Social Psychology Guided Notes
advertisement
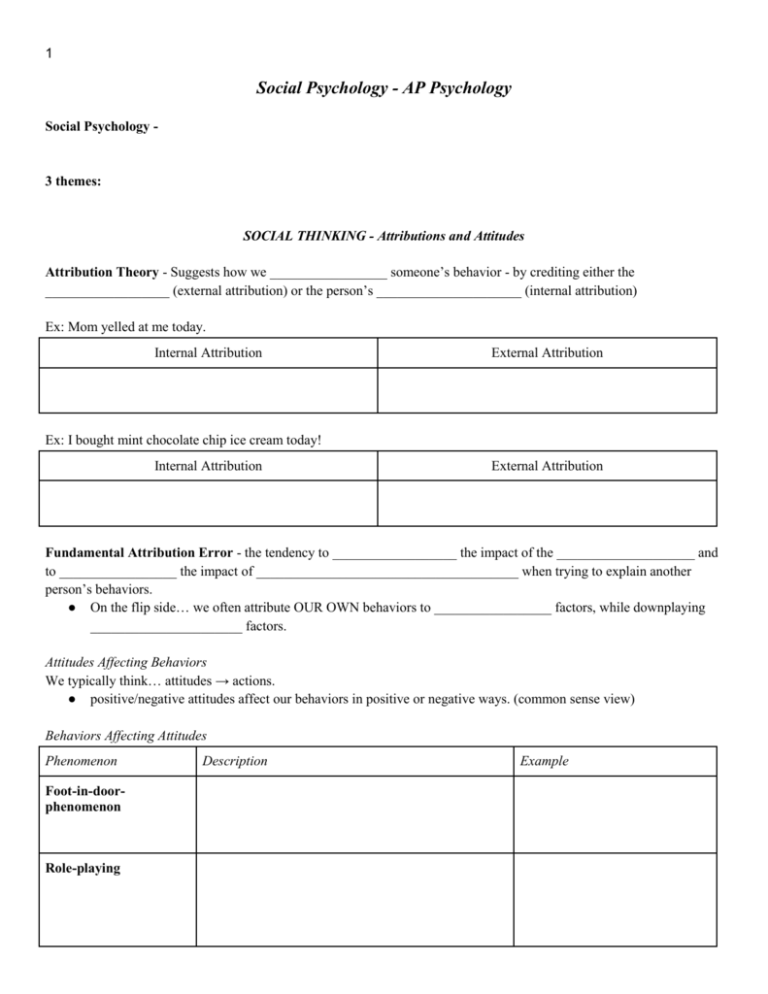
1 Social Psychology - AP Psychology Social Psychology - 3 themes: SOCIAL THINKING - Attributions and Attitudes Attribution Theory - Suggests how we _________________ someone’s behavior - by crediting either the __________________ (external attribution) or the person’s _____________________ (internal attribution) Ex: Mom yelled at me today. Internal Attribution External Attribution Ex: I bought mint chocolate chip ice cream today! Internal Attribution External Attribution Fundamental Attribution Error - the tendency to __________________ the impact of the ____________________ and to _________________ the impact of ______________________________________ when trying to explain another person’s behaviors. ● On the flip side… we often attribute OUR OWN behaviors to _________________ factors, while downplaying ______________________ factors. Attitudes Affecting Behaviors We typically think… attitudes → actions. ● positive/negative attitudes affect our behaviors in positive or negative ways. (common sense view) Behaviors Affecting Attitudes Phenomenon Foot-in-doorphenomenon Role-playing Description Example 2 Cognitive Dissonance SOCIAL INFLUENCE - Conformity and Obedience Conformity - Behaviors are contagious. ● _________________________________________ - mimicking others’ behaviors ● _________________________________________ - mimicking others’ emotions Solomon Asch’s Conformity Studies - 1955, asked participants to judge line lengths, when most confederates would answer wrong, the participant would conform more than ___________ of the time. ● Participant experienced ____________________________________, resulting from the conflicting beliefs/attitudes. When do people conform? Feelings of __________________ or ______________________. _______+ people present ___________________ consensus within group. Group’s ________________ or attractiveness is ______________ ___________________________ to any response Others in the group _____________ one’s behavior Why do people conform? Description NORMATIVE social influence Conforming to…. ● INFORMATIONAL social influence Conforming due to… ● Obedience - looking to others to get approval/avoid rejection. looking to others for information on what to do. Example 3 Stanley Milgram’s Obedience Studies - 1963, 1974, etc - paired ____________________ and ________________, the learner received a “shock” for every wrong answer; shocks increased in intensity as questions continued; _________% (of 40 in the original experiment) completed the shock hierarchy. ● Participants experienced __________________________________________. Why continue to shock? ● Presence of __________________________________. ● ________________________ institution (Yale vs community college) ● ___________________________________ and ______________________ of victims. ● _______________________________ for _______________________. Bottom line: When considering to conform/not conform or to obey/disobey, consider the ___________________ and the _______________________. Individuals in Groups Definition Example Social facilitation Others = arousal good at task better performance bad at task worse performance Remember Yerkes-Dodson law Social loafing Others = decreased effort in groups Deindividuation Possible when group member feel aroused (+/-) and anonymous lose self-consciousness and respond to the group experience Groups as Wholes Definition Group polarization "Preaching to the choir" Groupthink Considering few alternatives, selective gathering of info Example 4 Minority influence difficult but influential must be _______________________________. SOCIAL RELATIONS - Prejudice, Aggression, Conflict, Peacemaking, Attraction, Altruism Prejudice Stereotyped beliefs Negative feelings/emotions Discriminatory actions Prejudice = _____________________________________ for perceiving and reacting to events. Causes of Prejudice Definition Social inequities Haves vs. have-nots Examples Social groups US (________________) vs. THEM (_________________) Ingroup bias - Scapegoating The theory that prejudice offers an ___________________ for anger by providing someone to blame. _________________________________ phenomenon - the tendency to believe the world is just/fair and that people therefore get what they deserve and deserve what they get. Good is rewarded, evil is punished those who are rewarded are good? Those who suffer must be bad? Aggression - Biology (Nature)of Aggression Environment (Nurture) of Aggression _________________________ aggression - stems from feelings of _________________ and aimed at inflicting pain Frustration-aggression principle - reacting to aversive events in an aggressive manner. ex: bullying, trashing a locker room because you lost a game, punching a wall, etc. _________________________ aggression - serves as a means ________________________________ than causing pain. ex: stealing a toy because you want to play with it, tackling the ball carrier in football, self-defensive actions, etc. 5 Conflict ___________________________________ - situation in which an individual experiences a conflict, then acts to obtain short-term individual gains, which eventually leads in the long run to a loss for the group. o Pits our own self-interests against society's well-being. o People often _______________________________ their self-serving tendencies in various ways. Peacemaking Cooperation through ______________________________________________ - shared goals that override differences among people and require cooperation. o Working toward shared goals allows diverse people to discover their __________________________ and shared values. Attraction - 3 elements _______________________ – geographic nearness/closeness increased interactions o Familiarity breeds fondness. o __________________________________________ - the phenomenon that repeated exposure to novel stimuli increases liking of them. __________________________________________ o Evolutionary Masculine/dominant/mature men Youthful/healthy women o Cultural “Beauty is in the eye of the beholder” _________________________ o Opposites do not attract. o Similarity breeds content. o _______________________________________________ - we will like those whose behavior is rewarding to us and we will continue relationships that offer more rewards than costs. Romantic Love _______________________ love - an aroused state of intense positive absorption in another, usually present at the beginning of a relationship. _____________________________ love - the deep affectionate attachment we feel for those with whom our lives are intertwined. o ________________________ o ________________________ 6 Altruism _________________________________ - the tendency for any given bystander to be less likely to give aid if other bystanders are present. o reflects ________________________________ ___________________________________________ Why do we help others? In other words… Social exchange theory - social behavior is an exchange process that aims to maximize benefits and minimize costs. Social-responsibility norm - an expectation that people can and should help people who depend upon them. Reciprocity norm - the expectation to respond to a positive action with another positive action. Example