Incomplete Dominance, Codominance, Sex
advertisement

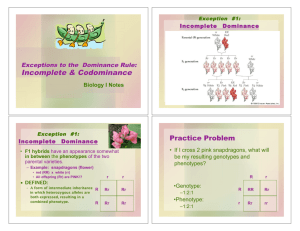
Incomplete Dominance, Codominance, Sexlinked and Polygenic Inheritance Incomplete Dominance • Offspring have an appearance somewhat in between the phenotypes of the two parents – “Mixed” – Blended R R W RW RW F1 generation W RW RW All Rr = pink (heterozygous pink) Incomplete Dominance • Incomplete dominance occurs when two or more alleles influence the phenotype • Neither allele is completely dominant over the other Incomplete Dominance Codominance • BOTH alleles are expressed equally in heterozygous individuals • Neither allele is dominant over the other – Example: blood type • Determined by whether or not you have A or B proteins • IA = A protein • IB = B protein • I = no protein • Another example Is the speckled chicken Codominance Codominance Problem • Example:homozygous male Type B (IBIB) • x heterozygous female Type A (IAi) IB IB IA IAIB IAIB i IBi IBi 1/2 = IAIB 1/2 = IBi Another Codominance Problem Example: male Type O (ii) x female type AB (IAIB) IA IB i IAi IBi i IAi IBi 1/2 = IAi 1/2 = IBi Codominance • Question: If a boy has a blood type O and his sister has blood type AB, what are the genotypes and phenotypes of their parents? boy - type O (ii) X girl - type AB (IAIB) Codominance • Answer: IA IB i i IAIB ii Parents: genotypes = IAi and IBi phenotypes = A and B Sex-linked Traits • Traits (genes) located on the sex chromosomes • Sex chromosomes are X and Y – XX genotype for females – XY genotype for males • Many sex-linked traits carried on X chromosome Sex – Linked Traits • Example: Colorblindness – If the mother carries the colorblindness gene on her X chromosome, her son could get it. – As long as one X chromosome X y is ok, a female will not cX c y X X C express the trait X X XX Xy Sex-linked Traits Example: Colorblindness Sex Chromosomes Colorblindness XX chromosome - female Xy chromosome - male Polygenic Inheritance • Inheritance pattern controlled by two or more genes • Genes can be on the same chromosome or on different chromosomes • Genotypes are written as AA, Aa, or aa except you will have three or more genes each with a dominant and recessive trait • Skin color is influenced by the additive effects of melanin by three to six genes. Eye color is also a result of melanin added from multiple genes. Polygenic Inheritance a pedigree Polygenic Inheritance of Skin Color Gametes ABC ABc ABC AABBCC AABBCc AbC Abc aBC AABbCc AaBBCC aBc ABc AbC Abc aBC AAbbcc aaBBCc aBc abC abc aaBbcc The table shows typical ranges of skin color combinations. Other polygenic influenced conditions include Spina bifida and Cleft palate. abC abc