Photosynthesis Jeopardy
advertisement
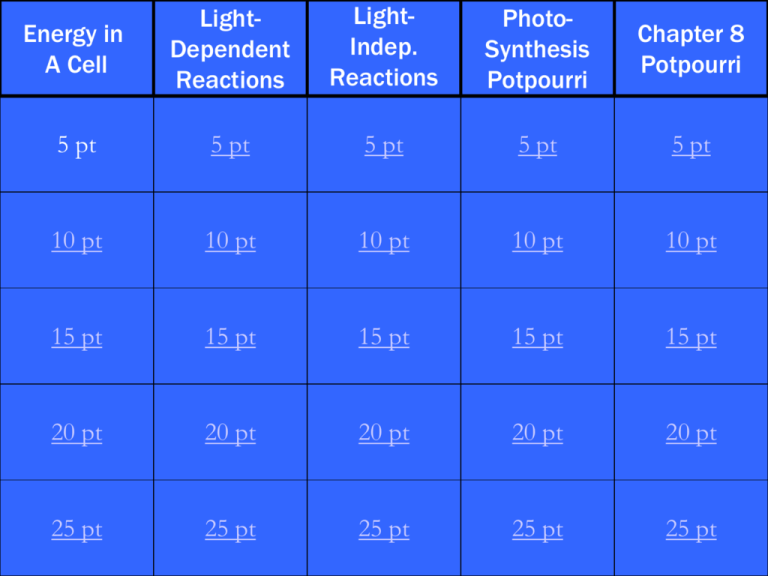
Energy in A Cell LightDependent Reactions LightIndep. Reactions PhotoSynthesis Potpourri Chapter 8 Potpourri 5 pt 5 pt 5 pt 5 pt 5 pt 10 pt 10 pt 10 pt 10 pt 10 pt 15 pt 15 pt 15 pt 15 pt 15 pt 20 pt 20 pt 20 pt 20 pt 20 pt 25 pt 25 pt 25 pt 25 pt 25 1pt Another name for adenosine triphosphate 2 What is ATP? 3 This is where the energy is stored within an ATP molecule 4 What is in the phosphatephosphate bonds? 5 When it is needed by the body, ATP gets broken down to this molecule 6 What is ADP (adenosine diphosphate)? 7 This is the reason that ATP can be broken down so easily 8 What is it takes a tremendous amount of energy to force the three phosphates together? 9 Because of this, the cell is relieved of having to store all of the ATP it needs 10 What is there are free phosphates in the body and the molecule recycles itself? 11 This is the process that plants use to trap the sun’s energy to make their own food 12 What is photosynthesis? 13 This is the main energy-trapping pigment within the chloroplast 14 What is chlorophyll? 15 The light-dependent reactions take place here 16 What is in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplast? 17 These are the two high-energy molecules produced in the lightdependent (light reactions) that are used to make glucose in the light-independent (dark reactions)? 18 What are ATP and NADPH? 19 Photolysis is necessary to replace electrons within the chlorophyll. Name the products of photolysis 20 What are 2 H+ ions, 2 electrons, and ½ molecule of oxygen gas? 21 This is another name for the light-independent reactions of photosynthesis 22 What is the Calvin Cycle? 23 This gas starts the lightindependent reactions of photosynthesis 24 What is CO2? 25 Two of these molecules leave the Calvin cycle and help make glucose for the cell 26 What is G3P? 27 This enzyme converts the 3carbon molecule G3P back into the 5-carbon molecule RuBP to continue the Calvin cycle 28 What is rubisco? 29 It takes this many rounds of the Calvin cycle to produce one glucose for the cell 30 What is 6? 31 This is the reason that plants contain different types of pigments 32 What is that different pigments absorb varying wavelengths of light? 33 During the light dependent phase, light energy is converted into this type of energy in the chlorphyll 34 What is chemical? 35 This structure within a plant cell allows for gas exchange 36 What is the stomata? 37 This is the name of the process in the light reactions where H+ ions are pumped across the membrane to produce energy for the plant cell during photosynthesis 38 What is chemiosmosis? 39 These are the names of the lightabsorbing molecules within the cell membrane during the light reactions of photosynthesis (Hint: There are two of them) 40 What are Photosystem II and Photosystem I? 41 Plants are categorized as this type of organism, which can produce its own food 42 What is an autotroph? 43 These are the products of photosynthesis 44 What are glucose and oxygen? 45 This enzyme in the light reactions pumps H+ ions across the membrane and converts ADP into ATP (Remember: Enzymes typically end in –ase) 46 What is ATP synthase? 47 This is the water-carrying tissue of the plant 48 What is the xylem? 49 This male part of the flower contains the pollen 50 What is the stamen? 51