ 13.3 10.7 10.5 10.1 7 4.6 60-64 18.2 17.3 17.3 16.6 13.7 55-59 17.5 17 14.1 12.8 11.9 11.4 10.9 10.5 10.5 9.8 9.8 22.6 19.8 18.1 18.5 18.1 15.1 14.7 9.2 3.5 Male Female 14.5 12.6 12.3 11.3 Male Female 7.6 7.1 6.46.9 10.1 10 9.2 6.6 4.6 5.3 0.6 0.4 0.8 4.9 4.7 9.3 10.1 7.4 5.3 9.5 8.9 8.5 8.3 7 5.5 4.3 3.3 1.2 1.61 3 1.5 1.7 0.9 42.4 39.9 31.6 4.7 17.9 16.9 16.2 0.5 39.2 35.5 31.8 7.1 0.2 0 4.9 2006 3.9 Primary Basic Secondary Primary Vocational Secomdary Vocational Higher Without education 0 0.2 4.4 2.8 2007 0.1 2008 Male Female 44 40.6 39 37.3 37.3 25.9 24.4 5.2 6.2 5.7 0 2006 25.1 23.1 22.6 44 25.9 24.4 22.3 12.4 11.9 0.5 44.4 41.3 8.6 3.8 0.1 0 2007 2.8 2.7 0.1 2008 4 0.1 0.4 4 0 2006 3.9 0.3 0 2007 2.8 0.1 2.7 2008 0.1 40000 39624 Education Humanities and Art 30000 Social Sciences, business and law 20000 18862 Science 13071 10000 11851 Engineering 8921 4430 4410 3714 138 0 Bachelor or Certified physician program 1413 897 1320 198 135 Magistracy or Residency 3.5 516 719 359 1064 90 368 High Professional Program 40000 30820 30000 20000 10000 0 17618 2407 7141 6488 6672 3754 Bachelor or Certified physician program 5002 361 1865 854 1233 130 228 Magistracy or Residency 1702 141 57 781 1137 673 High Professional Program Agriculture and veterinary Health and welfare •Museums •Libraries •Theaters •Publishers 17 Unemployed 62 Employed in their filed 266 116 Employed in other field Employed in Public Sector 84 Continue Studies Number of bachelors – 1530, number of respondents- 545 100 82 80 80 60 Unemployed Employed in their field 42 43 38 40 20 0 43 11 10 13 21 16 19 2 Law Faculty - 629 graduates, respondents - 109 Faculty of Economics and Business - 126 graduates, respondents - 94 24 22 9 14 1 Faculty of Education - 215 graduates, respondents - 47 5 Employed in other field 29 Employed in Public Sector 11 3 Faculty of Humanities,Political and Social Sciences - 316 graduates, respondents - 150 1 6 Faculty of Exact and Natural Sciences - 244 graduates, respondents - 128 Continue Studies S – strengths • Highly qualified academic personnel • Lowest tuition fee • Wide range of specialties at all three cycles of Higher Education •5 scientific and research institutions at the Humanities faculty •Educational programs in correspondence with the European credit transfer system •Transparent and flexible educational programs (major and minor courses) •Students’ self-government W – weaknesses • Programs give general, fundamental knowledge – lack of specialists of the specific profile • Lack of modern methods in the teaching process •Practice elements are less demonstrated in the educational programs •Faculty does not have a webpage •Material and technical resources require improvement and development •Non-sufficient number of computers, no copying and scanning machines •No implementation of exchange programs for students and academic staff O – opportunities •Implementation of new innovative teaching methods •Participation in different competitions and projects •Usage of new technologies in the teaching process •Establishing contacts with foreign universities and signing memorandums •Availability of exchange programs •Integration with European education system as a part of Bologna System •Contacts establishment with the potential employers, their engagement in the educational programs elaboration process, maintaining joint projects •Close collaboration with the Ministry of Education and Science of Georgia, National center of Education Quality •Improvement of the education quality using internal and external control mechanisms •Opportunities of finding additional financing sources T – threads •Loss or decreasing of interest in Humanities faculty •Tendency among the students to choose English philology educational program, less interest in other humanities program •High competition from larger and recognized state universities •Alumni’s employment low rate; employment not in the field of their specialty •A narrow segment of labor market •Poor economic situation which is reflected on the students’ solvency •Possibility of personnel and academic staff flow to other highly paid higher education institutions •Budget resources limitation which hinders the improvement of the infrastructure development •Possible tuition fee growth due to the current economic situation