Community Ecology
advertisement

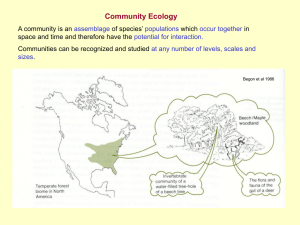
Community Ecology Concerned with community structure and population interactions Interactions Five categories 1. Competition 2. Predation 3. Mutualism 4. Commensalism 5. Parasitism Competition Competition • Interspecific competition – The competition between two or more species for some limiting resource – food or nutrients, space, mates, nesting sites • Resolutions – Competitive exclusion principle (Gause’s principle) – Resource partitioning – Character displacement – Realized niche Competitive interactions between organisms can have a great deal of influence on species evolution The Competitive Exclusion Principle • G.F. Gause-worked with 2 strains of Paramecium -States that two species competing for the same limiting resources cannot coexist in the same place • When two species compete, one is likely to be more successful. – Cannot coexist if they share the same niche. • One species could become extinct or evolve to exploit different resources resource partitioning) • Divergence in adaptation is called character displacement. Animation Ecological Niches • The ecological niche – Is the total of an organism’s use of the biotic and abiotic resources in its environment • The niche concept allows restatement of the competitive exclusion principle – Two species cannot coexist in a community if their niches are identical Clip Resource Partitioning • Resource partitioning is the differentiation of niches –That enables similar species to coexist in a community A. distichus perches on fence posts and other sunny surfaces. A. insolitus usually perches on shady branches. A. ricordii A. insolitus A. alinigar A. distichus A. christophei A. cybotes A. etheridgei Minimizes competition & maximizes success Resource Partitioning Resource partitioning is a way in which different species can use the same resource, such as food, without occupying the same physical location at the same point in time. In this example, the different warblers eat the same caterpillar, but they occupy different positions in the tree. Two primarily occupy the area near the trunk, with the others share the edges of the branches, but at different heights. The result is the warblers do not overtly compete for food in the same space. Character Displacement (niche shift) There is a tendency for characteristics to be more divergent in sympatric populations of two species than in allopatric populations of the same two species Speciation: Allopatric-geographic barriers Sympatric- no geo barrier Percentages of individuals in each size class –As a result of resource partitioning. G. fuliginosa –-Divergence in adaptation G. fortis Beak depth Santa María, San Cristóbal 40 20 0 Sympatric populations Los Hermanos 40 G. fuliginosa, allopatric 20 0 Daphne 40 20 0 G. fortis, allopatric 8 10 12 Beak depth (mm) 14 16 Realized Niche Niche theory distinguishes between fundamental & realized niches: – fundamental = all possible conditions under which population reproduces itself – realized niche = the actual niche exhibited in particular time & place • • • • Predation True predator Parasite Parasitoid Herbivore Snowshoe Hare and Canadian Lynx Camouflage -passive defense Cryptic coloration – Fur of snowshoe hare is white in winter and brown in summer – The larvae of some moths are colored like bird droppings – Marking on animals to blend in to background. Lizard • Aposematic coloration (warning coloration) – Coloration that warns predators – Predators learn to associate color with bad taste or harmful chemical • Mimicry – Two types • Mϋllerian • Batesian Müllerian mimicry – Two or more unpalatable species resemble each other (a) Cuckoo bee (b) Yellow jacket Batesian mimicry – A palatable or harmless species mimics an unpalatable or harmful model (b) Green parrot snake (a) Hawkmoth larva passive defense • Spins, thorns, poisons • Hiding, fleeing Community Interactions •Symbiosis •Predatory-Prey •Competition Symbiosis • Mutualism (+/+) • Commensalisms (+/o) • Parasitism (+/-) (+/+) Mutualism (+/o) Commensalism One species benefits and the other is not affected It is difficult to determine true commensalism because it is difficult to ensure host is not harmed. Ex: Barnacles that attach themselves to the backs of whales Parasitism (+/-) • Relationship in which one species benefits; while harming the other • Tomato hornworm covered with cocoons of pupating wasps Review of Community Interactions Ecological Succession Ecological Succession Ecological Succession • Primary succession – Occurs where no soil exists when succession begins – Starts with pioneer species (lichens & mosses) Ecological Succession • Secondary succession – Begins in an area where soil remains after a disturbance – takes place where a community has been removed, e.g., in a plowed field or a clearcut forest (a) Soon after fire. As this photo taken soon after the fire shows, the burn left a patchy landscape. Note the unburned trees in the distance. (b) One year after fire. This photo of the same general area taken the following year indicates how rapidly the community began to recover. A variety of herbaceous plants, different from those in the former forest, cover the ground.